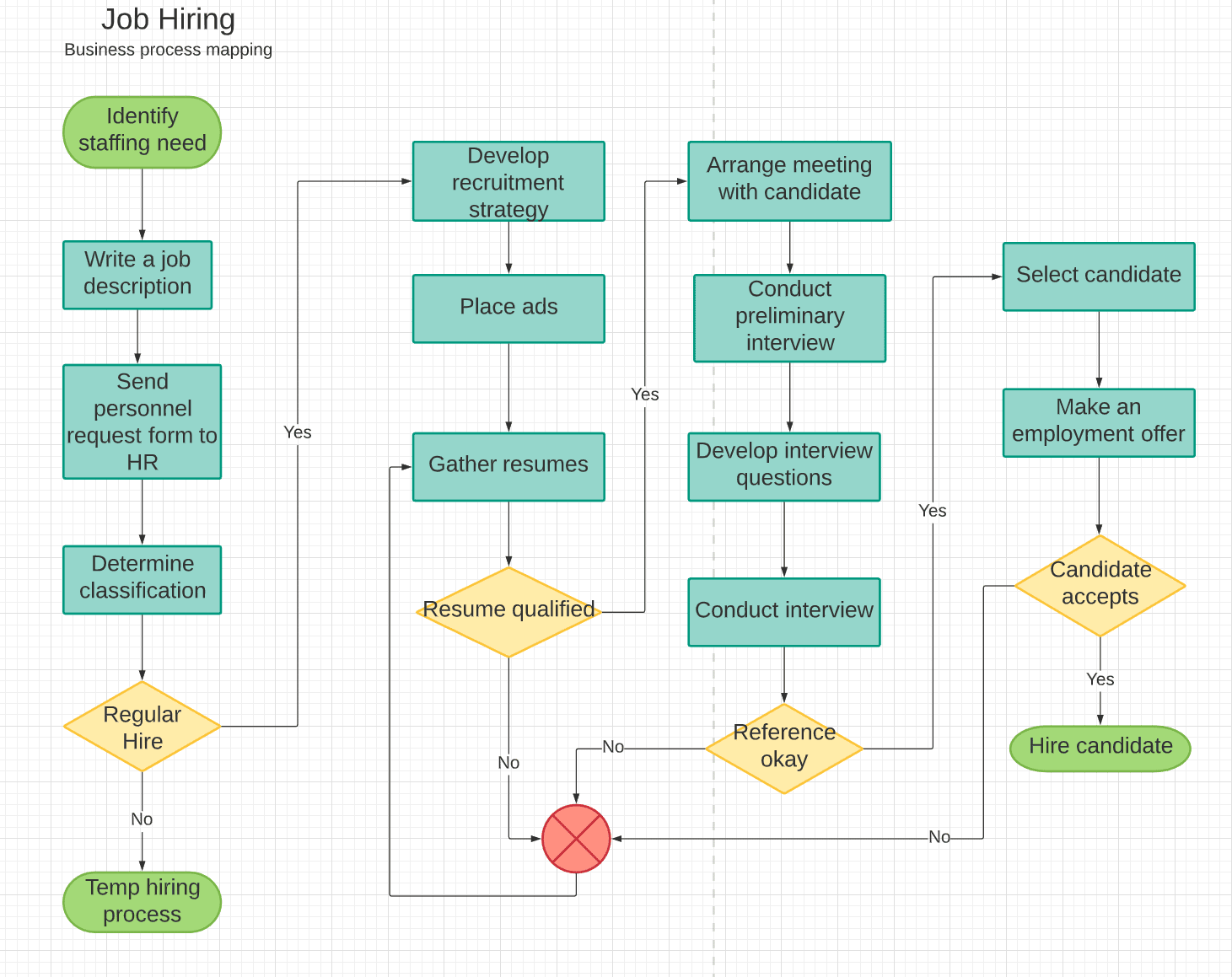
Business process mapping is no longer a ‘nice-to-have’ – it’s a critical component of modern business strategy. In today’s rapidly changing landscape, understanding and optimizing your workflows is paramount to efficiency, productivity, and ultimately, profitability. This article will delve into the core principles of business process mapping, exploring various techniques, benefits, and practical implementation strategies. Business process mapping is a fundamental tool for identifying bottlenecks, streamlining operations, and fostering continuous improvement. It’s about more than just documenting steps; it’s about visualizing the why behind those steps, revealing hidden inefficiencies and opportunities for optimization. Let’s explore how to effectively implement and leverage business process mapping to drive real results.
