Operational efficiency – the ability to accomplish more with less – is no longer a buzzword; it’s a critical driver of success in today’s competitive landscape. Businesses of all sizes are constantly seeking ways to streamline processes, reduce waste, and ultimately, improve their bottom line. It’s about more than just cutting costs; it’s about optimizing every aspect of an organization to achieve peak performance. This article will delve into the key strategies and techniques that can dramatically boost operational efficiency, providing actionable insights for businesses looking to gain a significant competitive advantage. We’ll explore how to identify bottlenecks, implement best practices, and foster a culture of continuous improvement. Ultimately, this exploration will demonstrate how prioritizing operational efficiency can unlock substantial value for your organization.
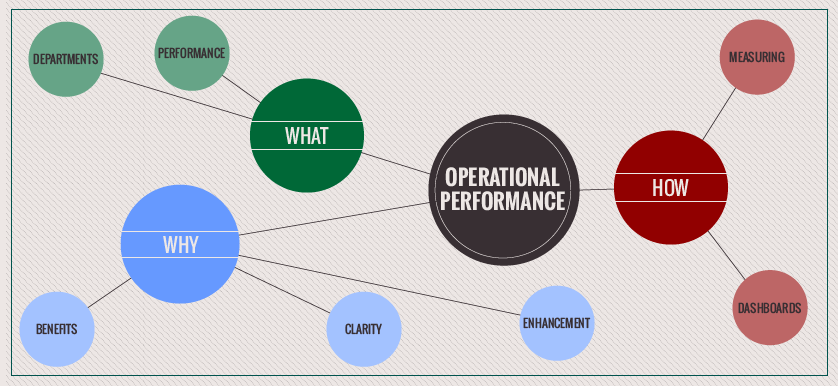
The concept of operational efficiency is deeply rooted in the understanding that resources – time, money, materials, and personnel – are finite. Inefficient processes consume these resources, leading to wasted effort, increased costs, and reduced profitability. Conversely, a well-managed and optimized operation delivers tangible results, allowing businesses to focus on strategic initiatives and capitalize on growth opportunities. Ignoring operational efficiency isn’t just a missed opportunity; it’s a risk. Companies that fail to adapt to changing market conditions and technological advancements often find themselves lagging behind their competitors. Therefore, a proactive and strategic approach to operational efficiency is essential for long-term sustainability and success. It’s about recognizing that operational efficiency isn’t a one-time fix, but rather a continuous journey of refinement and improvement.

1. Understanding the Foundations of Operational Efficiency

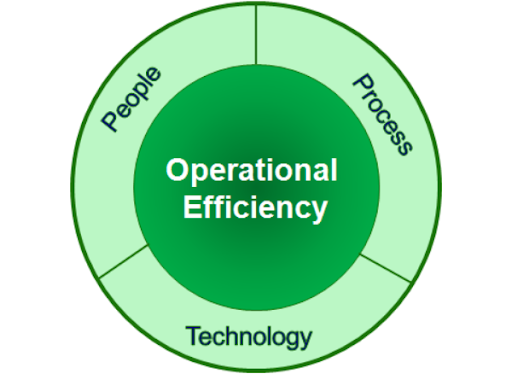
Before diving into specific strategies, it’s crucial to establish a solid understanding of what constitutes operational efficiency. It’s not simply about reducing costs; it’s about maximizing the value derived from every activity within an organization. This requires a holistic view, considering all stages of the business process – from procurement and production to marketing and customer service. Several key factors contribute to an organization’s operational efficiency:
-1.webp)
- Process Mapping: Visually documenting each step in a process helps identify redundancies, bottlenecks, and areas for improvement. Tools like flowcharts and process diagrams are invaluable here.
- Technology Adoption: Investing in appropriate technology – from automation software to cloud-based platforms – can significantly streamline operations and reduce manual errors.
- Employee Training & Empowerment: Well-trained and empowered employees are more likely to identify and address inefficiencies. Providing them with the skills and autonomy to improve processes is paramount.
- Data-Driven Decision Making: Collecting and analyzing data – key performance indicators (KPIs) – provides insights into operational performance and allows for informed decision-making.
2. Streamlining Procurement Processes
Procurement – the process of acquiring goods and services – often represents a significant source of waste and inefficiency. Poorly managed procurement can lead to inflated costs, delays, and quality issues. Here’s how to optimize this critical area:
- Supplier Relationship Management (SRM): Building strong, collaborative relationships with suppliers is essential. Regular communication, performance monitoring, and joint problem-solving can lead to better terms and reduced costs.
- Competitive Bidding: Implementing a competitive bidding process ensures that you’re getting the best possible prices.
- Negotiation Skills: Train employees to effectively negotiate contracts and pricing with suppliers.
- Centralized Procurement: Consolidating purchasing across multiple departments can leverage economies of scale and improve negotiation power.
- E-Procurement Systems: Utilizing digital platforms for purchasing can automate processes, reduce paperwork, and improve transparency.
3. Optimizing Production and Manufacturing
For businesses involved in manufacturing or production, operational efficiency is directly tied to the quality and speed of production. Several strategies can significantly improve this area:

