Risk management is no longer simply an afterthought; it’s a fundamental element of any successful business strategy. Ignoring potential threats can lead to significant financial losses, reputational damage, and operational disruptions. Effective risk management isn’t about eliminating all risk – that’s often unrealistic – but rather about understanding, assessing, and proactively mitigating the risks that do exist. This article will delve into the core principles of risk management, exploring various strategies and best practices to protect your organization. Risk management is a critical discipline for businesses of all sizes, and a proactive approach can significantly improve resilience and long-term sustainability. It’s about shifting from a reactive approach to a proactive one, anticipating challenges and preparing for the unexpected. The goal is to minimize negative impacts and maximize opportunities. Let’s explore how to build a robust risk management framework.

Understanding the Importance of Risk Management

The benefits of implementing a comprehensive risk management strategy are far-reaching. Firstly, it enhances operational efficiency by identifying and addressing bottlenecks before they escalate. Secondly, it protects assets – whether physical, financial, or intellectual property – by minimizing potential losses. Thirdly, it fosters a culture of accountability and encourages employees to identify and report potential issues. Finally, and perhaps most importantly, effective risk management builds trust with stakeholders, including investors, customers, and regulators. Without a clear understanding of potential risks, organizations are vulnerable to unforeseen events that can severely impact their bottom line. Consider the impact of a cyberattack on customer data, a supply chain disruption, or a regulatory fine – these are all examples of risks that can have devastating consequences. Ignoring these risks is simply not an option.

