Business process modeling methodologies are increasingly vital for organizations seeking to improve efficiency, reduce costs, and enhance customer satisfaction. In today’s dynamic business landscape, understanding and documenting how processes actually work is no longer a luxury – it’s a necessity. This article will delve into the core concepts of various business process modeling methodologies, providing a comprehensive overview of the most popular approaches and their practical applications. The central focus will be on understanding how these methodologies differ and how to choose the right one for your specific needs. Let's explore how these techniques can transform how your organization operates.
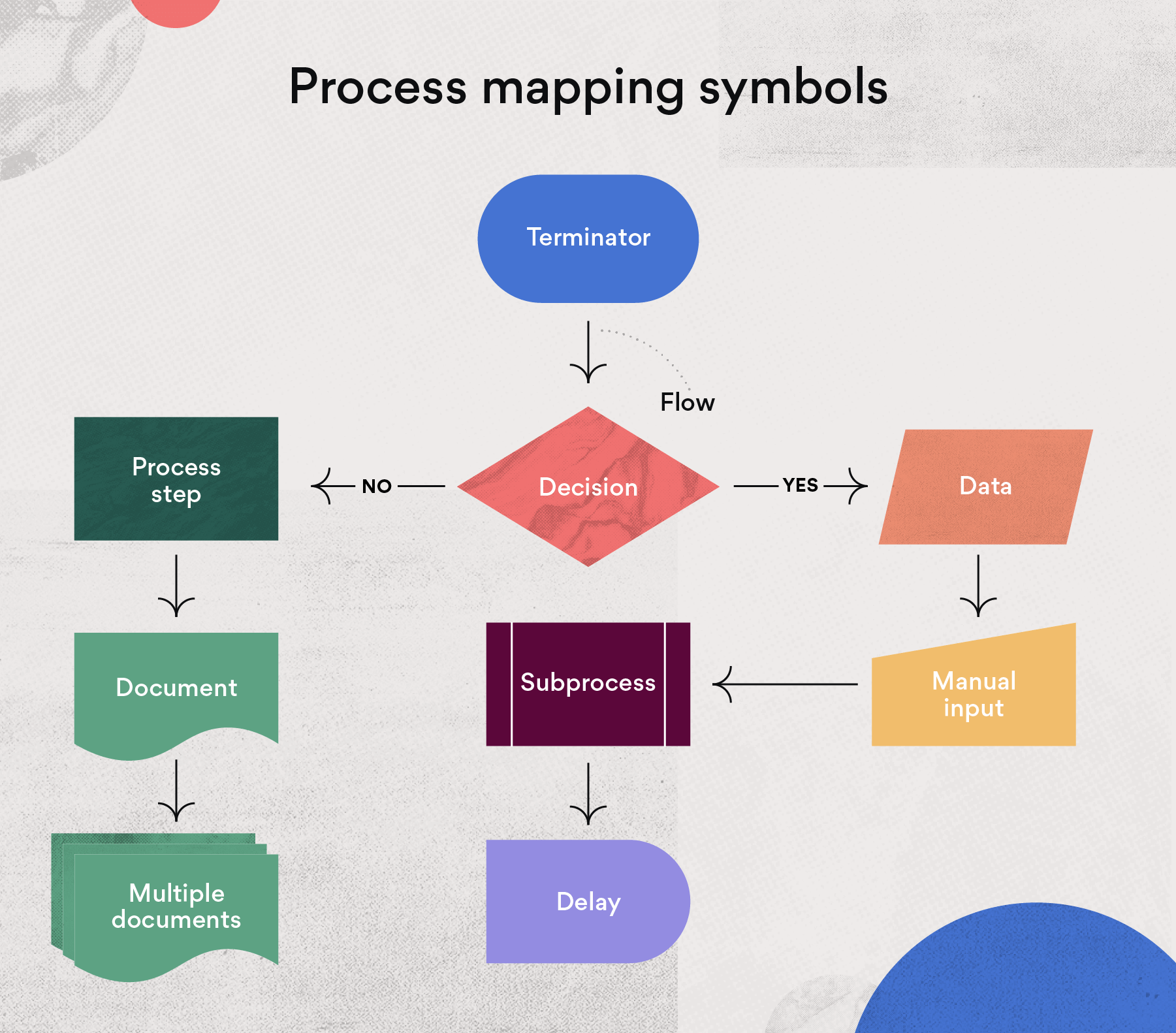
Understanding the Importance of Process Modeling
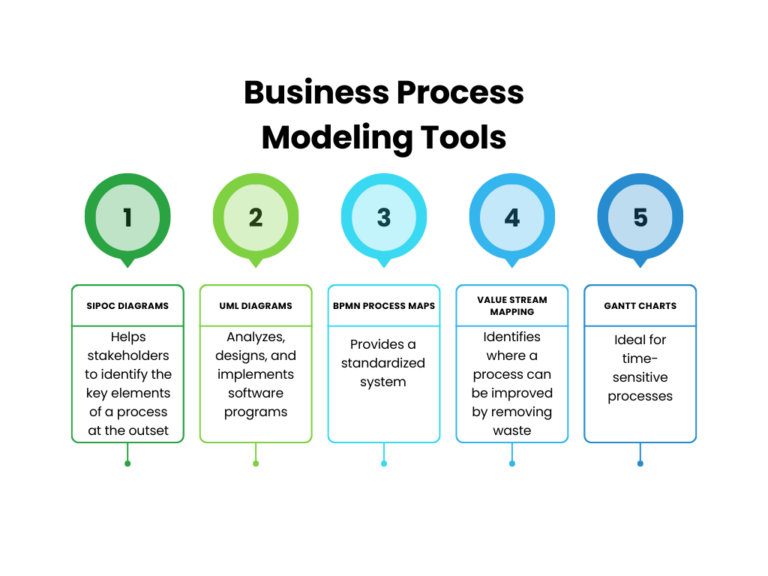
Before diving into specific methodologies, it’s crucial to grasp why process modeling is so important. Traditional, linear workflows often lead to inefficiencies, errors, and frustration. By mapping out processes visually, we can identify bottlenecks, redundancies, and areas for improvement. This proactive approach allows organizations to:
