Business process modeling is no longer a niche technical exercise; it’s a fundamental shift in how organizations approach efficiency, innovation, and overall performance. In today’s rapidly evolving business landscape, understanding and optimizing existing processes – and designing new ones – is critical for staying competitive. This article will explore various strategies for effective business process modeling, providing a comprehensive guide for businesses of all sizes. Business process modeling is increasingly recognized as a strategic imperative, enabling organizations to identify bottlenecks, streamline workflows, and ultimately, deliver better value to their customers. It’s about more than just documenting; it’s about understanding the why behind the what. This article will delve into the core principles, tools, and best practices for successful business process modeling.

Understanding the Importance of Business Process Modeling
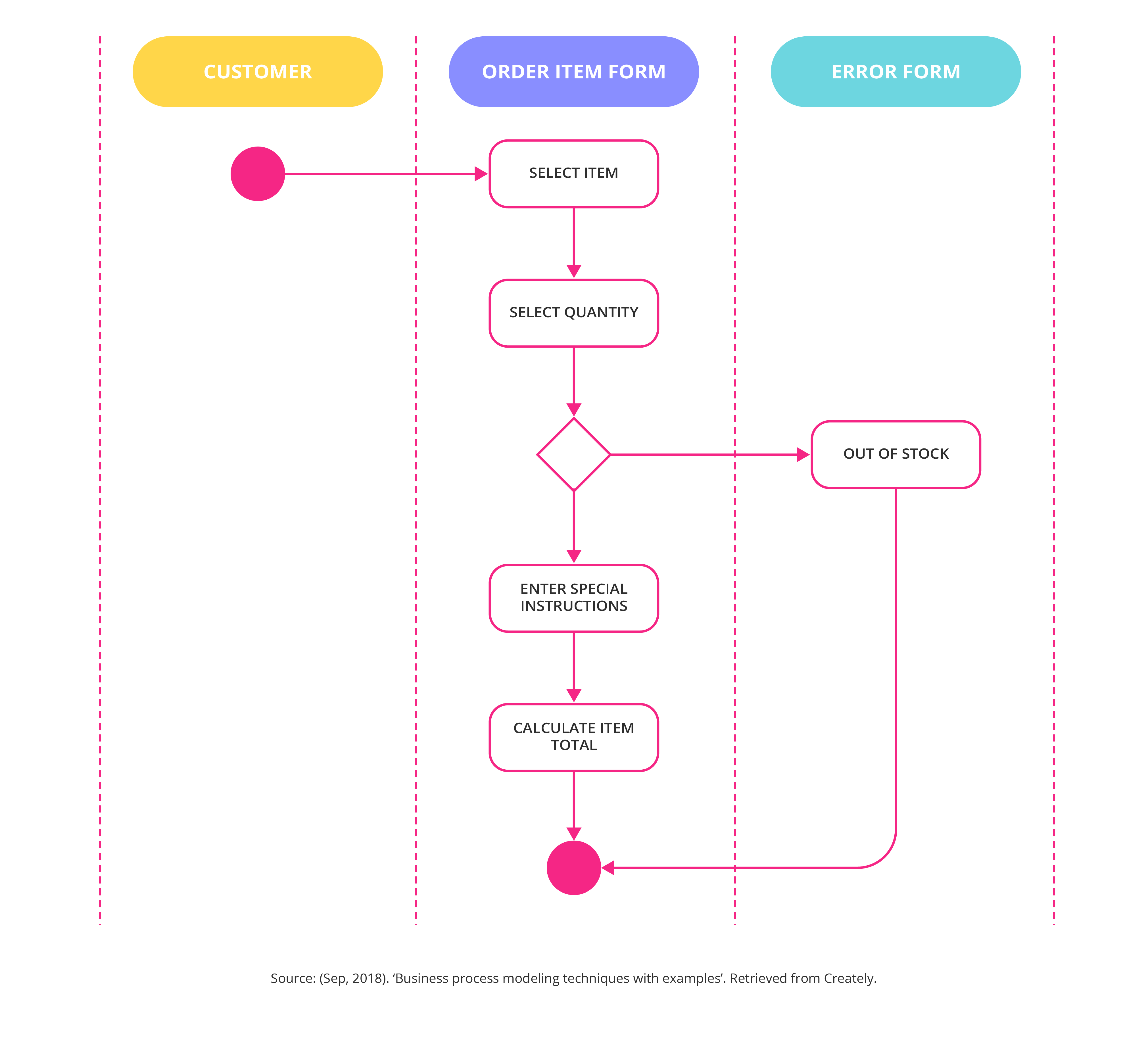
Before diving into specific techniques, it’s crucial to understand why business process modeling is so vital. Many organizations struggle with inefficient workflows, leading to wasted time, increased costs, and frustrated employees. Poorly designed processes often result in errors, delays, and a lack of customer satisfaction. Effective business process modeling provides a clear, visual representation of how work is performed, allowing teams to identify areas for improvement. It’s a proactive approach, rather than a reactive one, that can significantly enhance operational effectiveness. Furthermore, it facilitates better communication and collaboration across departments, ensuring everyone is aligned on goals and responsibilities. The ability to analyze and optimize processes is a key differentiator in today’s market, and businesses that embrace this capability are better positioned for long-term success. The benefits extend beyond simple efficiency gains; it fosters a culture of continuous improvement.