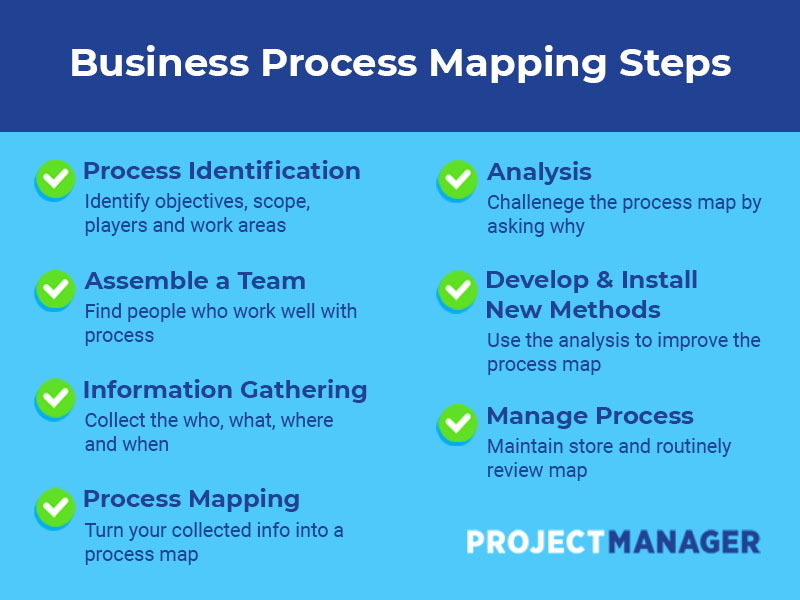
Understanding the Importance of Business Process Mapping

The traditional approach to managing operations often relied on reactive problem-solving – addressing issues after they’ve arisen. This is a costly and time-consuming method. Business process mapping, conversely, provides a proactive approach. By systematically documenting and analyzing workflows, organizations can identify areas where processes are flawed, redundant, or simply not performing optimally. This understanding allows for targeted interventions, leading to significant improvements in operational efficiency. Without a clear visual representation