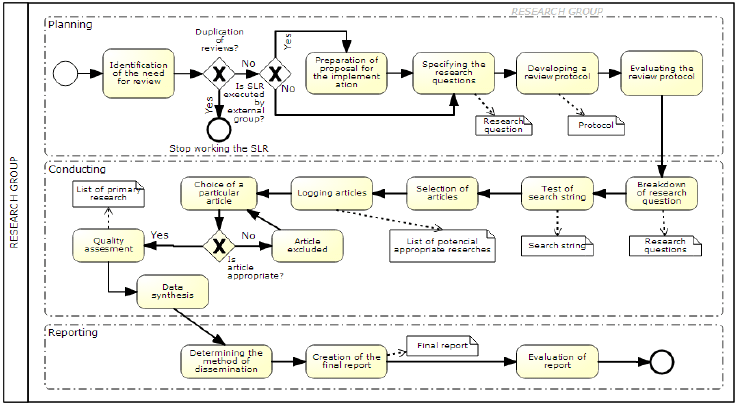
- Reduce Waste: Identify and eliminate unnecessary steps, minimizing waste and maximizing value.
- Improve Efficiency: Streamline processes, reducing cycle times and increasing throughput.
- Enhance Quality: Standardize processes and reduce errors, leading to higher quality outputs.
- Increase Customer Satisfaction: Faster, more reliable processes translate to happier customers.
- Support Digital Transformation: Modern methodologies are essential for implementing automation and digital solutions.
Waterfall Methodology: A Traditional Approach
The Waterfall methodology is a sequential, linear approach to process modeling. It’s often considered the foundational approach, particularly in projects with well-defined requirements. Each phase – requirements gathering, design, implementation, testing, and deployment – must be completed before the next begins.