- Lean Manufacturing Principles: Lean manufacturing focuses on eliminating waste – anything that doesn’t add value – throughout the production process. This includes reducing inventory, minimizing defects, and streamlining workflows.
- Six Sigma Methodology: Six Sigma is a data-driven approach to process improvement that aims to reduce variation and defects.
- Automation: Investing in automation technologies – robotics, automated guided vehicles (AGVs), and automated inspection systems – can significantly increase speed and accuracy.
- Predictive Maintenance: Using sensors and data analytics to predict equipment failures allows for proactive maintenance, minimizing downtime and repair costs.
- Just-in-Time (JIT) Inventory: Implementing JIT inventory management minimizes the amount of raw materials and finished goods held in storage, reducing waste and improving responsiveness.
4. Enhancing Customer Service Operations
Customer service is often a major driver of operational efficiency. Poor customer service can lead to lost sales, negative reviews, and damage to brand reputation. Here’s how to improve customer service operations:

- Customer Relationship Management (CRM) Systems: CRM systems provide a centralized view of customer interactions, enabling personalized service and improved communication.
- Self-Service Options: Offering self-service options – such as online portals and FAQs – empowers customers to resolve issues independently, reducing the workload on customer service representatives.
- Omnichannel Support: Providing support through multiple channels – phone, email, chat, social media – allows customers to choose the method that’s most convenient for them.
- Agent Training: Investing in comprehensive training for customer service representatives is crucial for providing excellent service.
- Feedback Mechanisms: Actively soliciting customer feedback – through surveys and reviews – allows for continuous improvement of service delivery.
5. Leveraging Technology for Data-Driven Insights
Technology plays a vital role in enabling operational efficiency. Leveraging data analytics and business intelligence tools can provide valuable insights into performance and identify areas for improvement.