of how work flows, it’s incredibly difficult to pinpoint root causes of problems and implement effective solutions. Furthermore, effective mapping facilitates better communication and collaboration across teams, ensuring everyone is aligned on goals and responsibilities. The benefits extend beyond simple efficiency gains; it fosters a culture of continuous improvement, empowering employees to identify and address challenges proactively.
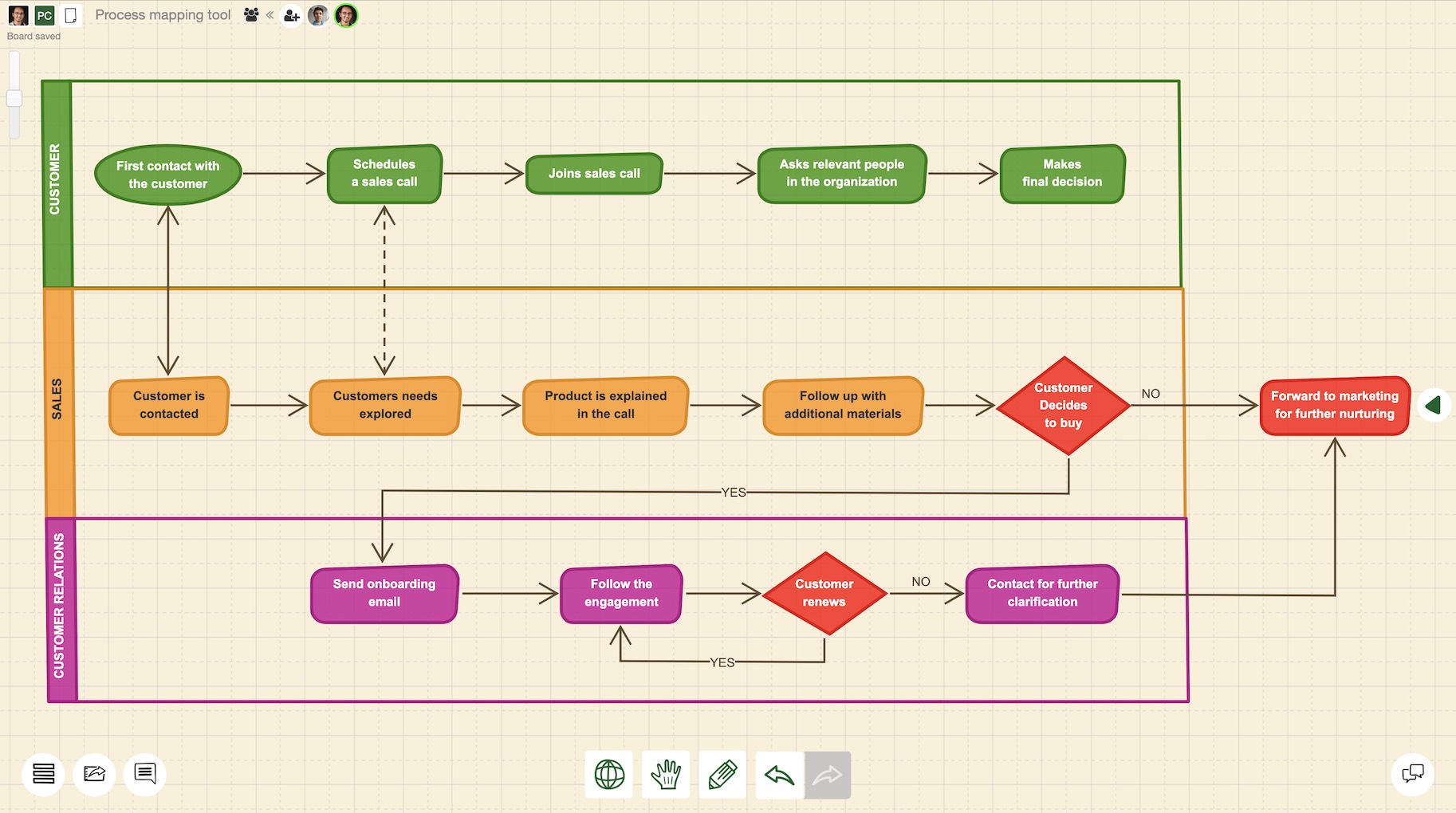
Techniques for Effective Business Process Mapping
There’s a wide range of techniques available for creating comprehensive business process maps. Choosing the right