Financial reporting is the process of compiling and presenting financial data to stakeholders – investors, creditors, regulators, and management – to inform decision-making. It’s more than just crunching numbers; it’s about transparency, accountability, and understanding a company’s financial health. Effective financial reporting isn’t just about complying with regulations; it’s about building trust and confidence. Financial reporting is a critical component of corporate governance and a cornerstone of economic stability. A robust and well-executed financial reporting system can significantly impact a company’s valuation, access to capital, and overall success. This article will delve into the key strategies and best practices for crafting compelling and reliable financial reports.

Understanding the Importance of Financial Reporting
The need for accurate and timely financial reporting stems from several factors. Investors rely on financial statements to assess risk and return on their investments. Creditors use them to evaluate a company’s ability to repay loans. Regulators mandate reporting to ensure transparency and protect consumers. Furthermore, internal management uses financial data to monitor performance, identify areas for improvement, and make strategic decisions. Without reliable financial reporting, these stakeholders are left with incomplete or misleading information, potentially leading to poor investment choices, increased risk, and regulatory scrutiny. Poorly managed financial reporting can damage a company’s reputation and erode investor confidence. Therefore, investing in strong financial reporting processes is a strategic imperative for any organization.
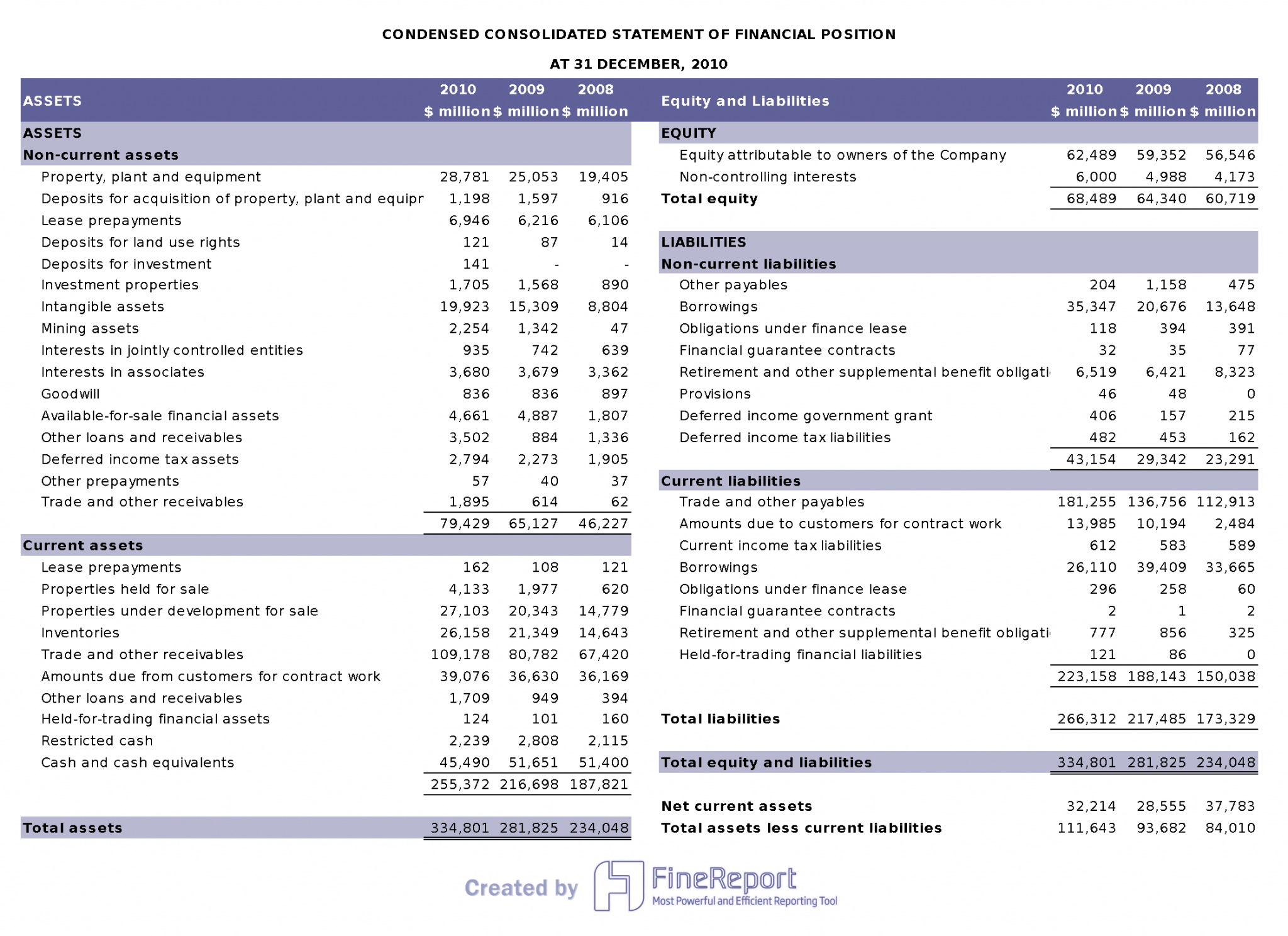
Key Components of a Comprehensive Financial Report
