Customer journey mapping is no longer a ‘nice-to-have’ – it’s a critical component of modern business strategy. In today’s competitive landscape, understanding how your customers interact with your brand, from initial awareness to post-purchase support, is paramount to success. It’s about more than just understanding what they do; it’s about understanding why they do it and how they feel along the way. This article will delve into the core principles of customer journey mapping, providing practical strategies and tools to create effective maps that drive business growth. Customer journey mapping is a powerful technique that allows businesses to visualize the entire customer experience, identify pain points, and ultimately, improve satisfaction and loyalty. It’s a shift from a product-centric view to a customer-centric one, recognizing that every interaction shapes the customer’s perception and ultimately, their behavior. Without a clear understanding of the customer journey, businesses risk alienating potential customers and failing to meet their evolving needs. Let’s explore how to build these maps and leverage them for real results.
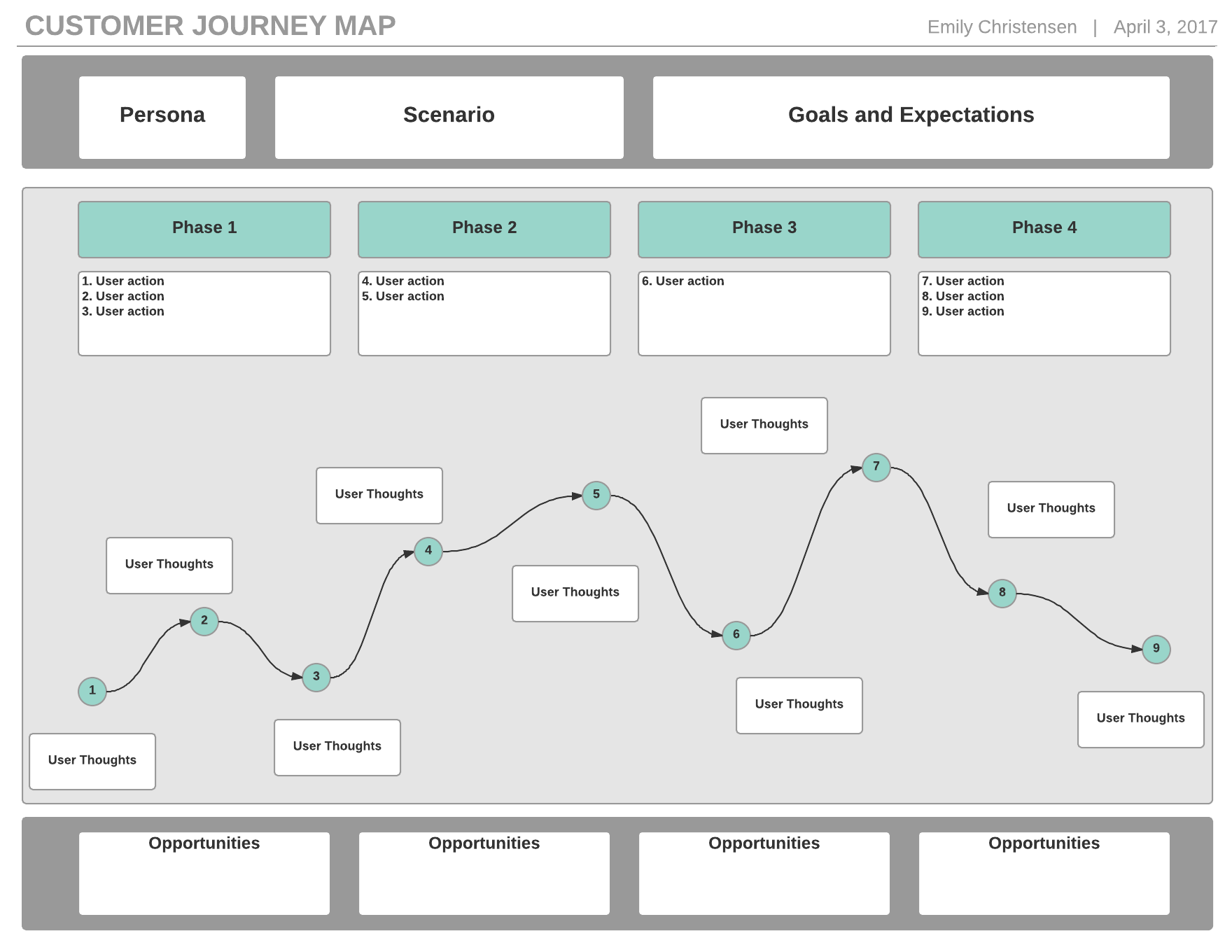
Understanding the Foundation: Why Customer Journey Mapping Matters
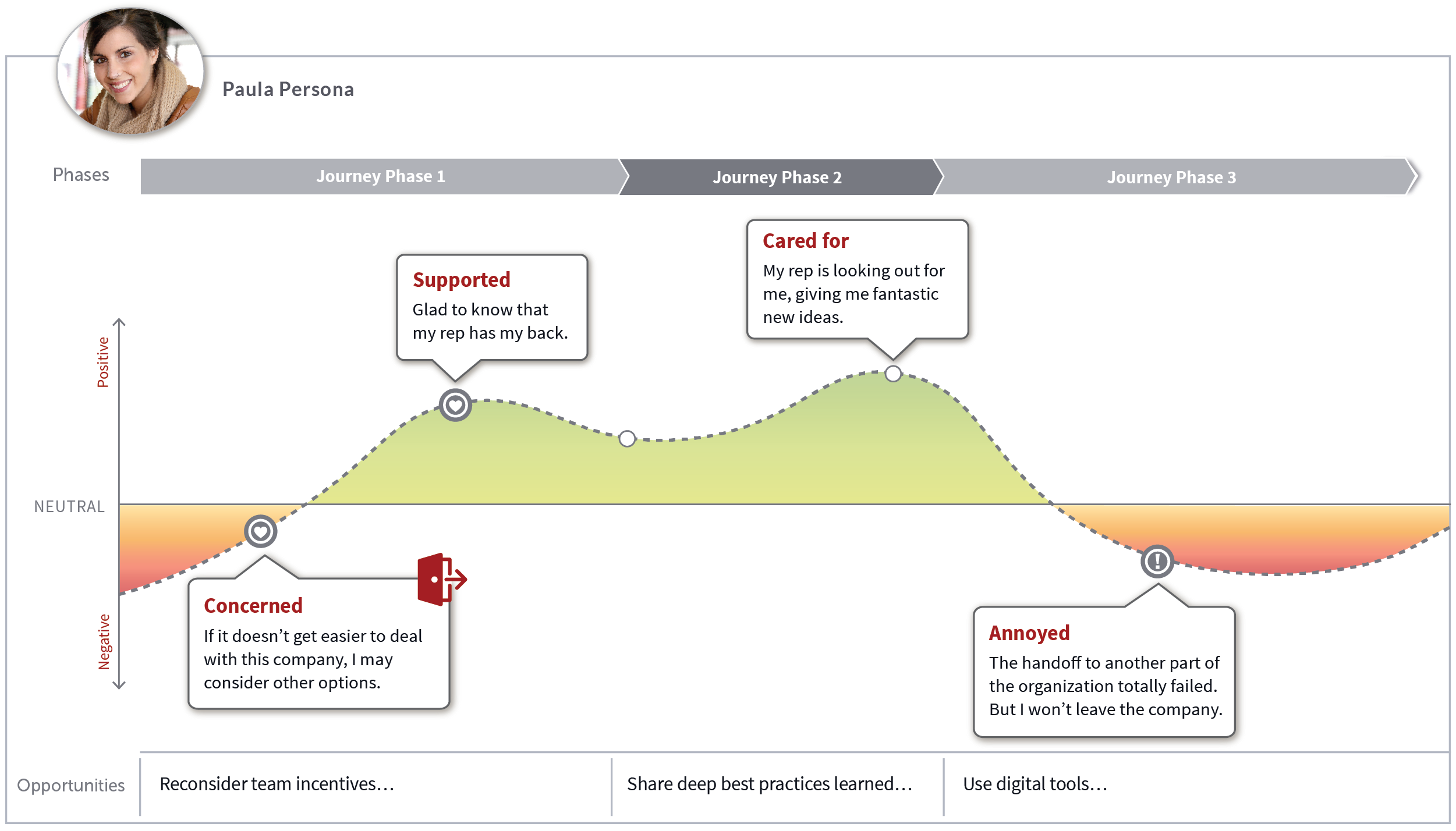
Before diving into the specifics, it’s important to understand why customer journey mapping is so valuable. Many businesses operate with a ‘one-size-fits-all’ approach, failing to account for the diverse experiences customers have. This leads to frustration, decreased loyalty, and lost revenue. Customer journey mapping addresses this by providing a holistic view of the customer’s experience across all touchpoints. It reveals the moments of truth – those crucial moments where a customer’s perception of your brand is shaped. By visualizing this journey, businesses can pinpoint areas for improvement and optimize the entire customer experience. The benefits extend beyond simple satisfaction; they include increased conversion rates, improved customer retention, and a stronger brand reputation. Furthermore, it allows for data-driven decision-making, moving away from guesswork and towards informed strategies. A well-executed customer journey map isn’t just a report; it’s a roadmap for continuous improvement.