method depends on the complexity of the process and the desired level of detail. Several popular approaches include:
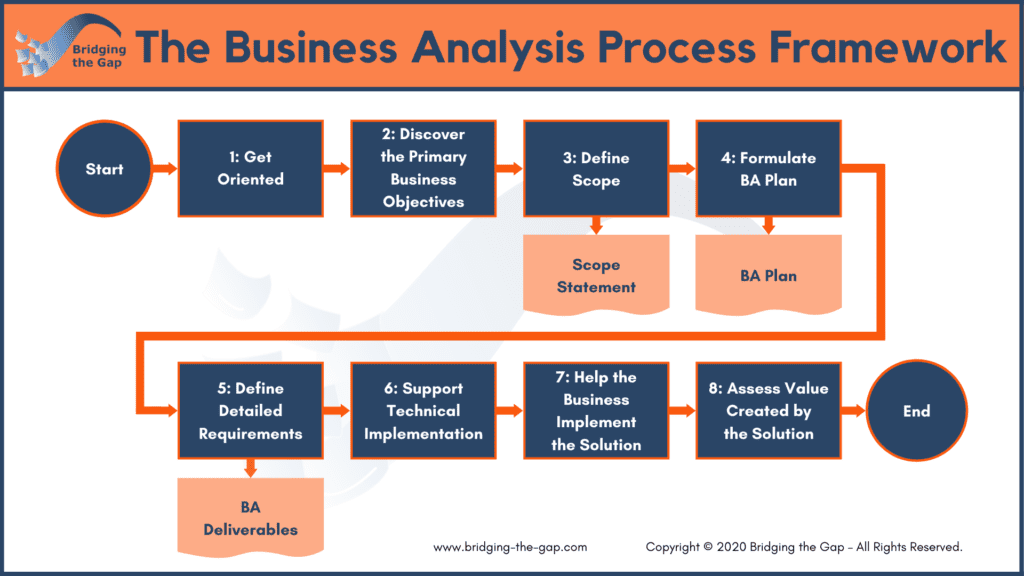
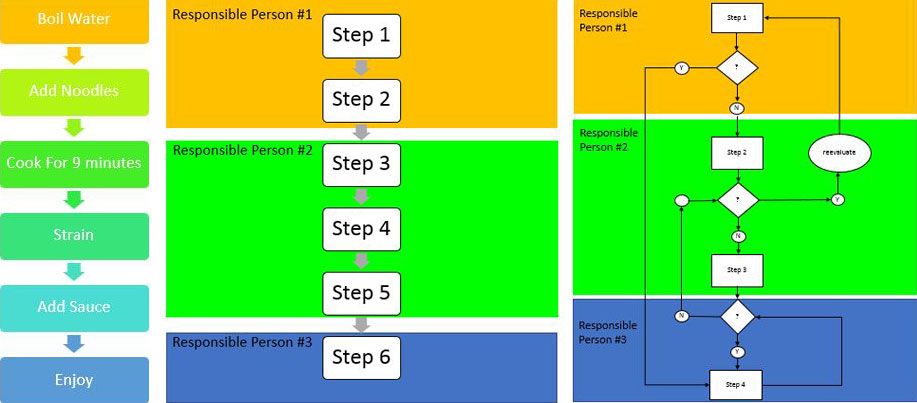
- Flowcharts: These are arguably the most common type of process map, visually representing the sequence of activities. They are particularly useful for illustrating linear processes.
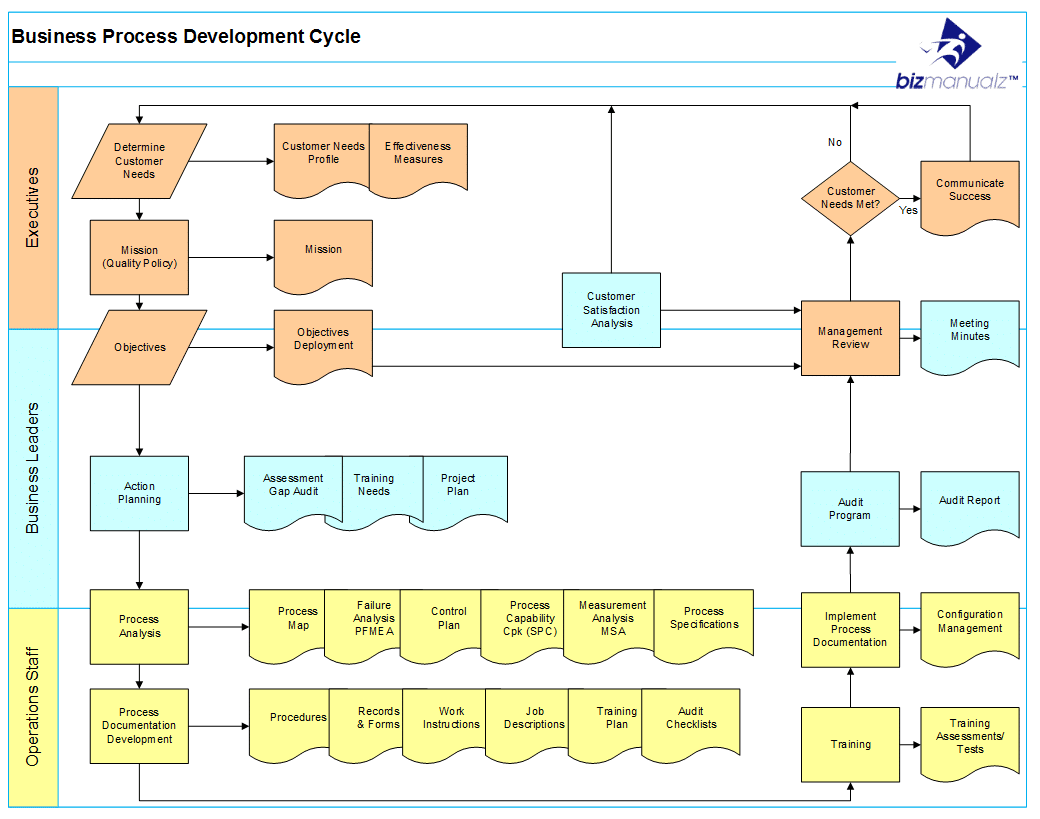
- Swimlane Diagrams: These diagrams visually separate different actors or roles involved in a process, making it clear who is responsible for each step. This is incredibly valuable for complex workflows with multiple stakeholders.