A typical financial report includes several key components. The balance sheet provides a snapshot of a company’s assets, liabilities, and equity at a specific point in time. The income statement details a company’s revenues, expenses, and profits over a period. The statement of cash flows outlines the movement of cash both into and out of the company, categorized by operating, investing, and financing activities. Finally, the statement of retained earnings shows the company’s accumulated equity. Each of these components is interconnected and contributes to a holistic view of the company’s financial position. Understanding the nuances of each section is crucial for interpreting the overall picture. Furthermore, the use of standardized accounting principles (like GAAP or IFRS) ensures comparability across different companies.
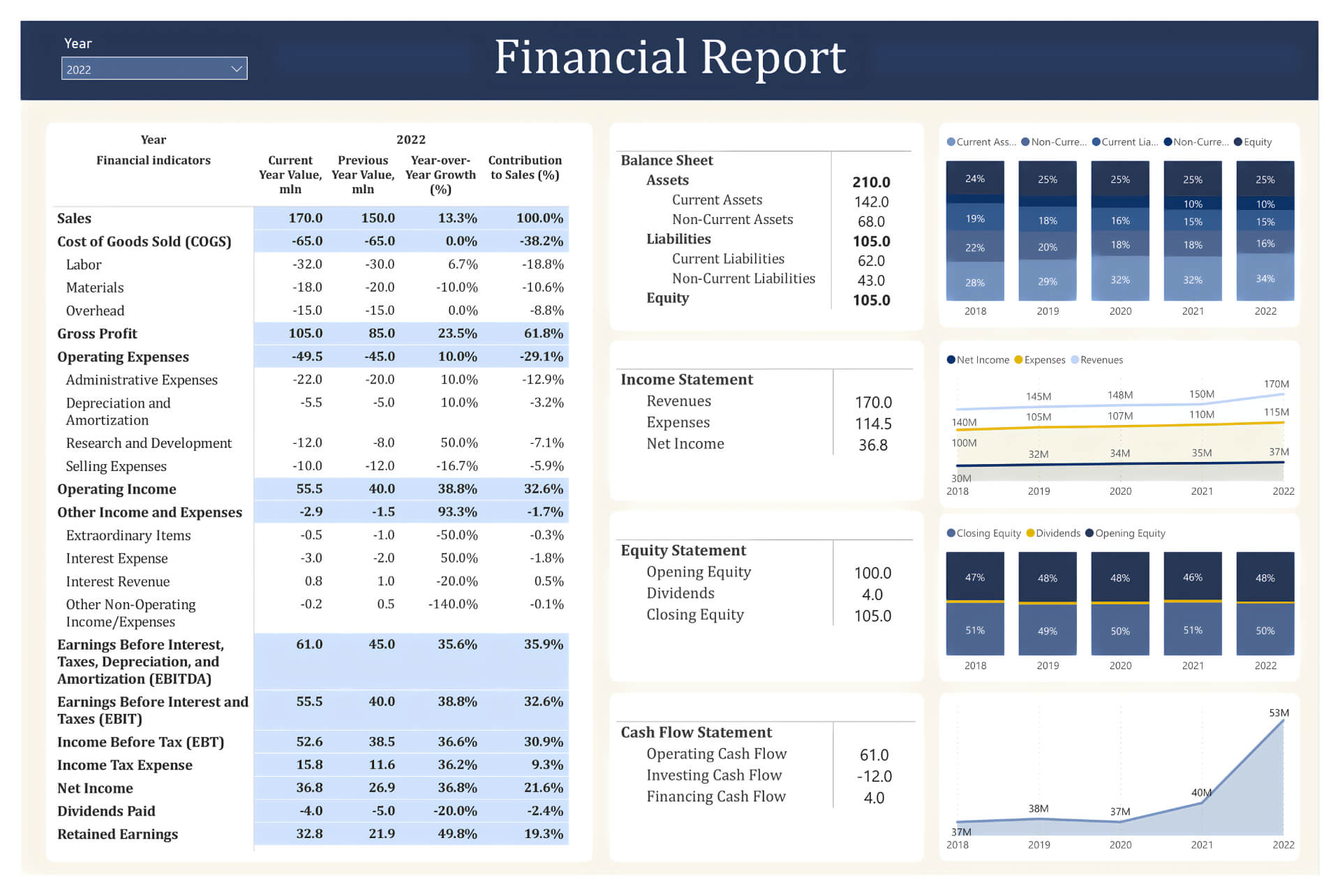
Strategies for Effective Financial Reporting
Several strategies can significantly enhance the quality and effectiveness of financial reporting. Firstly, data integrity is paramount. This involves meticulous data collection, validation, and verification processes to minimize errors and ensure the accuracy of the information presented. Regular audits by independent auditors are essential to identify and correct any discrepancies. Secondly, clear and concise language is vital. Financial statements should be written in a way that is easily understood by a broad audience, avoiding jargon and technical terms whenever possible. A well-structured report with clear headings and subheadings makes it easier for stakeholders to quickly grasp the key takeaways. Thirdly, timely reporting is crucial. Financial statements should be prepared and released promptly to provide stakeholders with timely information. Delayed reporting can lead to missed opportunities and potentially significant losses. Finally, consider incorporating technology to automate data collection and reporting processes. Systems like ERP (Enterprise Resource Planning) and specialized financial reporting software can significantly improve efficiency and accuracy.