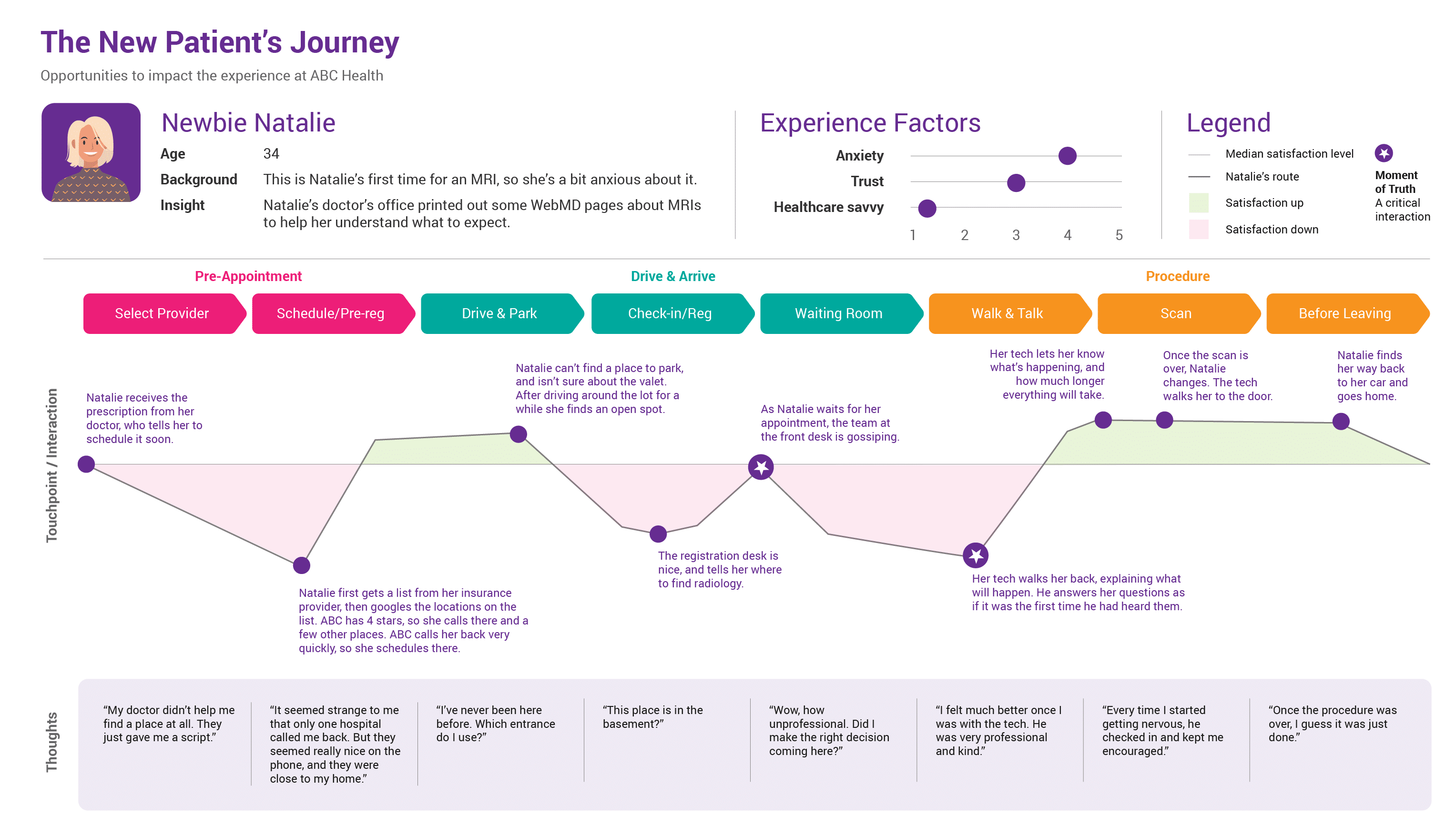
Defining the Customer Journey: A Step-by-Step Approach
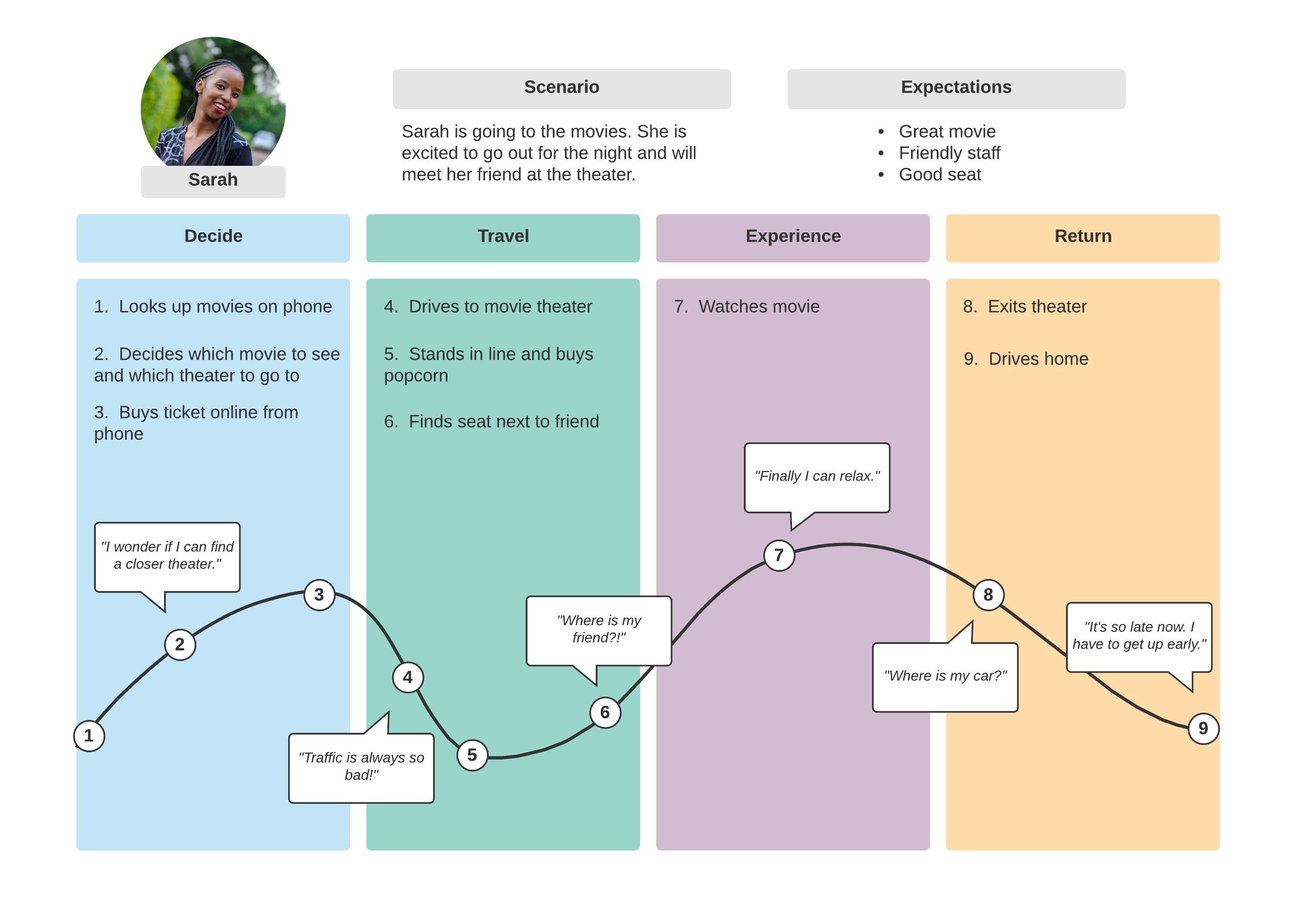
The first step in creating a robust customer