- Business Process Management (BPM) Software: BPM software helps automate and optimize business processes, improving efficiency and reducing errors.
- Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) Systems: ERP systems integrate all aspects of a business – finance, HR, supply chain, and more – providing a single source of truth for data.
- Data Visualization Tools: Tools like Tableau and Power BI allow for easy visualization of data, making it easier to identify trends and patterns.
- Cloud Computing: Cloud-based solutions offer scalability, flexibility, and cost savings.
6. Continuous Improvement – The Key to Sustained Efficiency
Operational efficiency isn’t a one-time project; it’s an ongoing process of continuous improvement. Regularly reviewing KPIs, identifying areas for improvement, and implementing changes are essential for maintaining and enhancing efficiency. A culture of experimentation and learning is critical. Encourage employees to suggest improvements and reward those who contribute to process optimization. The concept of "Kaizen" – continuous improvement – is a powerful philosophy for driving lasting efficiency gains.
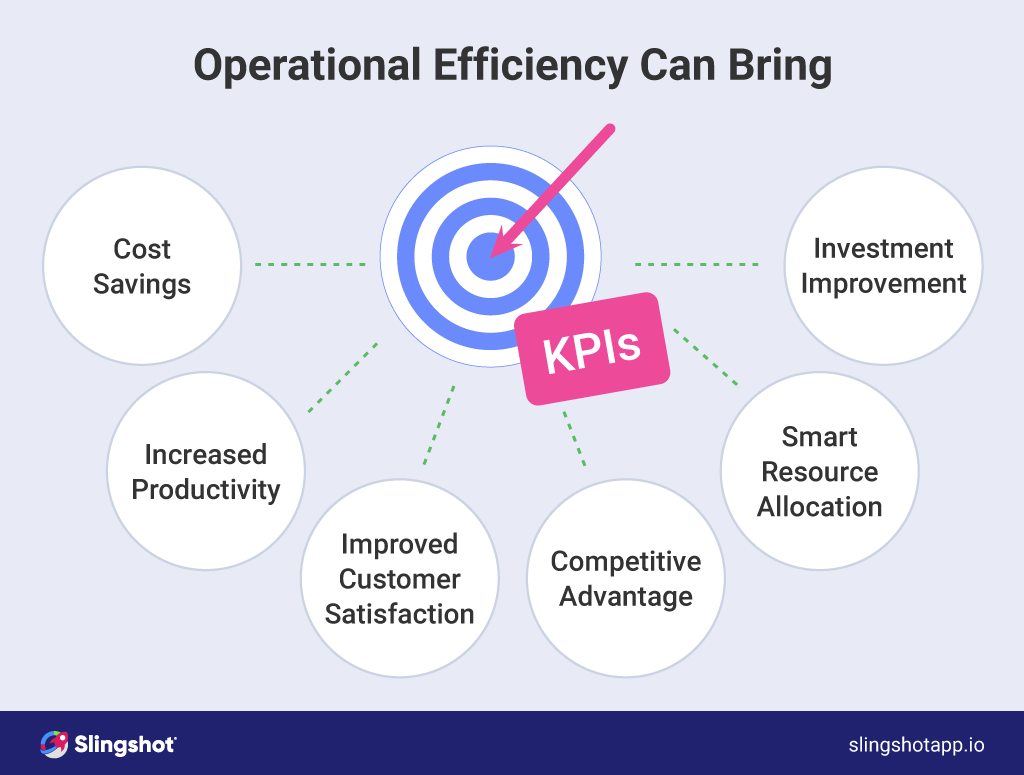
7. Measuring and Tracking Progress
Establishing clear metrics and tracking progress is vital for demonstrating the impact of operational efficiency initiatives. Key performance indicators (KPIs) should be aligned with strategic goals. Examples include:
![]()
- Cycle Time: The time it takes to complete a process.
- Defect Rate: The number of defects per unit of output.
- Inventory Turnover: The rate at which inventory is sold and replaced.
- Cost per Unit: The cost associated with producing one unit of output.
- Employee Productivity: The output generated per employee.
Regularly monitoring these metrics allows for a clear assessment of the effectiveness of operational efficiency initiatives and facilitates data-driven adjustments.
Conclusion
Boosting operational efficiency is no longer a luxury; it’s a necessity for businesses seeking to thrive in today’s dynamic environment. By implementing the strategies outlined in this article, organizations can streamline processes, reduce waste, improve customer service, and ultimately, achieve significant gains in profitability and competitiveness. A commitment to continuous improvement, coupled with a data-driven approach, is the key to unlocking sustained operational efficiency and long-term success. The investment in optimizing processes will yield a substantial return, positioning your organization for sustained growth and leadership. Remember, operational efficiency is a journey, not a destination – a continuous effort to refine and enhance every aspect of your business.