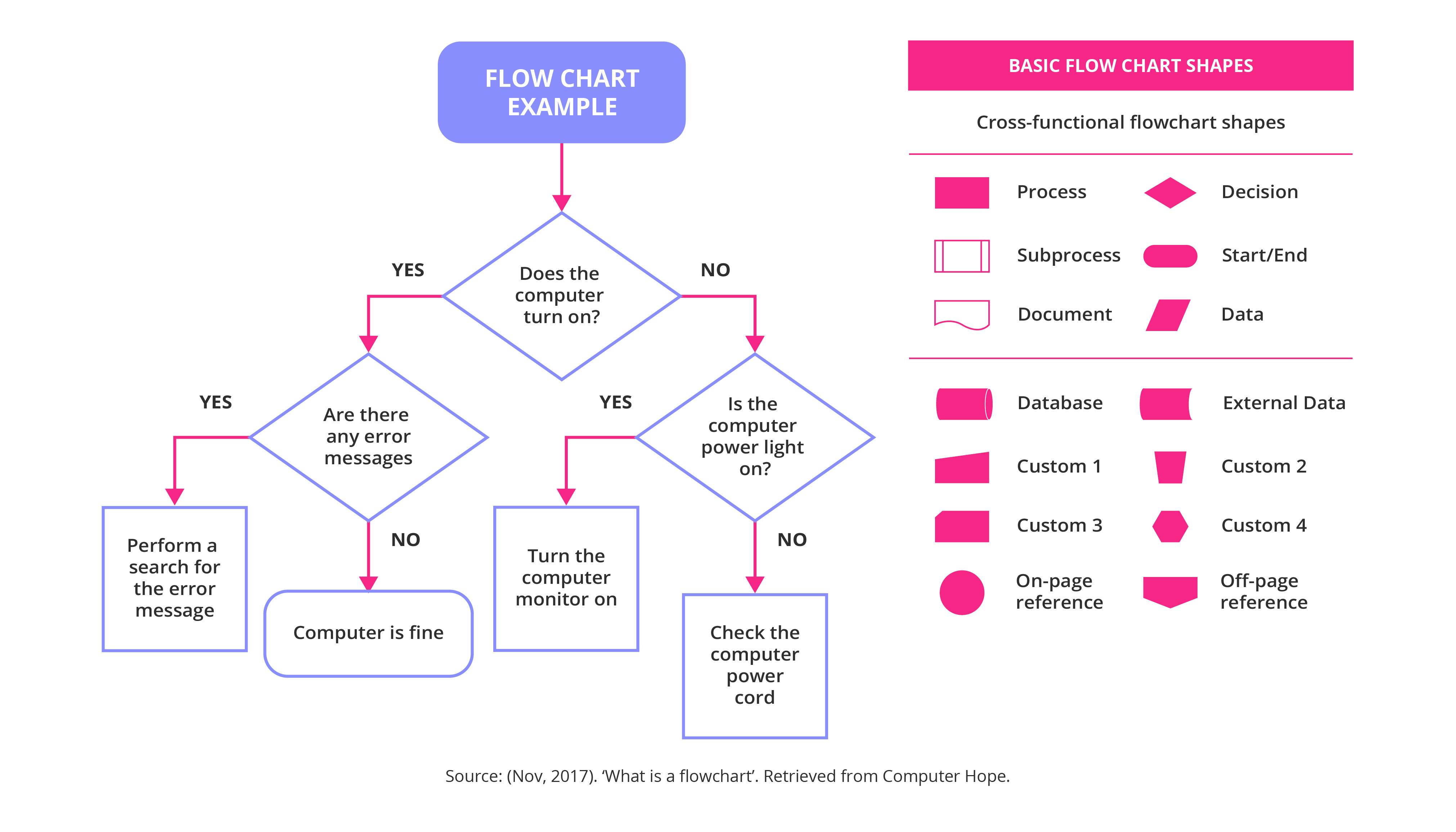
Requirements Gathering is the initial phase, meticulously documenting all the needs and expectations of the stakeholders. This involves extensive interviews, surveys, and analysis of existing data. Detailed process flow diagrams are then created to visually represent the steps involved. The design phase focuses on creating the blueprint for the new process, outlining the technology and infrastructure required. Testing and implementation follow, ensuring the new process functions as intended. Deployment involves putting the new process into production, and ongoing monitoring and refinement are crucial.

Challenges with Waterfall: The Waterfall approach can be inflexible and slow to adapt to changing requirements. It’s particularly challenging when requirements are not fully understood upfront. Changes late in the process can be costly and disruptive.