journey map is to clearly define what constitutes a journey. It’s not just about the steps a customer takes; it’s about the emotional experience. Consider these key elements:
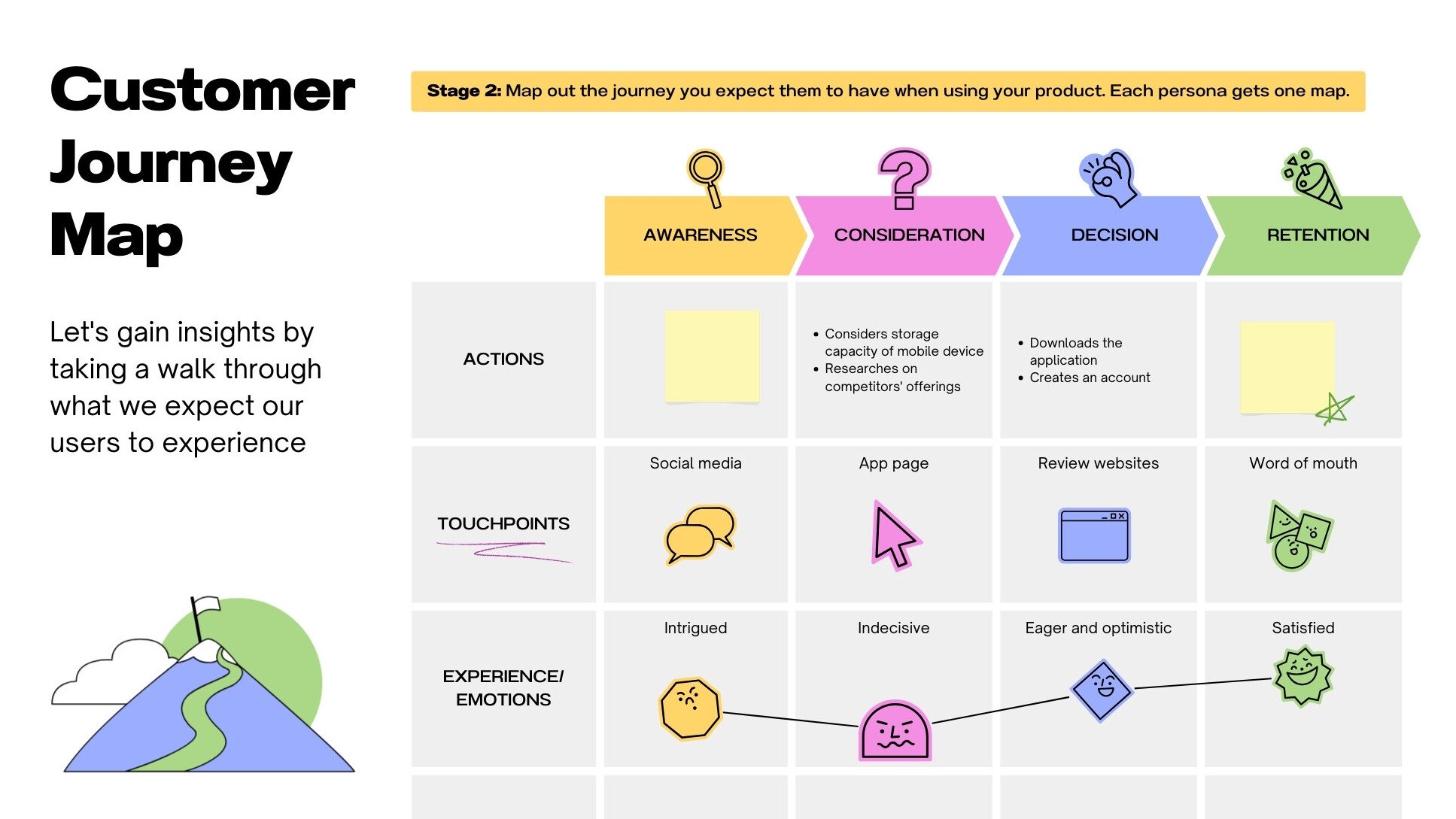
- Awareness: How does a customer first become aware of your brand? This could involve a social media ad, a search engine result, or word-of-mouth.