Identifying Potential Risks – The Initial Assessment
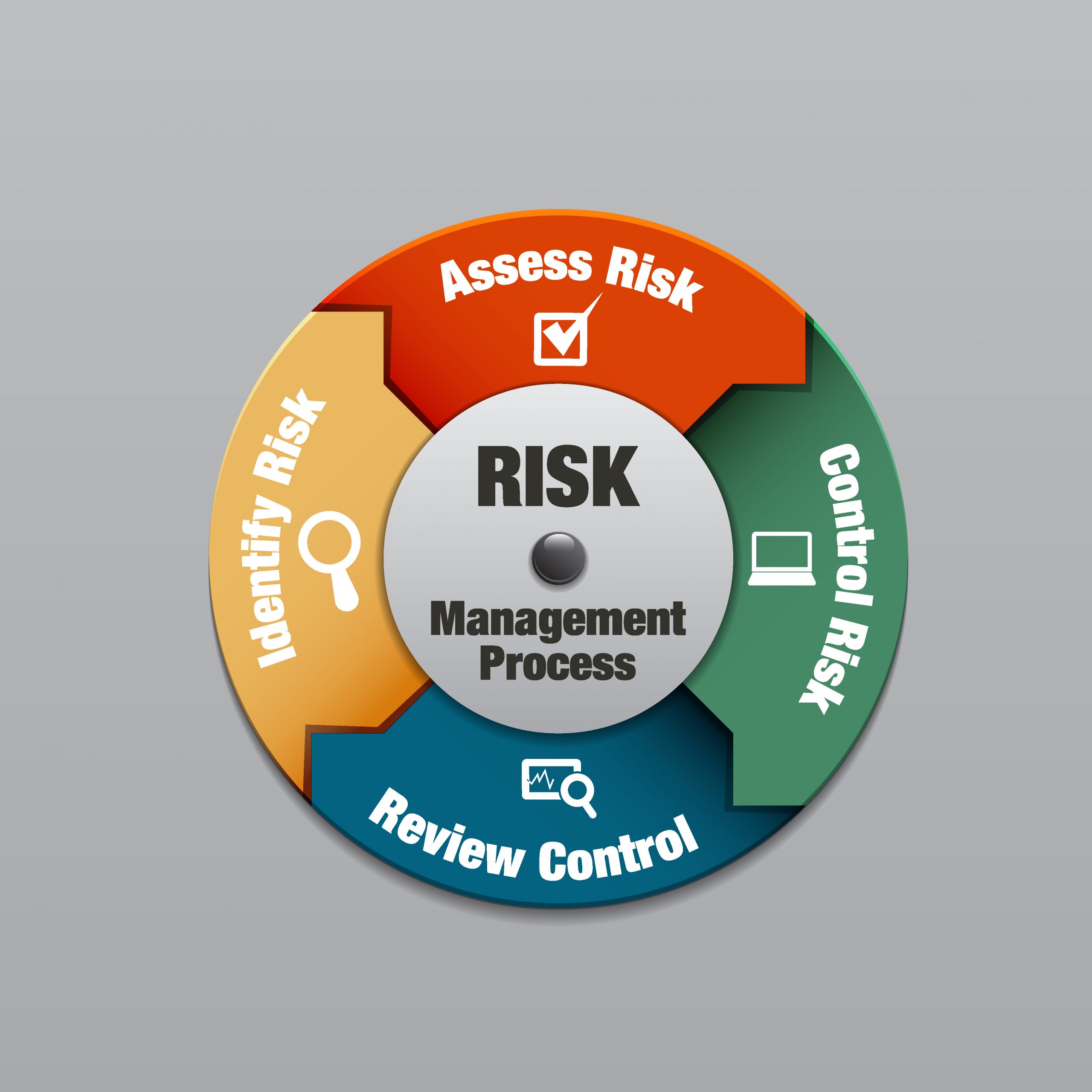
The first step in effective risk management is identifying potential risks. This requires a systematic process of assessment, often utilizing techniques like brainstorming, SWOT analysis, and industry benchmarking. It’s crucial to consider both internal and external factors. Internal risks stem from operational weaknesses, human error, or inadequate processes. External risks, on the other hand, arise from factors outside the organization’s control, such as economic downturns, natural disasters, or changes in regulations. A robust risk register should document all identified risks, along with their potential impact and likelihood of occurrence. Don’t just list risks; analyze why they exist. Understanding the root causes of risk is just as important as identifying the risks themselves. For example, a lack of employee training could lead to errors that result in financial losses. Regularly reviewing and updating the risk register is essential to ensure it remains relevant and accurate. Furthermore, consider the 'triple failure' scenario – a failure of the strategy, the implementation, and the execution.

Risk Response Strategies – Mitigating the Threats
Once risks have been identified, the next step is to develop appropriate response strategies. These strategies aim to either mitigate the risk (reduce its likelihood or impact) or transfer it to another party (e.g., through insurance). Common risk response strategies include:
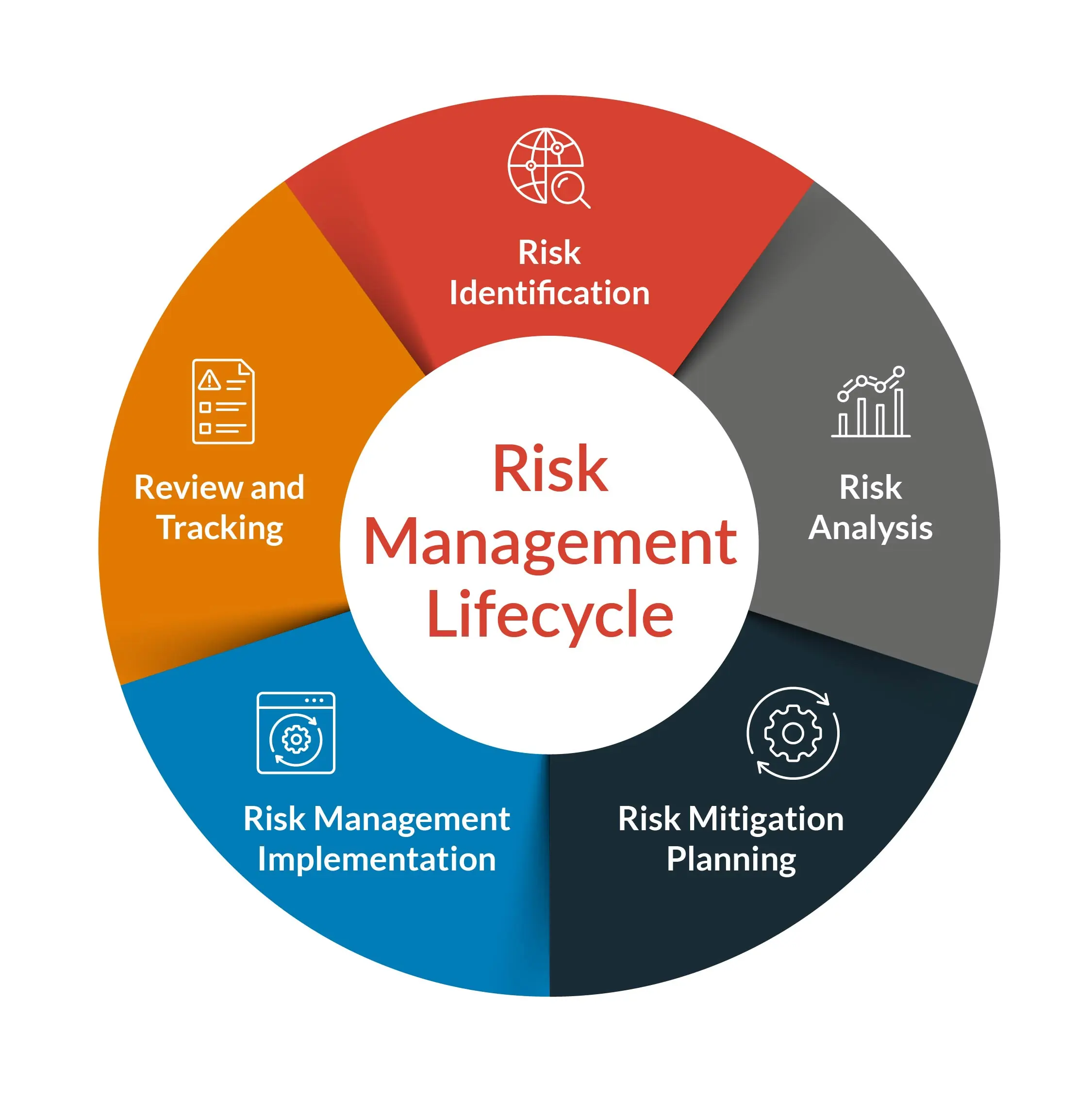
- Avoidance: Completely eliminating the risk by choosing not to engage in the activity that creates it. This is often the most drastic option but can be appropriate for highly risky activities.