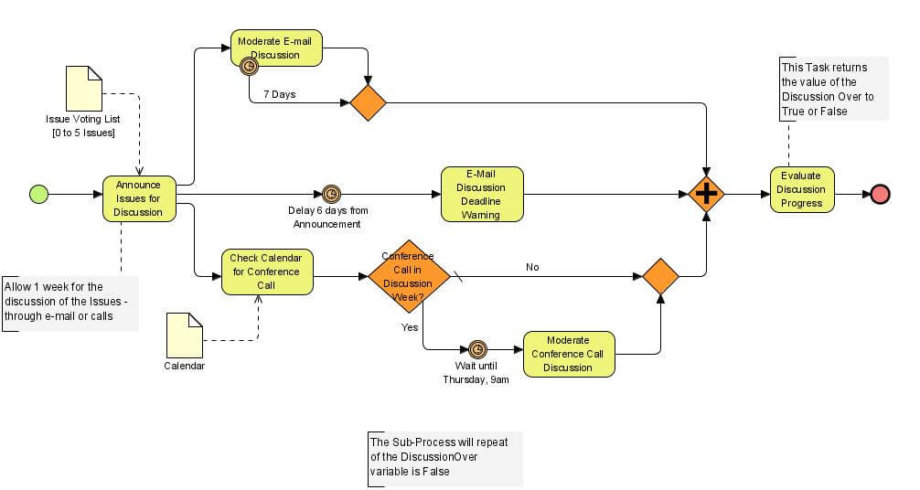
BPMN (Business Process Model and Notation): A Modern Standard
Business Process Model and Notation (BPMN) is a widely adopted standard for modeling business processes. It provides a graphical language for describing processes in a standardized and easily understandable format. BPMN focuses on the what of a process, rather than the how.

Key elements of BPMN include:
- Activities: Represented by rectangles, indicating a task or action.
- Gateways: Represent decision points, such as "if-then-else" statements.
- Sequence Flows: Show the order in which activities are performed.
- Pools: Group activities together, representing a logical unit of work.
- Events: Mark points of initiation or completion of a process.
Benefits of BPMN: BPMN promotes clarity, consistency, and collaboration. It’s easily shared with stakeholders across different departments and facilitates process improvement initiatives. Many BPMN tools are available, ranging from simple diagramming software to sophisticated modeling platforms.
Lean Process Modeling: Focusing on Value
Lean process modeling emphasizes identifying and eliminating waste – anything that doesn’t add value to the customer. It’s a highly iterative and data-driven approach, focusing on continuous improvement.
Key Lean Principles Applied to Process Modeling:
- Value Stream Mapping: Visually maps the entire flow of materials and information required to deliver a product or service, identifying areas of waste.
- Root Cause Analysis: Uses techniques like the 5 Whys to identify the underlying causes of problems, rather than just treating symptoms.
- Kaizen: A philosophy of continuous improvement, encouraging small, incremental changes to optimize processes.
- Standardized Work: Documenting and implementing standardized procedures to ensure consistency and efficiency.
Benefits of Lean Process Modeling: Lean methodologies are particularly effective for organizations seeking to reduce costs, improve efficiency, and enhance customer satisfaction. They are well-suited for industries with high levels of complexity and variability.