- Consideration: What are the customer’s initial thoughts and research processes? This includes exploring your website, reading reviews, and comparing your offerings to competitors.
- Decision: What factors influence the customer’s decision to purchase? This involves understanding pricing, features, and benefits.
- Purchase: What’s the process of making the purchase? This includes payment options, shipping, and order fulfillment.
- Post-Purchase: How does the customer experience your product or service after they’ve made a purchase? This is crucial for building loyalty and advocacy.
- Retention: How does the customer continue to engage with your brand after the initial purchase? This involves ongoing support, communication, and value delivery.
It’s important to remember that each customer journey is unique. There’s no one-size-fits-all approach. A successful journey map will acknowledge these variations and tailor the map to specific customer segments. Conducting user research – surveys, interviews, and usability testing – is essential to understanding the nuances of each journey.

Identifying Key Stages and Touchpoints
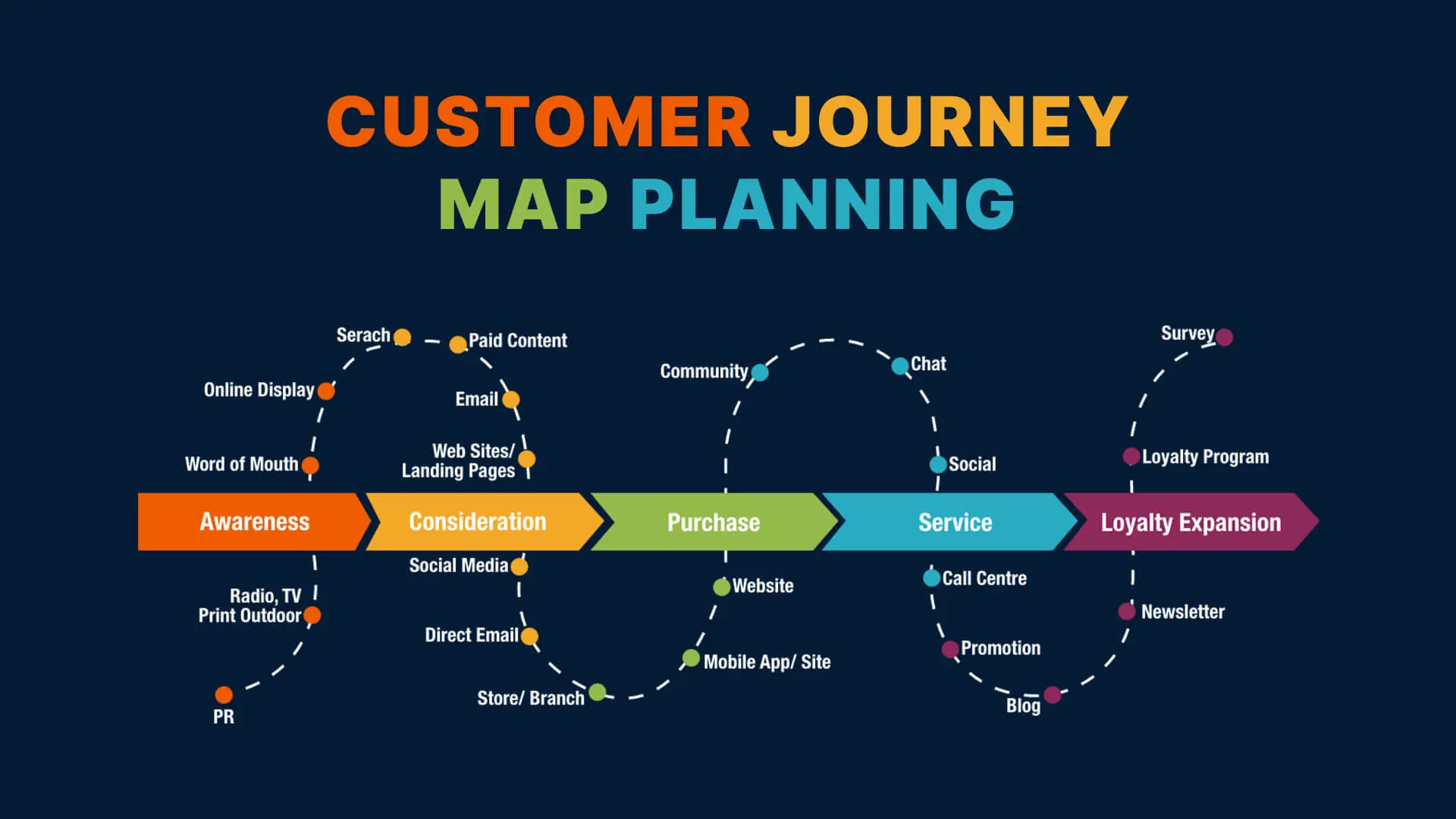
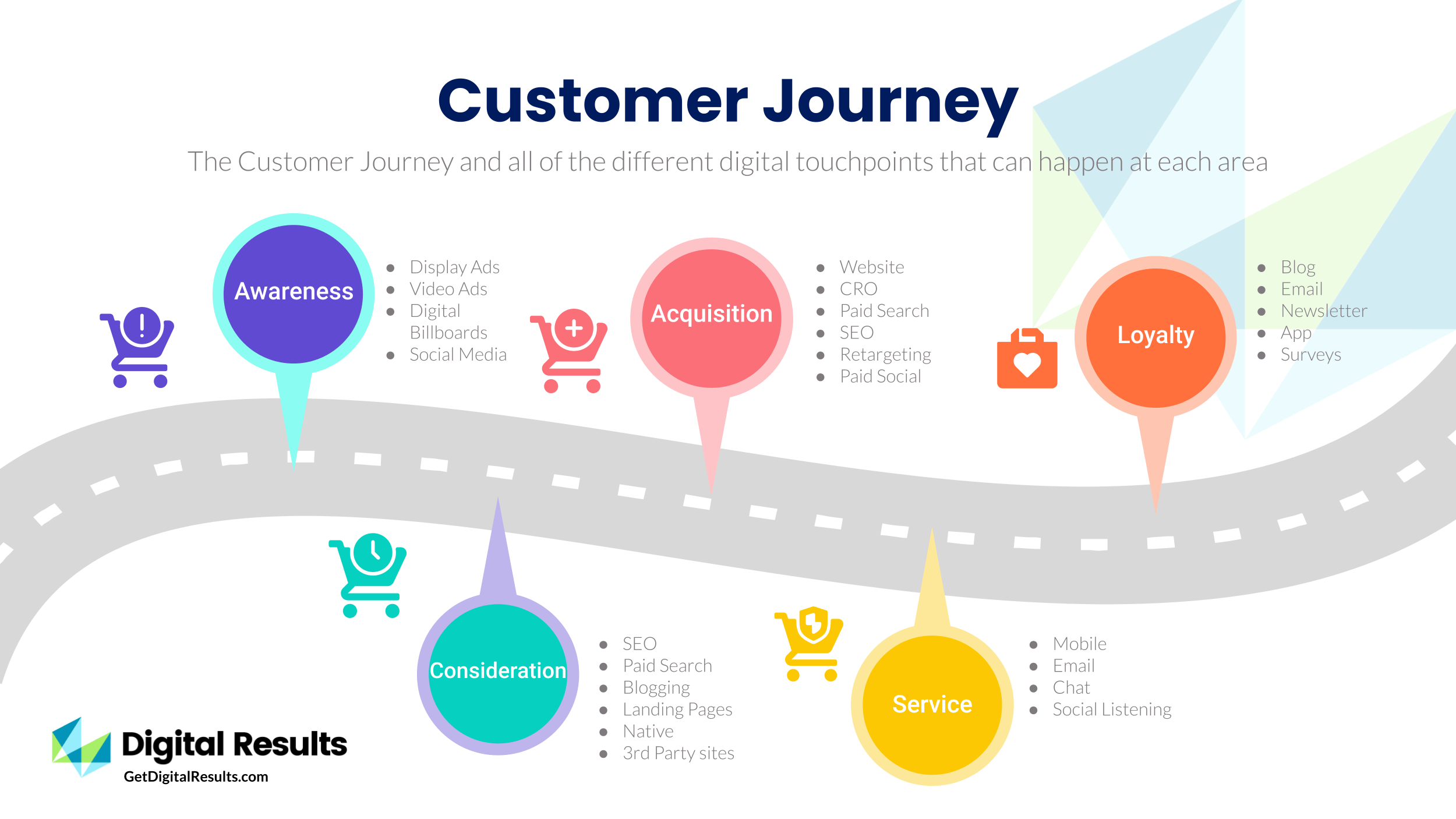
A well-structured customer journey map typically includes several key stages and touchpoints. Let’s look at some examples:
- Awareness: This stage involves reaching potential customers through marketing campaigns, social media, or other channels. It’s about generating interest and introducing your brand.
- Consideration: This stage involves customers researching your products or services and comparing them to competitors. This is where website content, product reviews, and advertising play a significant role.