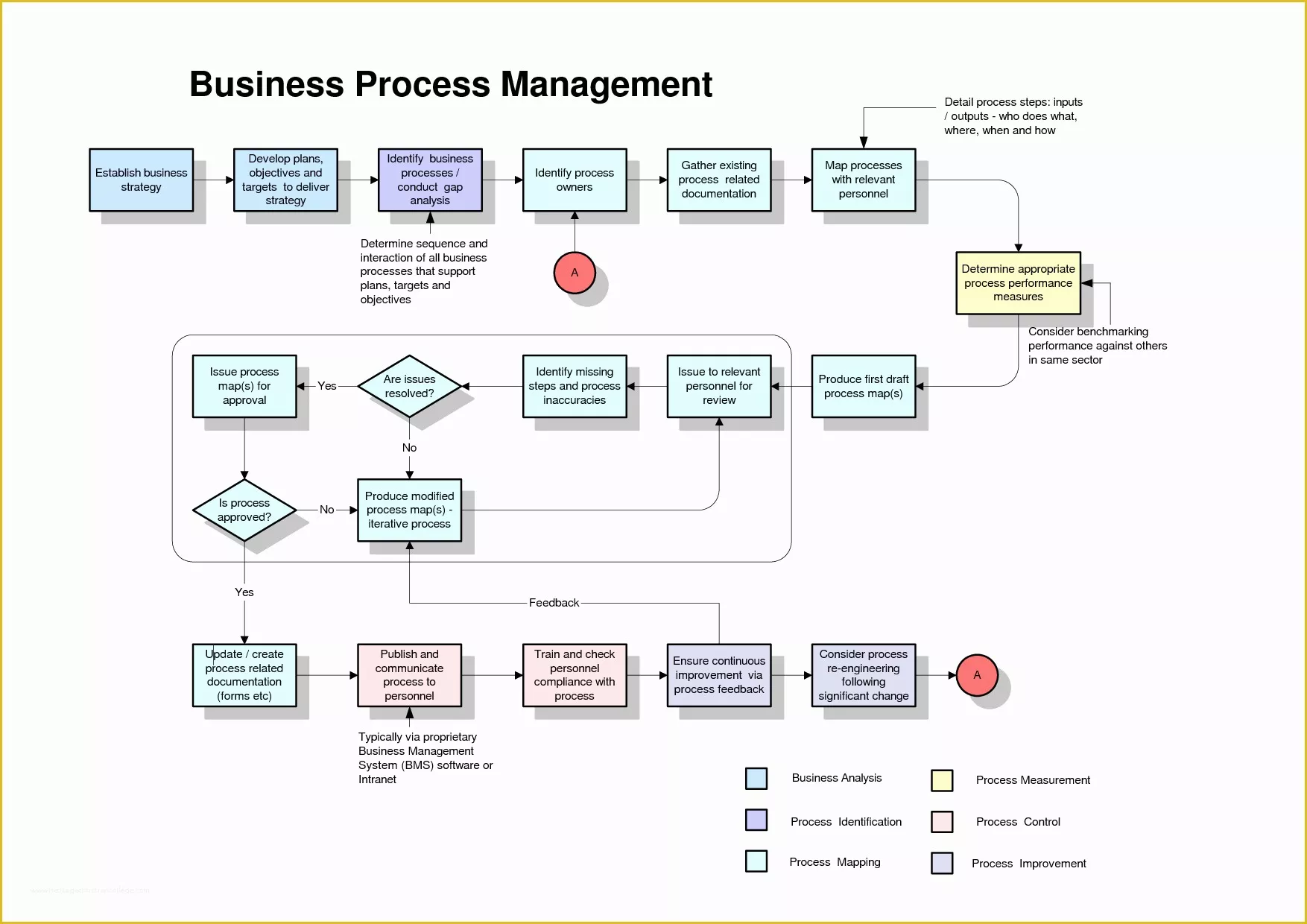
- SIPOC (Suppliers, Inputs, Process, Outputs, Customers): This technique provides a high-level overview of a process, focusing on the key elements involved. It’s a useful starting point for understanding the overall scope of a process.
- Value Stream Mapping: This technique focuses on identifying the steps required to deliver a product or service to the customer, highlighting waste and opportunities for improvement. It’s particularly effective for optimizing value creation.