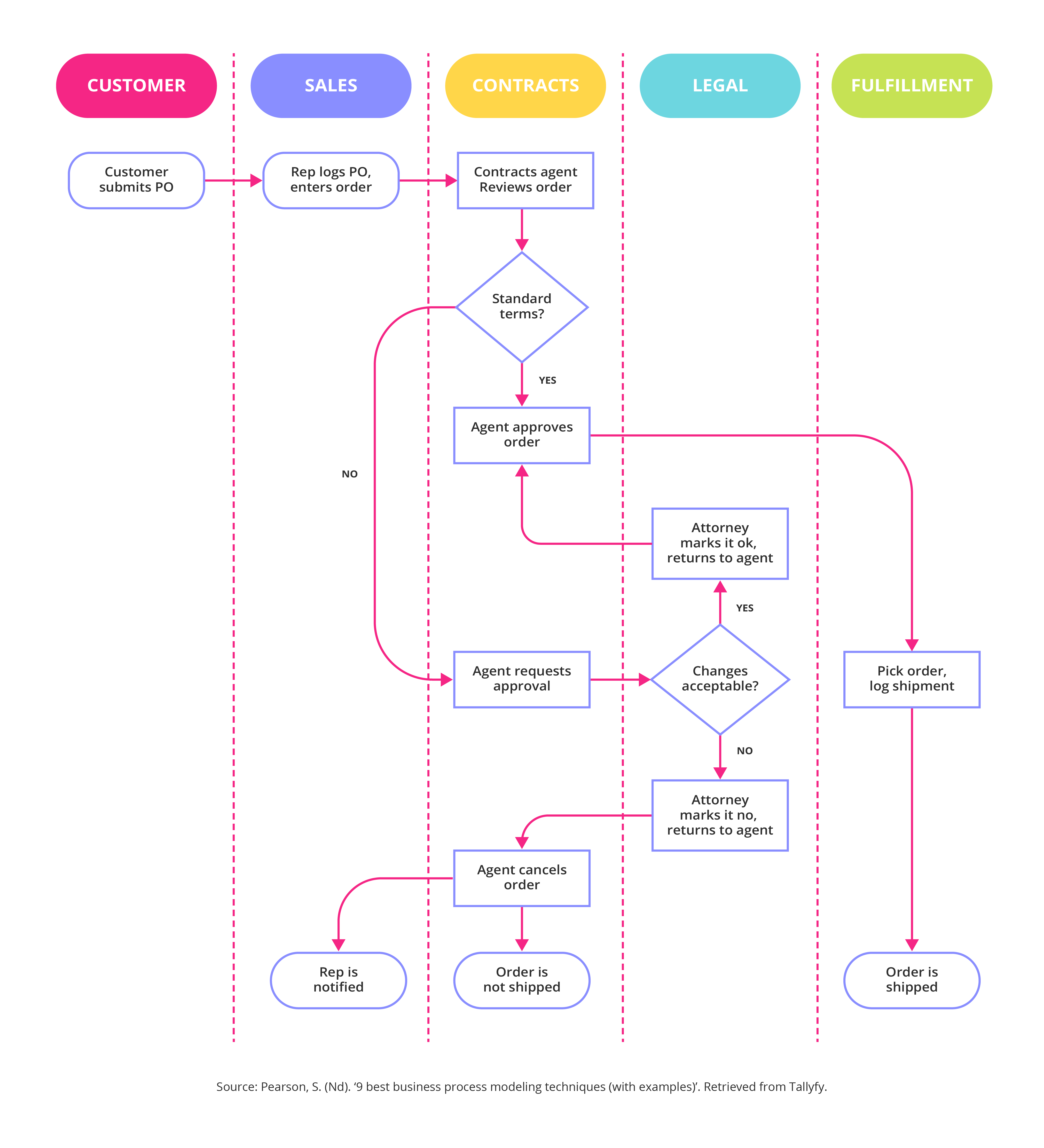
Core Principles of Business Process Modeling
Several core principles underpin successful business process modeling. Firstly, clarity is paramount. The model should accurately reflect the actual process, avoiding unnecessary complexity or jargon. Secondly, completeness is essential – capturing all steps, decision points, and potential variations within the process. Thirdly, accuracy demands meticulous detail, ensuring the model is a true representation of the workflow. Finally, usability is critical – the model should be easily understood