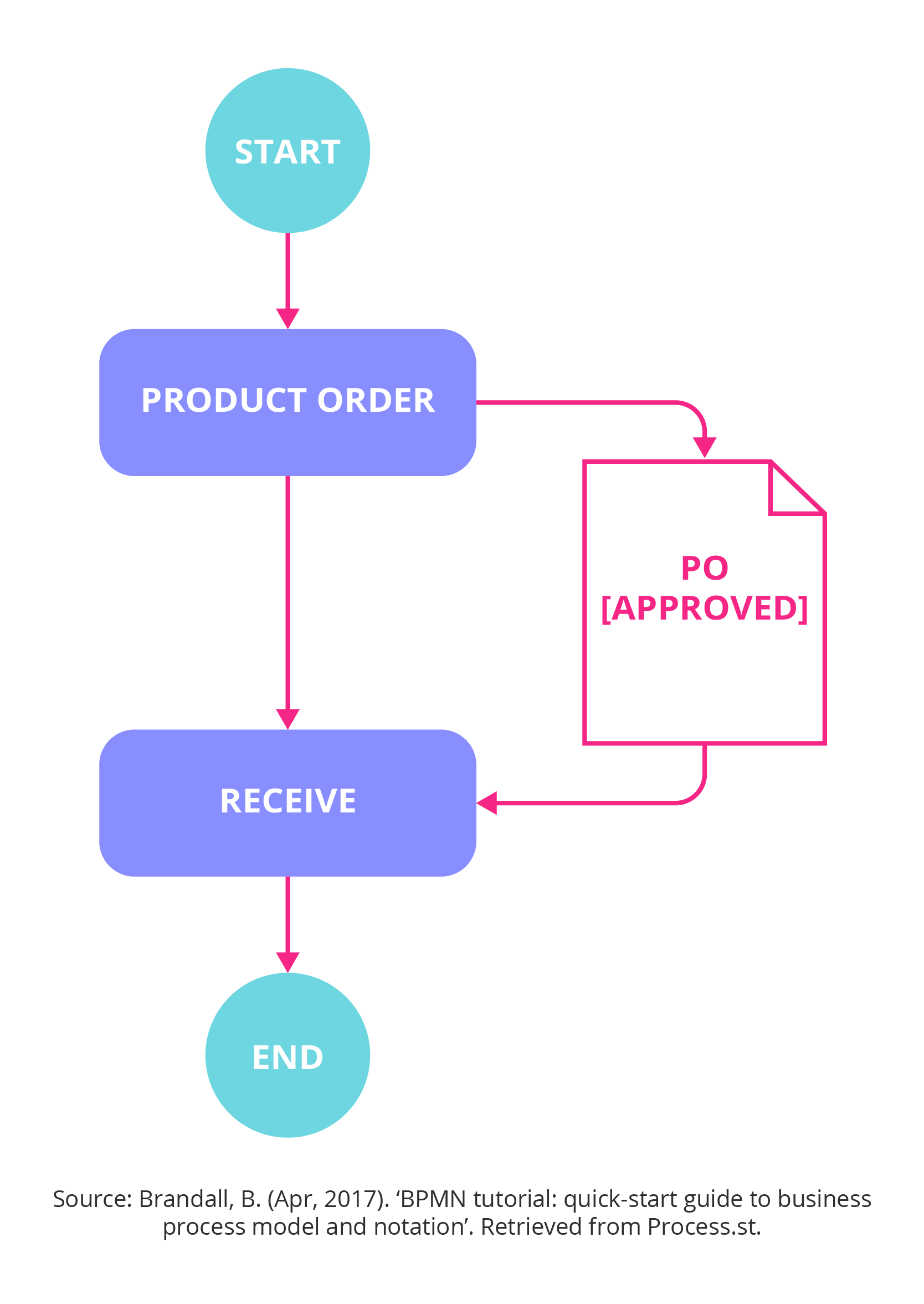
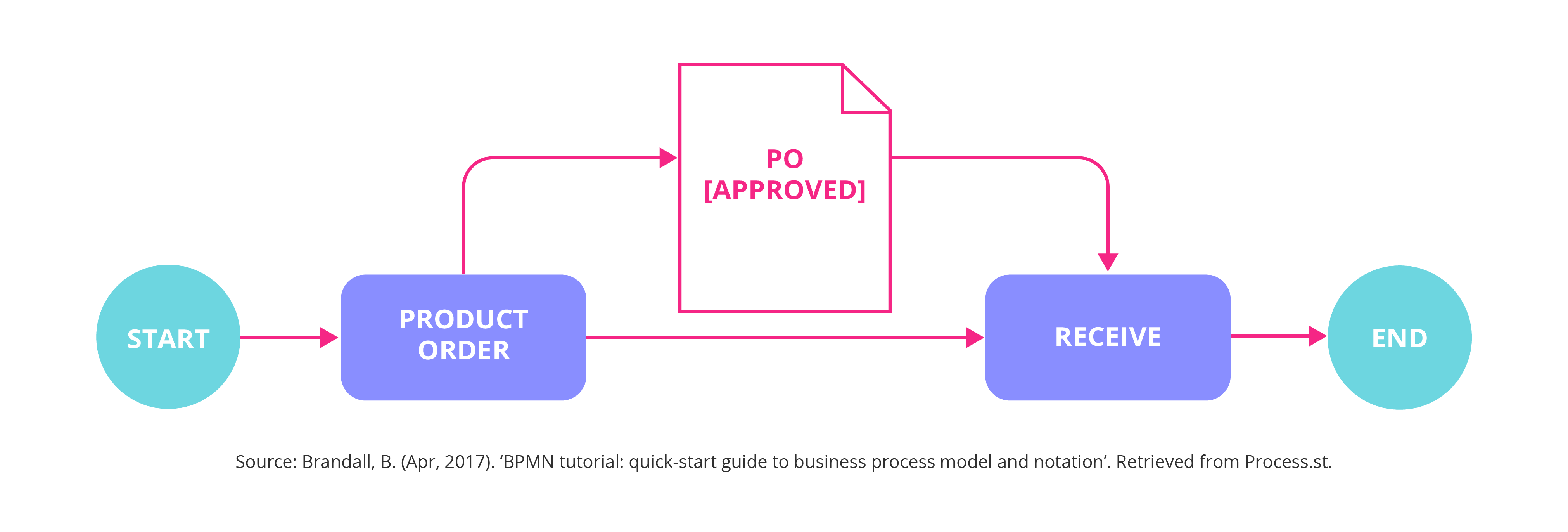
Process Flowcharting: A Visual Approach
Process flowcharts are a simple yet powerful way to visually represent a process. They use standard symbols to depict the sequence of steps, decision points, and data flows. While less formal than BPMN, they are often sufficient for basic process documentation and communication.
Common Symbols Used in Process Flowcharts:
- Oval: Represents the start or end of the process.
- Rectangle: Represents a process step.
- Diamond: Represents a decision point.
- Arrow: Indicates the flow of the process.
Benefits of Process Flowcharts: Process flowcharts are easy to understand and can be used to communicate complex processes to a wide audience. They are particularly useful for training and documentation.
Agile Process Modeling: Embracing Flexibility
Agile process modeling is a methodology that emphasizes iterative development and continuous feedback. It’s particularly well-suited for organizations that need to respond quickly to changing requirements. Agile process modeling often utilizes Kanban boards and other visual tools to track progress and identify bottlenecks.
Key Agile Principles Applied to Process Modeling:
- Iterative Development: Processes are broken down into smaller, manageable iterations.
- Continuous Feedback: Regularly gathering feedback from stakeholders to ensure the process is meeting their needs.
- Collaboration: Close collaboration between developers, testers, and stakeholders.
- Adaptability: The ability to quickly adapt to changing requirements.
Benefits of Agile Process Modeling: Agile methodologies are effective for organizations that need to deliver value quickly and iteratively.