The Role of Internal Controls
Internal controls are a critical element of effective financial reporting. These controls are designed to safeguard assets, prevent fraud, and ensure the accuracy of financial data. Segregation of duties – dividing responsibilities among different individuals – is a fundamental principle of internal controls. Regular testing of internal controls is essential to identify weaknesses and ensure they are operating effectively. Authorization procedures – requiring approval for transactions – help prevent unauthorized spending. Physical controls – such as securing cash and inventory – protect assets from theft or damage. A strong internal control framework significantly reduces the risk of errors and fraud, bolstering the reliability of the financial statements. Furthermore, risk assessments should be conducted to identify areas where controls are lacking and where improvements are needed.

Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) for Financial Reporting
Beyond the traditional financial statements, tracking key performance indicators (KPIs) provides valuable insights into a company’s performance. Revenue growth indicates the company’s ability to attract and retain customers. Profit margins measure the profitability of a company’s operations. Return on assets (ROA) assesses how efficiently a company is using its assets to generate profits. Debt-to-equity ratio indicates the level of financial leverage. Current ratio measures a company’s ability to meet its short-term obligations. Analyzing these KPIs alongside the financial statements provides a more comprehensive understanding of a company’s financial health and its ability to achieve its strategic goals. Regular monitoring of KPIs allows for proactive adjustments to strategy and operations.

The Impact of Technology on Financial Reporting
Technology has revolutionized financial reporting, transforming it from a manual, time-consuming process to a more efficient and automated one. Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) systems integrate various business functions, including accounting, inventory management, and customer relationship management, providing a centralized platform for financial data. Cloud-based accounting software offers greater accessibility and collaboration. Data analytics tools enable deeper insights into financial data, identifying trends and patterns that would be difficult to detect manually. Automated reporting tools streamline the generation of financial reports, reducing errors and saving time. Furthermore, blockchain technology is emerging as a potential solution for enhancing the security and transparency of financial transactions. The adoption of these technologies is accelerating, driving greater efficiency and accuracy in financial reporting.

Regulatory Compliance and Reporting Standards
Financial reporting is subject to numerous regulations and standards designed to ensure transparency and accountability. Generally Accepted Accounting Principles (GAAP) are widely used in the United States, while International Financial Reporting Standards (IFRS) are increasingly adopted globally. Sarbanes-Oxley Act (SOX) in the United States requires companies to establish and maintain internal controls over financial reporting. SEC (Securities and Exchange Commission) regulations govern the disclosure of financial information to investors. Staying abreast of these regulations and ensuring compliance is a critical responsibility for any organization. Failure to comply can result in significant penalties and reputational damage. Regular training and audits are essential to maintain compliance.

Future Trends in Financial Reporting
Several trends are shaping the future of financial reporting. ESG (Environmental, Social, and Governance) reporting is gaining increasing importance, as investors and stakeholders demand greater transparency regarding a company’s sustainability practices. Digital transformation is driving the adoption of new technologies, such as artificial intelligence and machine learning, to automate reporting processes and improve data analysis. Real-time reporting – providing up-to-the-minute financial data – is becoming increasingly common, particularly for companies operating in dynamic industries. Data visualization – presenting financial data in a visually appealing and easily understandable format – is enhancing the effectiveness of reporting. Blockchain technology is poised to play a significant role in enhancing the security and transparency of financial transactions. Ultimately, the future of financial reporting will be characterized by greater automation, data-driven insights, and a heightened focus on transparency and accountability.

Conclusion
Financial reporting is a complex and evolving field. It’s far more than simply compiling numbers; it’s a strategic discipline that underpins corporate decision-making and stakeholder confidence. By understanding the key components of a comprehensive financial report, implementing effective strategies, leveraging technology, and staying abreast of regulatory changes, organizations can ensure that their financial information is accurate, reliable, and readily accessible. Financial reporting is a continuous process of improvement, requiring ongoing attention and adaptation to changing business environments and regulatory requirements. Investing in robust financial reporting systems and processes is an investment in the long-term success and sustainability of any organization. Ultimately, effective financial reporting is a vital tool for building trust and fostering a sustainable business model. Financial reporting is a cornerstone of responsible corporate governance and a critical element of economic prosperity.