and used by the people who will be performing the process. A poorly designed model is useless, regardless of its technical sophistication. Consider incorporating a process flow diagram as a starting point, but remember that this is a representation, not a rigid blueprint. The goal is to provide a framework for improvement, not a definitive set of rules.
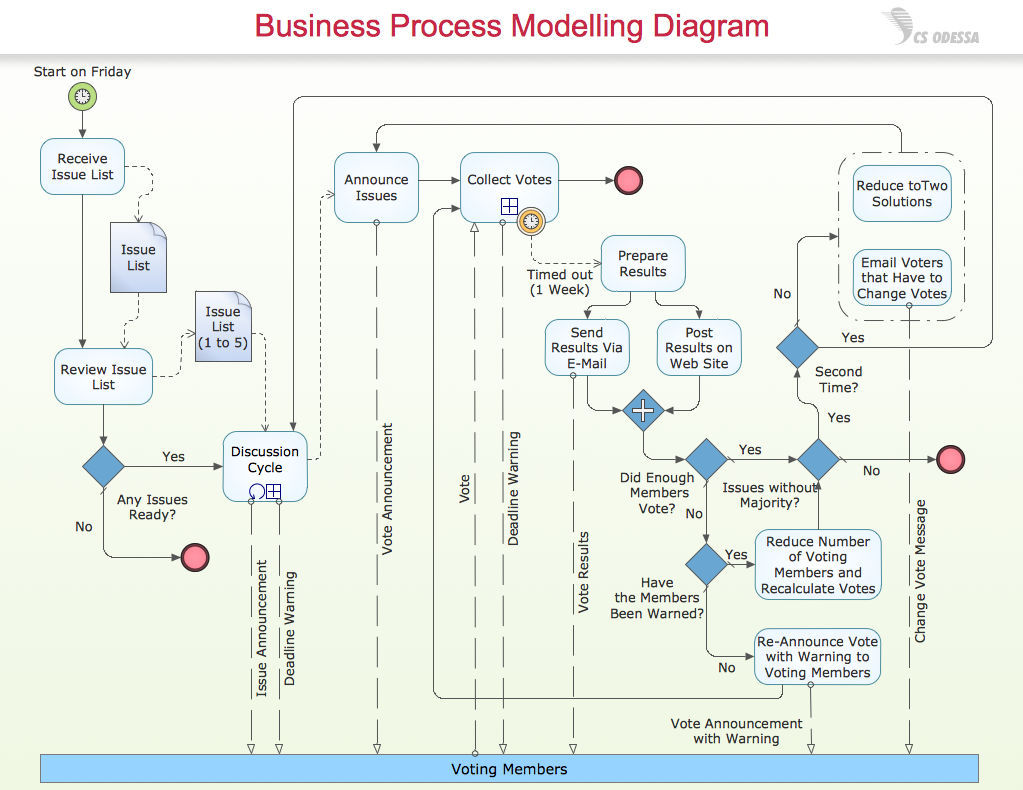
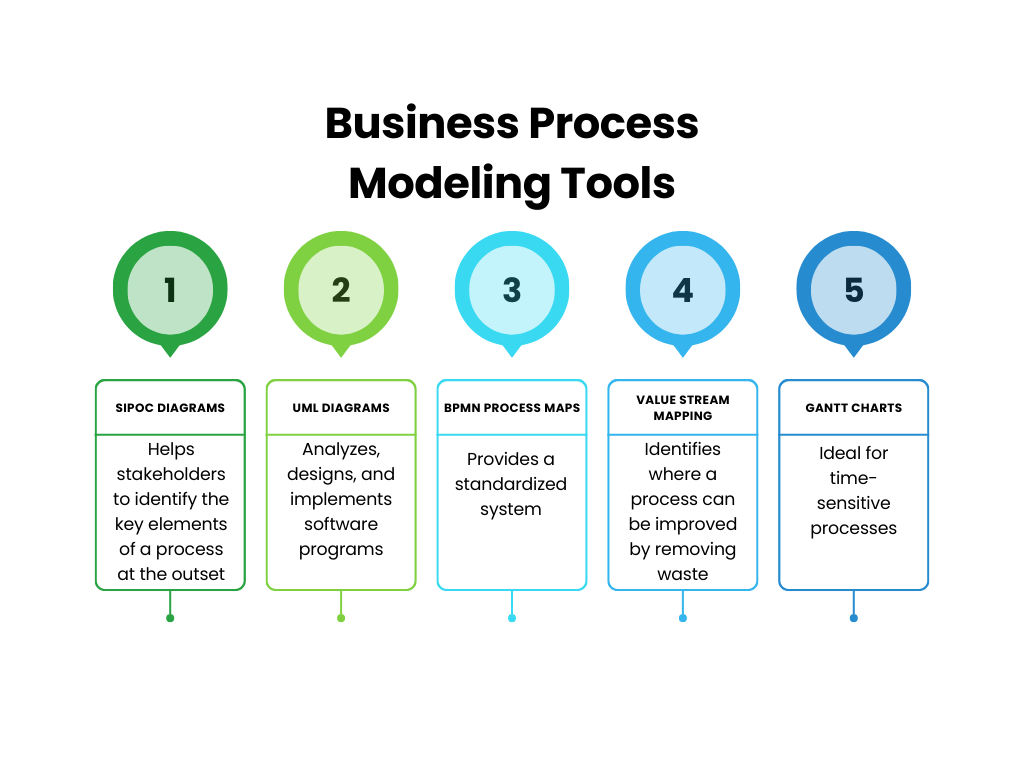
Techniques for Business Process Modeling
There’s a wide range of techniques available for business process modeling, each with its own strengths and weaknesses. Here are a few popular approaches:
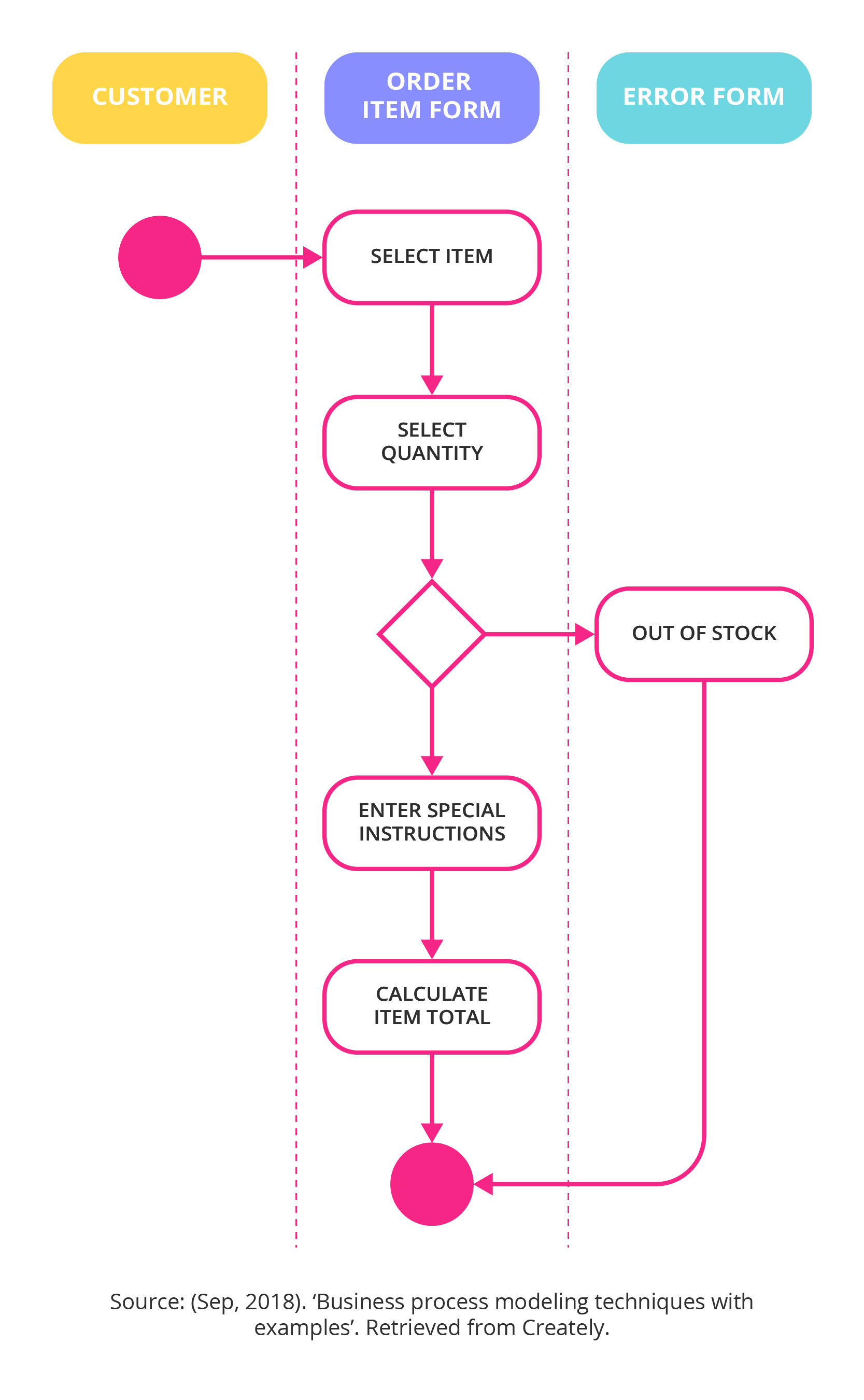
1. Flowcharts
Flowcharts are perhaps the most widely recognized type of process model. They use standard symbols to represent activities, decisions, and data flows. They are particularly effective for visualizing simple, linear processes. However, flowcharts can become complex and difficult to maintain for intricate processes. They are best suited for documenting straightforward workflows. Tools like Lucidchart and Microsoft Visio are commonly used to create and edit flowcharts.