- Mitigation: Taking steps to reduce the likelihood or impact of the risk. This is the most common approach and often involves implementing controls and procedures.
- Transfer: Shifting the risk to another party, typically through insurance or outsourcing.
- Acceptance: Acknowledging the risk and deciding to take no action, typically when the cost of mitigation outweighs the potential benefits. This should be a conscious decision based on a thorough assessment of the risk.
Specific mitigation techniques include implementing robust cybersecurity measures, diversifying supply chains, developing business continuity plans, and conducting regular audits. The choice of strategy depends on the specific risk and the organization’s risk appetite. A well-defined risk response plan is critical for ensuring that risks are effectively managed.

Risk Appetite and Risk Tolerance – Defining Boundaries
Understanding an organization’s risk appetite and risk tolerance is crucial for establishing a sound risk management framework. Risk appetite defines the level of risk an organization is willing to accept in pursuit of its strategic objectives. It’s often expressed as a percentage or a range. Conversely, risk tolerance represents the acceptable level of risk an organization is willing to accept. It’s a more subjective measure and often reflects the organization’s values and culture. A clear understanding of both is essential for guiding risk management decisions. For example, a financial institution with a high-risk appetite might be willing to accept a higher level of risk in pursuit of higher returns, while a more conservative organization would prioritize lower risk. It’s important to communicate risk appetite and tolerance clearly to all employees to ensure everyone understands the boundaries of acceptable risk.