- BPMN (Business Process Model and Notation): A standardized notation for modeling business processes, often used in enterprise software development and implementation.
Benefits of Implementing Business Process Mapping
The advantages of investing in business process mapping are numerous and far-reaching. Here’s a breakdown of key benefits:
- Improved Efficiency: By visualizing workflows, organizations can identify bottlenecks and streamline processes, reducing waste and improving throughput.
- Reduced Costs: Streamlined processes translate directly into lower operational costs. Eliminating redundant steps, reducing errors, and optimizing resource allocation all contribute to cost savings.
- Enhanced Productivity: Clearer workflows empower employees to work more effectively, leading to increased productivity and output.
- Better Communication & Collaboration: Process maps provide a common language and visual representation, facilitating communication and collaboration across teams.
- Increased Customer Satisfaction: Streamlined processes often result in faster turnaround times, fewer errors, and improved customer service, ultimately boosting customer satisfaction.
- Improved Compliance: Process mapping can help organizations document and demonstrate compliance with regulations and internal policies.
- Data-Driven Decision Making: Process maps provide a foundation for data collection and analysis, enabling informed decision-making regarding process improvement.
Specific Examples of Business Process Mapping Applications
Let’s look at how business process mapping can be applied across various industries:

- Healthcare: Mapping patient flow through the hospital system, from registration to discharge, can identify areas for improvement in patient care and operational efficiency.
- Manufacturing: Visualizing the production process, from raw materials to finished goods, can help identify bottlenecks and optimize production schedules.
- Retail: Mapping the customer journey, from browsing to checkout, can reveal opportunities to improve the customer experience and increase sales.
- Finance: Mapping the loan application process can identify areas for streamlining approvals and reducing processing times.
- Customer Service: Mapping the customer support process can help identify pain points and improve response times and resolution rates.
Best Practices for Effective Business Process Mapping
To maximize the value of your business process mapping efforts, consider these best practices:
- Start with a Clear Goal: Define the specific objectives you want to achieve with the mapping exercise. What problem are you trying to solve?
- Involve Key Stakeholders: Include representatives from all relevant departments and teams in the mapping process.
- Focus on the "As-Is" State: Thoroughly document the current state of the process – what’s happening now, and what’s not working.
- Use Visual Tools: Employ flowcharts, swimlane diagrams, and other visual aids to make the map easy to understand.
- Iterate and Refine: Process mapping is an ongoing process. Regularly review and update the map to reflect changes in the business.
- Prioritize Improvements: Focus on addressing the most impactful changes first.
The Role of Technology in Business Process Mapping
While manual process mapping is possible, technology is increasingly playing a vital role. Various tools are available, ranging from simple flowcharting software to sophisticated BPMN modeling platforms. These tools can automate the mapping process, improve collaboration, and provide real-time insights. Consider tools like Lucidchart, Microsoft Visio, or dedicated BPMN modeling software when planning your mapping efforts. Choosing the right tool depends on the complexity of your processes and your team’s technical expertise.
Challenges and Considerations in Business Process Mapping
Despite its benefits, implementing business process mapping isn’t without its challenges. Common obstacles include:
.png#keepProtocol)
- Resistance to Change: Employees may be resistant to changes that require them to work differently. Effective communication and training are crucial to overcome this resistance.
- Lack of Buy-in: Without strong support from leadership, process mapping efforts may lack momentum.
- Complexity of Processes: Complex processes can be difficult to map accurately. Start with simpler processes and gradually expand the scope.
- Data Accuracy: The accuracy of the map depends on the quality of the data used to create it.
Conclusion: Embracing the Power of Business Process Mapping
Business process mapping is no longer a luxury – it’s a necessity for organizations seeking to thrive in today’s competitive environment. By systematically documenting and analyzing workflows, businesses can unlock significant improvements in efficiency, productivity, and customer satisfaction. The ability to visualize and understand complex processes is increasingly critical for strategic decision-making. Investing in effective business process mapping strategies is an investment in the future success of your organization. Business process mapping provides a powerful framework for driving operational excellence and achieving sustainable competitive advantage. As technology continues to evolve, the tools and techniques available for mapping will undoubtedly become even more sophisticated, further enhancing the value of this critical practice. Don’t underestimate the transformative potential of a well-executed process mapping initiative.