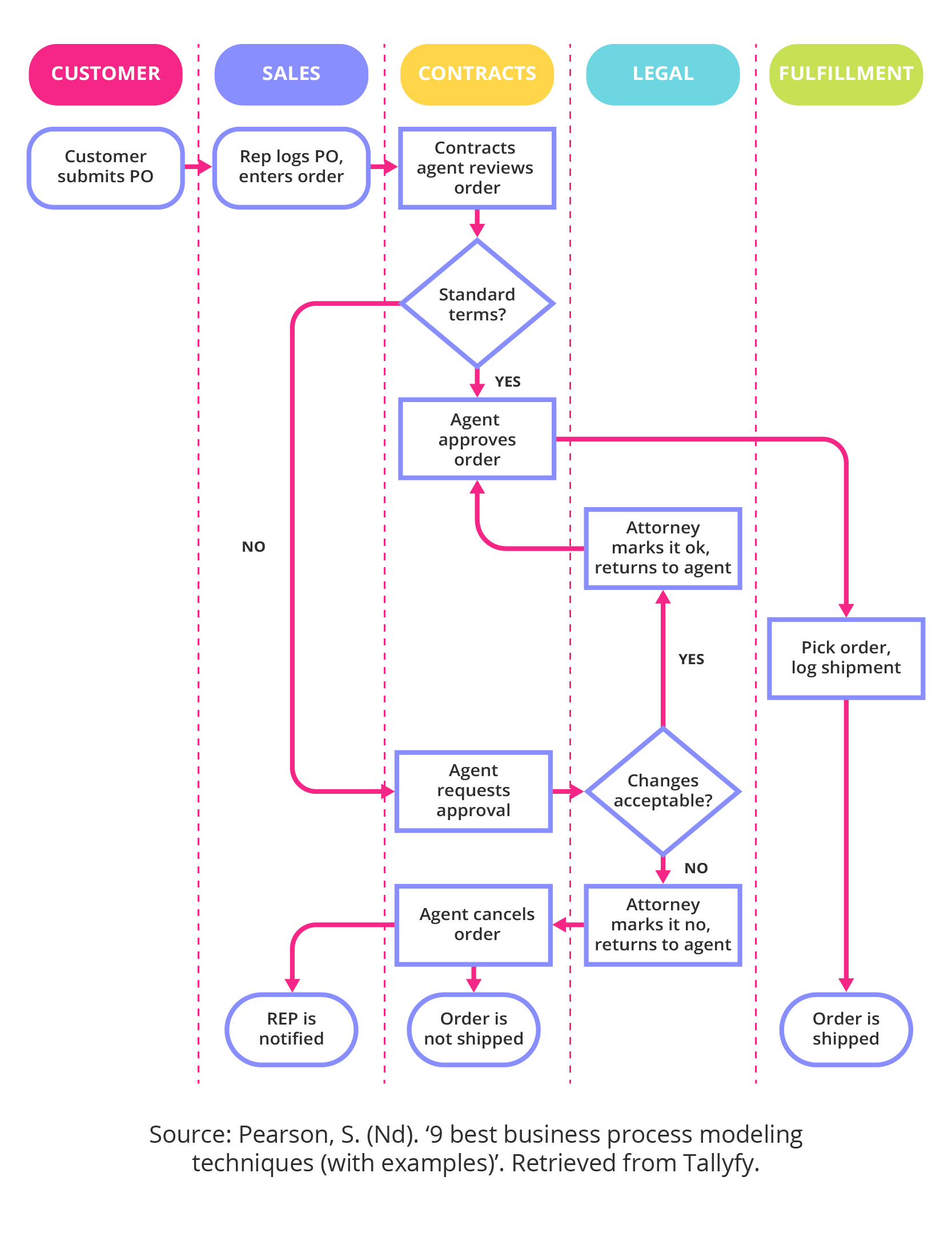
2. BPMN (Business Process Model and Notation)
BPMN is a standardized notation developed by the OMG (Object Management Group) that provides a more structured and visually appealing way to represent business processes. It’s particularly useful for complex, multi-step processes and is widely adopted in the industry. BPMN offers a richer set of capabilities than simple flowcharts, including the ability to model decision points, parallel activities, and data exchange. Numerous online tools, such as Signavio and Bizagi, support BPMN modeling.