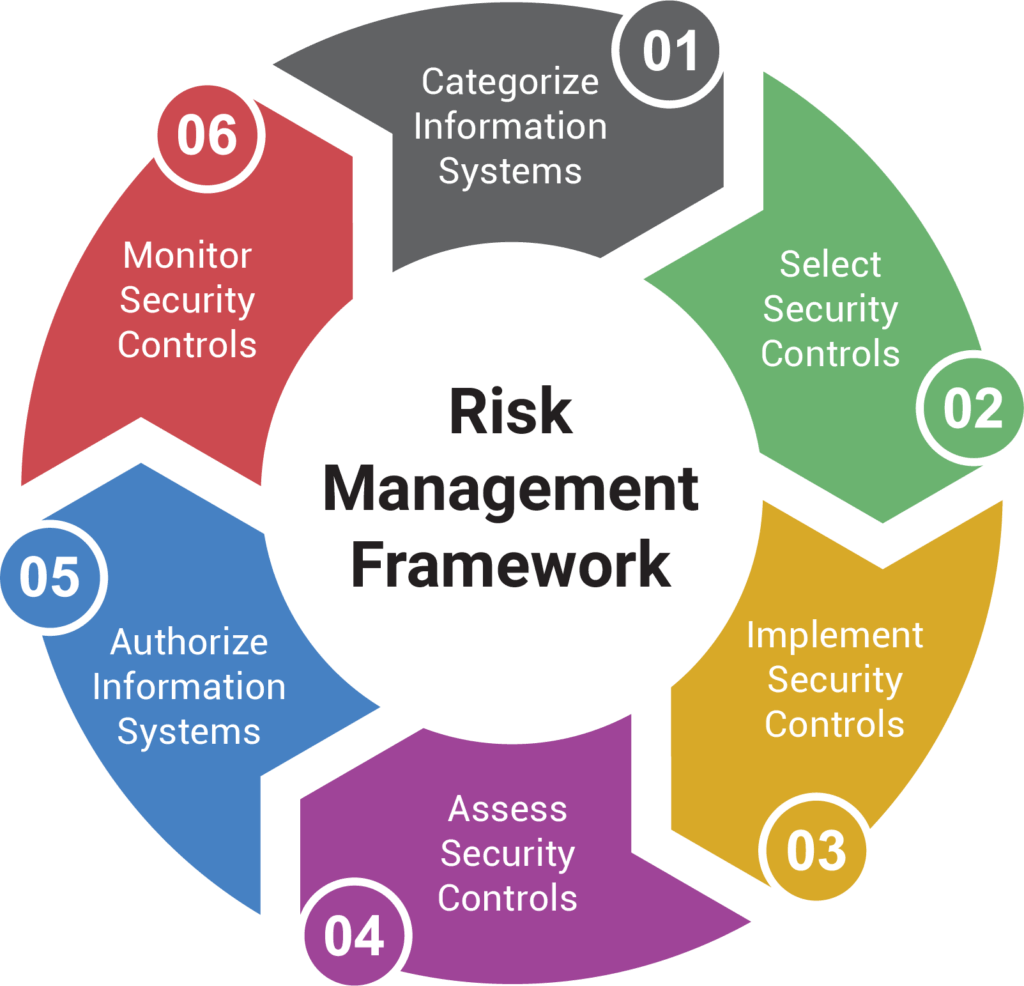
Implementing a Risk Management Framework – Best Practices
Implementing a robust risk management framework requires a systematic approach. Here are some best practices:
- Establish a Risk Management Committee: This committee should include representatives from various departments to ensure a holistic view of risks.
- Develop Risk Policies and Procedures: Clearly defined policies and procedures provide a framework for managing risks and ensure consistency.
- Conduct Regular Risk Assessments: Periodic risk assessments help identify new risks and reassess existing ones.
- Implement Controls: Implement controls to mitigate identified risks.
- Monitor and Review: Continuously monitor the effectiveness of risk management controls and review the risk register regularly.
- Document Everything: Maintain thorough documentation of all risk management activities.
The Role of Technology in Risk Management
Technology is playing an increasingly important role in risk management. Various software solutions are available to automate risk assessments, monitor compliance, and track risk events. These tools can significantly improve efficiency and accuracy. Examples include:
- Risk Management Software: Platforms like RSA Archer, MetricStream, and ServiceNow offer comprehensive risk management capabilities.
- Data Analytics: Utilizing data analytics to identify patterns and trends can help predict potential risks.
- Compliance Management Systems: These systems help ensure compliance with regulations and internal policies.
Conclusion – Building Resilience Through Risk Management
Risk management is not a one-time activity; it’s an ongoing process. By proactively identifying, assessing, and mitigating risks, organizations can protect their assets, enhance operational efficiency, and build resilience. A well-defined risk management framework, coupled with a commitment to continuous improvement, is essential for navigating the complexities of the modern business environment. Ultimately, effective risk management is about building a sustainable and successful organization. Risk management is an investment, not an expense. It’s a strategic imperative for any organization seeking to thrive in a dynamic and uncertain world. Remember, the ability to anticipate and respond to potential threats is the key to long-term success. Don’t underestimate the power of a proactive approach to risk.