Choosing the Right Methodology
Selecting the appropriate business process modeling methodology depends on several factors, including the complexity of the process, the organization’s culture, and the specific goals of the project. Waterfall is a good choice for well-defined, stable processes. BPMN is a versatile option for a wide range of processes. Lean is ideal for organizations focused on continuous improvement. Process flowcharts are suitable for simple processes. Agile methodologies are best suited for rapidly changing environments.
Tools for Process Modeling
Numerous tools are available to support process modeling, ranging from simple diagramming software to sophisticated modeling platforms. Some popular options include:
- Microsoft Visio: A widely used diagramming tool.
- Lucidchart: A cloud-based diagramming tool.
- Draw.io: A free and open-source diagramming tool.
- Bizagi Modeler: A BPMN modeling tool.
- Signavio Process Manager: A comprehensive process management platform.
Conclusion
Business process modeling methodologies provide a powerful framework for understanding, documenting, and improving business processes. By adopting the right approach, organizations can unlock significant benefits, including increased efficiency, reduced costs, and improved customer satisfaction. The key is to choose a methodology that aligns with your specific needs and to continuously refine your processes based on feedback and data. As technology continues to evolve, so too will the methodologies used to model and manage business processes, ensuring that organizations remain competitive in today’s rapidly changing world. Investing in process modeling is an investment in the future success of your organization.