Revenue management is no longer just a buzzword; it’s a critical business strategy for organizations of all sizes seeking to maximize profitability. In today’s competitive landscape, understanding how to influence customer demand and optimize pricing is essential for sustained success. This article will delve into the core principles of revenue management, exploring various techniques and providing practical insights to help you implement effective strategies. Revenue management is about proactively anticipating and responding to changes in demand, ensuring you capture the maximum value from your offerings. It’s about understanding your customers, your products, and the market dynamics at play. Without a robust revenue management system, businesses risk losing revenue and falling behind their competitors. Let’s explore how to build a system that drives sustainable growth.
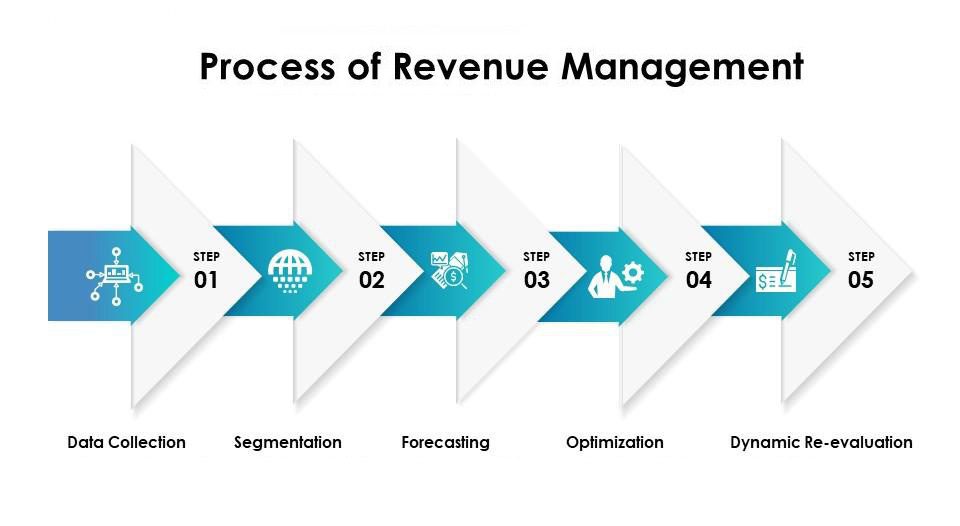
Understanding the Fundamentals of Revenue Management

At its heart, revenue management is about balancing supply and demand. It’s a complex discipline that involves forecasting, pricing, inventory control, and channel management. It’s not simply about setting prices; it’s about creating a dynamic system that adapts to real-time market conditions. A successful revenue management strategy requires a deep understanding of your customer behavior, your product lifecycle, and the broader economic environment. It’s a continuous process of analysis, optimization, and adaptation. The goal is to proactively influence customer choices, maximizing revenue and minimizing losses. Different industries require different approaches, but the underlying principles remain consistent.

Forecasting Techniques – Predicting Future Demand
Accurate forecasting is the cornerstone of any effective revenue management system. There are several techniques available, each with its own strengths and weaknesses. Statistical forecasting methods, such as moving averages and exponential smoothing, can provide a baseline estimate of future demand. However, these methods are often limited by the accuracy of the underlying data. More sophisticated techniques, like time series analysis and regression modeling, can incorporate external factors like seasonality, trends, and promotional activity to generate more precise forecasts. Revenue management relies heavily on the ability to anticipate shifts in customer behavior and market trends. Regularly reviewing and updating forecasts is crucial for maintaining a competitive edge. Tools like CRM systems and data analytics platforms can significantly enhance forecasting accuracy.