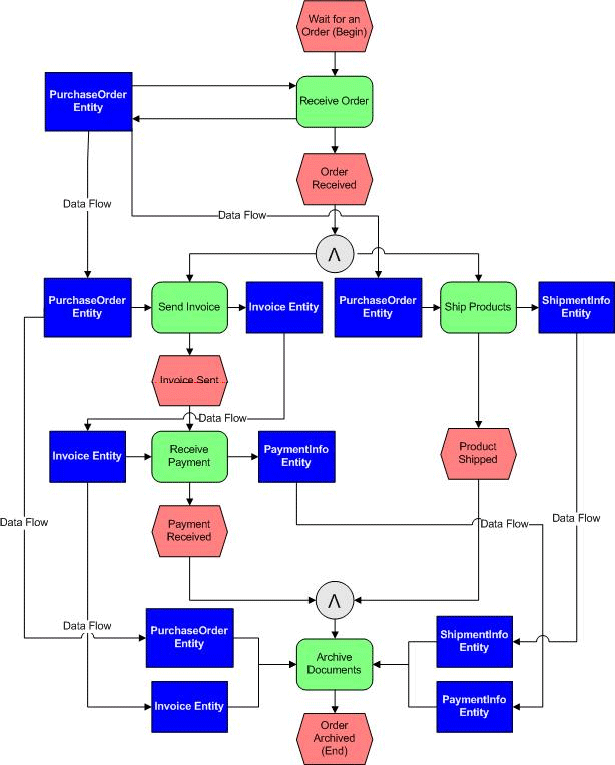
3. Swimlane Diagrams
Swimlane diagrams are a powerful technique for visualizing the flow of work within a process, particularly when dealing with multiple actors or responsibilities. They clearly delineate who is responsible for each step, improving clarity and accountability. They are excellent for understanding the roles and interactions involved in a process. They are often used to identify bottlenecks and areas for process improvement.
