The modern business landscape is characterized by rapid change, increasing competition, and the need for greater efficiency. Businesses are constantly striving to optimize operations, reduce costs, and improve customer experiences. At the heart of this transformation lies business process automation (BPA) – a strategic approach to streamlining workflows and eliminating manual tasks. It’s no longer a futuristic concept; BPA is a vital tool for organizations of all sizes to thrive in today’s dynamic environment. This article will explore the benefits, key technologies, and practical considerations of implementing BPA solutions to unlock significant operational improvements.

What is Business Process Automation?

Simply put, business process automation (BPA) is the use of technology to automate repetitive, rule-based tasks within an organization. It’s about moving away from manual, error-prone processes and towards more efficient, data-driven workflows. Instead of employees manually entering data, sending emails, or performing other routine tasks, BPA systems can handle these activities automatically. This frees up human employees to focus on higher-value activities requiring creativity, critical thinking, and strategic decision-making. The core principle is to reduce human intervention and increase speed and accuracy. It’s about augmenting, not replacing, human workers; the goal is to enhance productivity and reduce operational costs. Effective BPA isn’t just about technology; it’s about redesigning processes to be more efficient.
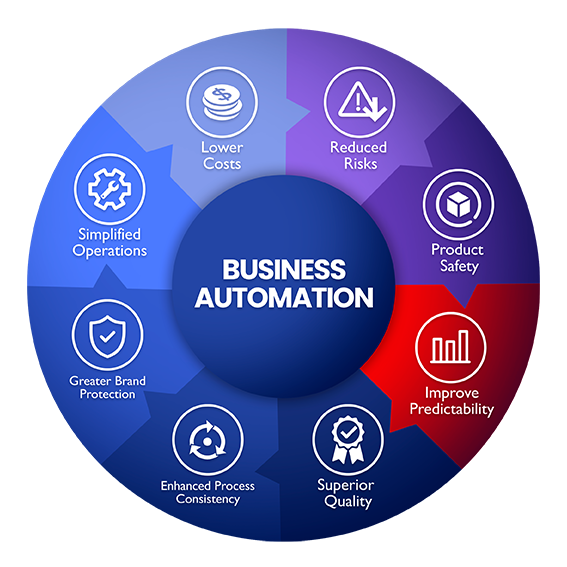
The Benefits of Implementing Business Process Automation
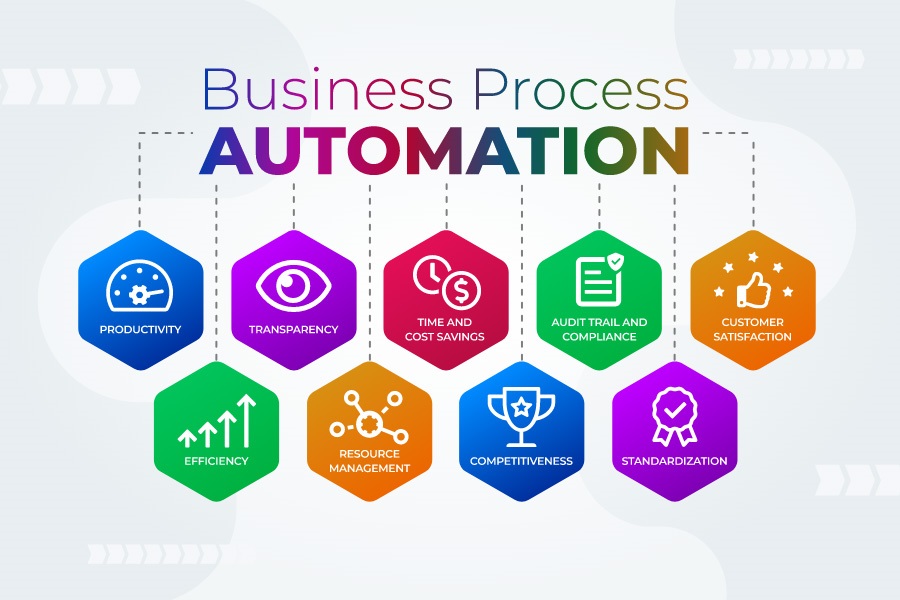
The advantages of adopting BPA are numerous and far-reaching. Here’s a breakdown of the key benefits:

- Increased Efficiency: Automation drastically reduces the time it takes to complete tasks, leading to significant gains in productivity.
- Reduced Costs: By minimizing errors, reducing labor costs, and optimizing resource allocation, BPA directly contributes to cost savings.
- Improved Accuracy: Automation minimizes human error, leading to more accurate data and fewer mistakes.
- Enhanced Customer Experience: Faster response times, personalized service, and streamlined processes contribute to a better customer experience.
- Scalability: BPA solutions can easily scale to accommodate growing business needs, without requiring significant additional resources.
- Better Compliance: Automated processes can be designed to adhere to regulatory requirements, reducing the risk of non-compliance.
- Data-Driven Insights: Many BPA systems generate valuable data and analytics, providing insights into process performance and identifying areas for improvement.
Key Technologies Driving Business Process Automation
Several technologies are playing a crucial role in enabling successful BPA implementations. Understanding these technologies is key to selecting the right solutions for your specific needs:
- Robotic Process Automation (RPA): RPA uses software robots to mimic human actions, automating repetitive tasks across various applications and systems. This is arguably the most popular type of BPA currently.
- Workflow Automation: This focuses on automating the entire workflow of a process, from initiation to completion, using visual workflow builders and drag-and-drop interfaces.
- Business Process Management (BPM) Software: BPM platforms provide a comprehensive suite of tools for designing, executing, monitoring, and optimizing business processes.
- Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML): AI and ML are increasingly being integrated into BPA solutions to automate complex decision-making, predict outcomes, and personalize customer experiences.
- Optical Character Recognition (OCR): OCR technology converts scanned documents and images into machine-readable text, enabling automated data extraction and processing.
- Low-Code/No-Code Platforms: These platforms allow business users to build and deploy automation solutions with minimal coding, accelerating the implementation process.
Common Business Process Automation Use Cases
BPA isn’t just for large enterprises. It’s applicable across a wide range of industries and business functions:

- Invoice Processing: Automating invoice data entry, approval workflows, and payment processing.
- Order Management: Streamlining order fulfillment, tracking shipments, and managing returns.
- Customer Service: Automating ticket routing, chatbot interactions, and knowledge base searches.
- Human Resources: Automating onboarding, payroll processing, and benefits administration.
- Marketing Automation: Automating email campaigns, lead nurturing, and social media posting.
- Supply Chain Management: Optimizing inventory levels, tracking shipments, and managing logistics.
- Data Entry & Validation: Automating data entry tasks and ensuring data accuracy.
Implementing Business Process Automation: A Step-by-Step Approach
Successfully implementing BPA requires a strategic approach. Here’s a suggested roadmap:
- Identify Pain Points: Begin by thoroughly analyzing your existing business processes to identify areas where automation can have the greatest impact.
- Map the Current Process: Document the current workflow, including all steps, data flows, and human interactions.
- Define Goals & Objectives: Clearly define what you want to achieve with BPA – increased efficiency, reduced costs, improved accuracy, etc.
- Select the Right Technology: Research and evaluate different BPA solutions based on your specific needs and budget.
- Pilot Project: Start with a small-scale pilot project to test the chosen technology and refine your implementation plan.
- Training & Change Management: Provide adequate training to employees on how to use the new automation tools and manage the transition.
- Monitor & Optimize: Continuously monitor the performance of your BPA solutions and make adjustments as needed to maximize their effectiveness.
The Future of Business Process Automation
The future of BPA is bright, driven by advancements in AI, cloud computing, and the Internet of Things (IoT). We’ll see even more sophisticated automation solutions emerge, including:

- Hyperautomation: Combining multiple automation technologies to create end-to-end process automation.
- Digital Twins: Creating virtual representations of physical processes to simulate and optimize automation.
- Predictive Automation: Using AI and ML to anticipate and proactively automate tasks.
- Low-Code/No-Code Automation: Empowering business users to build and deploy automation solutions with minimal coding.
Ultimately, business process automation is no longer a luxury; it’s a necessity for organizations seeking to thrive in the digital age. By embracing automation, businesses can unlock significant operational improvements, reduce costs, and gain a competitive advantage. The key is to approach it strategically, focusing on the right technologies and carefully planning the implementation process.

Conclusion
Business process automation offers a transformative opportunity for organizations of all sizes. By streamlining workflows, reducing manual tasks, and leveraging the power of technology, BPA can drive significant improvements in efficiency, cost savings, and customer satisfaction. As technology continues to evolve, the benefits of BPA will only continue to grow, making it an increasingly essential investment for businesses looking to succeed in today’s dynamic marketplace. Don’t let your processes become bottlenecks – embrace the power of automation to unlock your business’s full potential.