Pricing Strategies – Finding the Sweet Spot
Pricing is a critical element of revenue management. It’s not just about setting a price; it’s about finding the optimal price point that maximizes revenue and profitability. Several pricing strategies can be employed, each with its own advantages and disadvantages. Cost-plus pricing involves calculating the cost of providing a product or service and adding a markup. Value-based pricing focuses on the perceived value of the offering to the customer. Dynamic pricing, also known as demand-based pricing, adjusts prices in real-time based on factors like demand, competitor pricing, and inventory levels. Revenue management often involves a combination of these strategies, tailored to specific products and market conditions. A/B testing different pricing models is a valuable tool for identifying what works best.
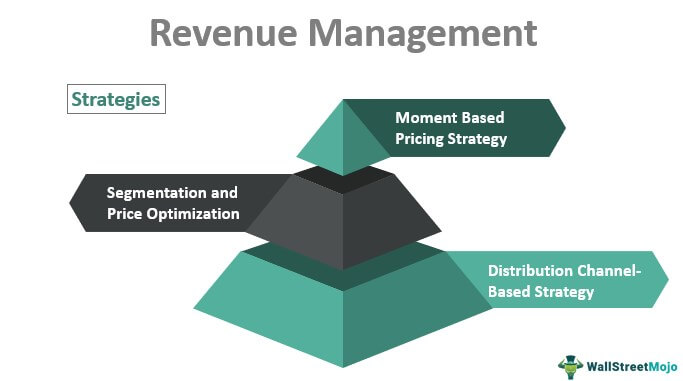
Key Revenue Management Techniques
Several specific techniques are commonly used within revenue management frameworks. These include:

Inventory Optimization – Balancing Supply and Demand
Inventory management is closely linked to revenue management. Holding too much inventory ties up capital and increases storage costs. Holding too little inventory can lead to lost sales and dissatisfied customers. Inventory optimization involves carefully managing stock levels to meet demand while minimizing holding costs. This often involves using techniques like Economic Order Quantity (EOQ) and safety stock calculations. Revenue management teams work closely with procurement and logistics to ensure optimal inventory levels.

Channel Management – Reaching the Customer
Revenue management extends beyond the direct sales channel. It involves strategically managing relationships with distributors, retailers, and other channels to reach customers effectively. Channel management includes optimizing pricing and promotions across different channels, ensuring a consistent customer experience. Understanding the channel dynamics and their impact on revenue is crucial for maximizing profitability. Revenue management often involves negotiating favorable terms with channel partners.

Segmentation – Tailoring Offers to Specific Groups
Recognizing that customers are not a homogenous group, revenue management often involves segmenting customers based on their needs, preferences, and purchasing behavior. This allows for the creation of targeted offers and promotions that are more likely to resonate with each segment. For example, a loyalty program can be tailored to reward frequent customers, while a promotional offer can be targeted to customers who have recently purchased a specific product. Revenue management relies on data analytics to identify and segment customer groups effectively.
Bundling – Creating Value
Bundling products or services together can increase perceived value and drive sales. Bundling can be offered as a discount, or as a package of complementary products or services. Careful consideration must be given to the bundling strategy to ensure that the combined value is greater than the sum of the individual components. Revenue management teams often analyze competitor bundling strategies to identify opportunities for differentiation.

The Role of Technology in Revenue Management
Technology has revolutionized revenue management, providing powerful tools and capabilities to improve efficiency and accuracy. CRM (Customer Relationship Management) systems are essential for capturing and analyzing customer data, while data analytics platforms can provide insights into customer behavior and market trends. ERP (Enterprise Resource Planning) systems can integrate revenue management with other business functions, such as finance, supply chain, and marketing. Cloud-based solutions offer scalability and flexibility, allowing businesses to adapt to changing needs. Artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning are increasingly being used to automate forecasting, personalize offers, and optimize pricing.
Advanced Analytics – Predictive Modeling
Beyond basic forecasting, advanced analytics techniques are becoming increasingly important. Machine learning algorithms can identify complex patterns in data that would be difficult for humans to detect. These algorithms can be used to predict demand, optimize pricing, and personalize offers. Regression analysis can be used to identify the factors that most strongly influence revenue. Clustering can be used to segment customers based on their purchasing behavior. These techniques require specialized expertise but can deliver significant value.
Conclusion – Maximizing Revenue Through Strategic Implementation
Revenue management is a dynamic and evolving discipline that requires a strategic and data-driven approach. By understanding the fundamental principles of revenue management, implementing effective forecasting techniques, utilizing appropriate pricing strategies, and leveraging technology, businesses can significantly improve their revenue performance. Revenue management is not a one-time project; it’s an ongoing process of continuous improvement. Regularly reviewing and adapting your revenue management system to changing market conditions is essential for maintaining a competitive advantage. Ultimately, successful revenue management is about anticipating customer needs, optimizing your offerings, and maximizing profitability. Investing in the right tools and training is crucial for success. The ability to proactively manage demand and optimize pricing is a key differentiator in today’s competitive marketplace. Don’t underestimate the power of a well-executed revenue management strategy.