4. Value Stream Mapping (VSM)
VSM is a technique used to analyze and improve the flow of materials and information required to deliver a product or service. It focuses on identifying waste and inefficiencies throughout the entire value stream – from raw materials to the customer. It’s a valuable tool for identifying opportunities to streamline processes and reduce lead times. While primarily focused on operational efficiency, VSM can inform process modeling efforts.
Implementing Business Process Modeling
Successfully implementing business process modeling requires a strategic approach. First, identify the key processes that need to be modeled. This should be based on a thorough assessment of the organization’s operations. Second, select the appropriate modeling technique based on the complexity of the process and the desired level of detail. Third, engage the right people – those who will be performing the process – to participate in the modeling process. Their input is crucial for ensuring the model accurately reflects the reality of the work. Finally, document the model clearly and comprehensively. This documentation should include a description of the process, the roles involved, and any potential variations.
Benefits of Effective Business Process Modeling
Investing in business process modeling yields significant benefits. Improved efficiency translates to reduced costs and increased productivity. Reduced errors and rework minimize waste and improve quality. Enhanced communication and collaboration streamline workflows and foster a more engaged workforce. Better visibility into processes allows for proactive identification and resolution of problems. Furthermore, process modeling facilitates continuous improvement, enabling organizations to adapt to changing market conditions and maintain a competitive advantage. Ultimately, a well-executed process model is a strategic asset that drives organizational success.
Challenges and Considerations
While the benefits of business process modeling are clear, implementing it effectively can present challenges. One common challenge is resistance to change. Employees may be reluctant to adopt new processes, especially if they perceive them as disruptive. Another challenge is lack of executive support. Without buy-in from senior management, it can be difficult to secure the resources needed to implement and maintain the model. Data quality is also a critical consideration – inaccurate or incomplete data will lead to a flawed model. Finally, complexity can be a significant hurdle. Large, intricate processes can be difficult to model and manage effectively. It’s important to start small, focusing on the most critical processes and gradually expanding the scope of the model as needed.
Future Trends in Business Process Modeling
The field of business process modeling is constantly evolving. Several emerging trends are shaping the future of this discipline:
- Digital Process Modeling: The integration of process modeling tools with digital technologies, such as cloud computing and artificial intelligence, is enabling more dynamic and automated process modeling.
- Process Mining: Process mining techniques are being used to extract insights from existing process data, providing a more real-time view of process performance.
- Low-Code/No-Code Process Modeling: Platforms that allow users to create and manage process models with minimal coding are becoming increasingly popular, democratizing process modeling capabilities.
- AI-Powered Process Optimization: Artificial intelligence is being used to analyze process data and identify opportunities for optimization, automating tasks and improving decision-making.
Conclusion
Business process modeling is no longer a luxury; it’s a necessity for organizations seeking to thrive in today’s competitive environment. By understanding the principles, techniques, and challenges involved, businesses can effectively model their processes, identify areas for improvement, and ultimately, achieve greater operational efficiency and business value. Business process modeling is a continuous journey, requiring ongoing refinement and adaptation. Embracing this approach is an investment in the future of your organization. Remember to consistently evaluate and update your models to reflect evolving business needs and technological advancements. The key to success lies in a commitment to continuous improvement and a clear understanding of the value that process modeling brings.