Data security solutions are no longer a luxury; they’re a fundamental necessity for businesses of all sizes. In today’s digital landscape, threats are constantly evolving, and the potential consequences of a data breach can be devastating – ranging from financial losses and reputational damage to legal liabilities and loss of customer trust. A proactive and comprehensive approach to data security is therefore paramount. This guide will delve into the key aspects of data security solutions, exploring the various technologies, best practices, and expert insights needed to protect your valuable information assets. Data security solutions are increasingly complex, requiring a layered approach that addresses both technical and operational considerations. Ignoring these elements leaves your organization vulnerable to a wide range of cyberattacks. Let’s explore how to build a robust defense against evolving threats.

Understanding the Growing Threat Landscape

The rise of cybercrime has dramatically increased in recent years, driven by factors such as sophisticated phishing attacks, ransomware, and increasingly targeted attacks against specific industries. Businesses of all sectors – from healthcare to finance – are prime targets. Data breaches are no longer simply a matter of inconvenience; they can have significant financial repercussions. The average cost of a data breach can exceed $4 million, and regulatory fines can be substantial. Furthermore, the public’s trust in organizations is eroding, with consumers increasingly demanding greater data protection. Understanding the specific threats your organization faces is the first step towards implementing effective security measures. Consider factors like industry regulations (e.g., HIPAA for healthcare), data sensitivity, and the potential impact of a breach on your customers. A clear understanding of these risks allows you to tailor your security strategy to address your specific vulnerabilities.
Key Data Security Technologies
A variety of technologies play a crucial role in safeguarding data. These include:
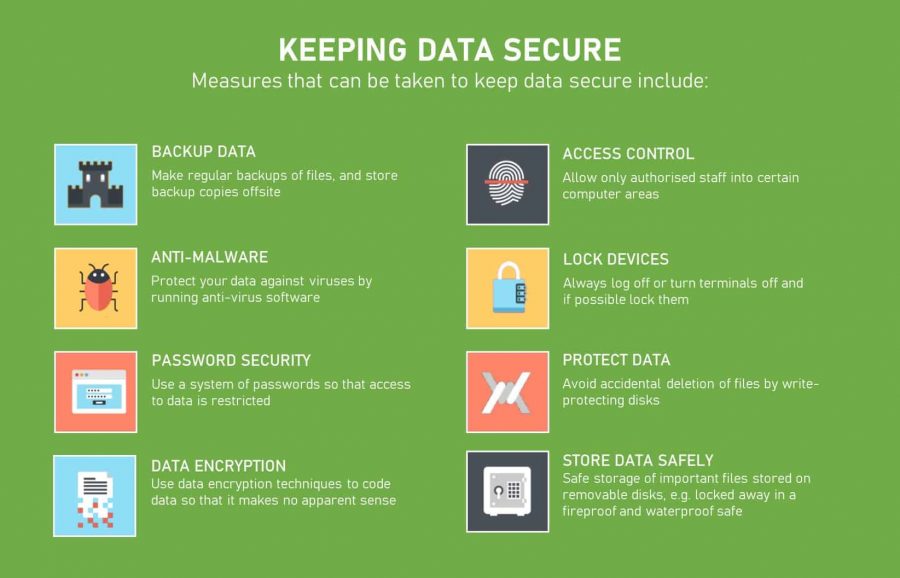
- Encryption: This is arguably the most fundamental security measure. Encryption transforms data into an unreadable format, protecting it even if it’s intercepted. Data security solutions often incorporate robust encryption protocols, such as AES-256, to ensure data remains confidential.
- Firewalls: Firewalls act as a barrier between your network and the outside world, blocking unauthorized access. They examine network traffic and block connections that don’t meet pre-defined security rules.
- Intrusion Detection and Prevention Systems (IDS/IPS): IDS/IPS systems monitor network traffic for suspicious activity and automatically block or alert administrators to potential threats.
- Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA): MFA requires users to provide multiple forms of identification, such as a password and a code sent to their mobile device, significantly reducing the risk of unauthorized access.
- Data Loss Prevention (DLP) Solutions: DLP tools monitor data movement within an organization, preventing sensitive information from leaving the control of the company.
- Endpoint Detection and Response (EDR): EDR solutions provide real-time monitoring and threat detection on individual devices, helping to identify and respond to threats before they can cause damage.
Implementing a Comprehensive Data Security Strategy
Building a truly effective data security strategy requires a holistic approach. It’s not just about implementing individual technologies; it’s about establishing a culture of security throughout your organization. Here’s a breakdown of key steps:

1. Risk Assessment and Vulnerability Scanning
Before implementing any security measures, it’s essential to conduct a thorough risk assessment. This involves identifying potential threats and vulnerabilities within your organization. Regular vulnerability scanning using tools like Nessus or Qualys can help identify weaknesses in your systems and applications. Data security solutions should be integrated with these assessments to provide a continuous view of your security posture.

2. Access Control and Identity Management
Robust access control is critical. Implement the principle of least privilege – granting users only the access they need to perform their jobs. Utilize strong password policies, multi-factor authentication, and role-based access control (RBAC) to restrict access to sensitive data. Consider implementing a centralized identity and access management (IAM) system to streamline user management and enforce consistent security policies.

3. Data Encryption and Backup
Encrypting data at rest and in transit is vital. Ensure that your data is encrypted when stored on servers, laptops, and mobile devices. Regularly back up your data to a secure, offsite location. Test your backup and recovery procedures to ensure they work effectively. Data security solutions that offer automated backup and recovery capabilities are invaluable.

4. Security Awareness Training
Human error is a significant factor in data breaches. Regular security awareness training is essential to educate employees about phishing attacks, social engineering, and other threats. Simulate phishing attacks to test employees’ awareness and identify areas for improvement.

5. Incident Response Plan
Develop and regularly test an incident response plan to guide your organization’s response to data breaches. The plan should outline roles and responsibilities, communication protocols, and steps for containment, eradication, and recovery. Having a well-defined incident response plan can minimize the damage caused by a breach and help you restore operations quickly.

The Role of Cloud Security
Cloud computing has revolutionized the way businesses store and process data. However, it also introduces new security challenges. Cloud security solutions are designed to address these challenges. Key considerations include:
- Shared Responsibility Model: Understand the shared responsibility model between you and your cloud provider. The provider is responsible for the security of the cloud, while you are responsible for the security in the cloud.
- Cloud Access Security Broker (CASB): A CASB provides visibility and control over cloud applications, helping you to identify and mitigate risks.
- Data Residency and Compliance: Ensure that your data is stored in a location that complies with relevant regulations.
Advanced Data Security Technologies
Beyond the basics, several advanced technologies are gaining traction:
- Data Masking and Tokenization: These techniques obscure sensitive data while still allowing it to be used for testing and development purposes.
- Threat Intelligence Platforms (TIPs): TIPs aggregate and analyze threat intelligence data from various sources to provide actionable insights for security teams.
- Security Information and Event Management (SIEM): SIEM systems collect and analyze security logs from various sources to detect and respond to threats.
Conclusion
Data security solutions are a continuous investment, not a one-time fix. The threat landscape is constantly evolving, and organizations must adapt their security strategies accordingly. By implementing a layered approach that combines technology, policies, and training, businesses can significantly reduce their risk of data breaches and protect their valuable information assets. Data security solutions are not just about preventing breaches; they’re about building a resilient and trustworthy organization. Prioritizing data security is an investment in the future of your business. Ultimately, a proactive and informed approach to data security is the key to success in today’s digital world.