- Decision: This stage involves customers evaluating your offerings and making a purchase decision. Factors like pricing, features, and customer service are critical here.
- Purchase: This stage involves the actual transaction – placing an order and completing the payment process. Streamlining this process is vital for a positive experience.
- Post-Purchase: This stage involves providing ongoing support, addressing customer inquiries, and encouraging repeat business. This is where customer loyalty is built.
Each of these stages involves numerous touchpoints – the specific interactions a customer has with your brand. These touchpoints can range from a simple website visit to a complex phone call with a customer service representative. Documenting these touchpoints is a key part of the mapping process.

Visualizing the Customer Journey: Tools and Techniques
There are numerous tools available to help you create and visualize customer journey maps. Here are a few popular options:

- Miro: A collaborative online whiteboard platform that’s excellent for creating visual maps.
- Lucidchart: A diagramming tool that allows you to create flowcharts and journey maps.
- Meeples: A mobile-first tool specifically designed for journey mapping.
- Google Sheets/Excel: While less visually appealing, these tools can be used to create basic journey maps.
Regardless of the tool you choose, the key is to create a clear and intuitive visual representation of the customer’s experience. Don’t just list touchpoints; illustrate the flow of the journey. Consider using sticky notes, flowcharts, or even simple sketches to bring the map to life.
Analyzing and Optimizing: The Power of Feedback
Creating a customer journey map is only the first step. The real value comes from analyzing the map and using the insights to optimize the customer experience. Here are some key areas to focus on:
- Identify Pain Points: Where are customers experiencing frustration or difficulty? These are critical areas for improvement.
- Assess Opportunities: Where can you improve the customer experience? Are there opportunities to streamline processes, enhance communication, or offer more value?
- Prioritize Improvements: Not all pain points are created equal. Prioritize those that have the biggest impact on customer satisfaction and business goals.
- Test and Iterate: Implement changes based on your analysis and continuously monitor the results. Customer journey mapping is an iterative process – you’ll need to refine your maps over time.
Conclusion: Embracing a Customer-Centric Approach
Customer journey mapping is no longer a luxury; it’s a necessity for businesses that want to thrive in today’s competitive environment. By understanding the entire customer experience, businesses can identify opportunities for improvement, enhance satisfaction, and build stronger relationships. It’s a continuous process of observation, analysis, and optimization. Customer journey mapping empowers businesses to move beyond simply reacting to customer needs and proactively shape them. Investing in this approach yields significant returns in terms of increased customer loyalty, revenue growth, and brand advocacy. Ultimately, a customer-centric approach, fueled by a deep understanding of the customer journey, is the key to long-term success. Remember to consistently gather feedback and adapt your maps to reflect evolving customer expectations. Continuous improvement is the cornerstone of a successful customer-centric strategy.