The modern business landscape is increasingly competitive, demanding businesses to optimize every aspect of their operations. One of the most impactful areas to focus on is production efficiency, a critical driver of profitability and competitiveness. Simply increasing output isn’t enough; businesses must strive to minimize waste, streamline processes, and maximize the value derived from their resources. This article will delve into the key factors contributing to improved production efficiency, exploring strategies and technologies that can transform how businesses operate and deliver superior results. Understanding the principles behind boosting production efficiency is no longer a luxury – it’s a necessity for sustained success.

Why Production Efficiency Matters

The benefits of enhanced production efficiency are far-reaching and extend beyond simply producing more goods or services. It directly impacts a company’s bottom line, reducing costs, increasing profitability, and ultimately, enhancing its market position. Consider these specific advantages:
- Reduced Costs: Streamlined processes and minimized waste translate directly into lower operational expenses. Less time spent on rework, less material used, and reduced energy consumption all contribute to significant cost savings.
- Increased Output: Optimized workflows and improved resource allocation lead to a higher volume of goods or services produced per unit of time.
- Improved Quality: A focus on efficiency often necessitates a heightened attention to detail, leading to higher quality products and services, reducing returns and improving customer satisfaction.
- Enhanced Competitiveness: Businesses with superior production efficiency are better positioned to respond to market demands, innovate faster, and compete effectively with rivals.
- Increased Employee Satisfaction: When employees are empowered to work more efficiently and have a clear understanding of their roles and responsibilities, morale and productivity naturally increase.
Key Drivers of Production Efficiency
Several interconnected factors contribute to a significant boost in production efficiency. It’s rarely a single solution, but rather a combination of strategic initiatives and technological advancements. Let’s examine some of the most crucial drivers:

1. Lean Manufacturing Principles
Lean manufacturing is a philosophy centered on eliminating waste – anything that doesn’t add value to the customer. It’s a systematic approach to identifying and eliminating inefficiencies throughout the entire production process. Key lean principles include:

- Value Stream Mapping: Visualizing the entire flow of materials and information from raw materials to the finished product. This helps identify bottlenecks and areas for improvement.
- 5S Methodology: A workplace organization system that focuses on sorting, systematizing, cleaning, standardizing, and sustaining – creating a clean, organized, and efficient workspace.
- Just-in-Time (JIT) Inventory: Minimizing inventory levels by receiving materials only when they are needed for production. This reduces storage costs and the risk of obsolescence.
- Kaizen: Continuous improvement – a philosophy of small, incremental changes aimed at enhancing all aspects of the operation.
2. Technology Adoption
Technology plays a pivotal role in driving production efficiency today. Investing in the right tools and systems can dramatically transform how goods are produced.
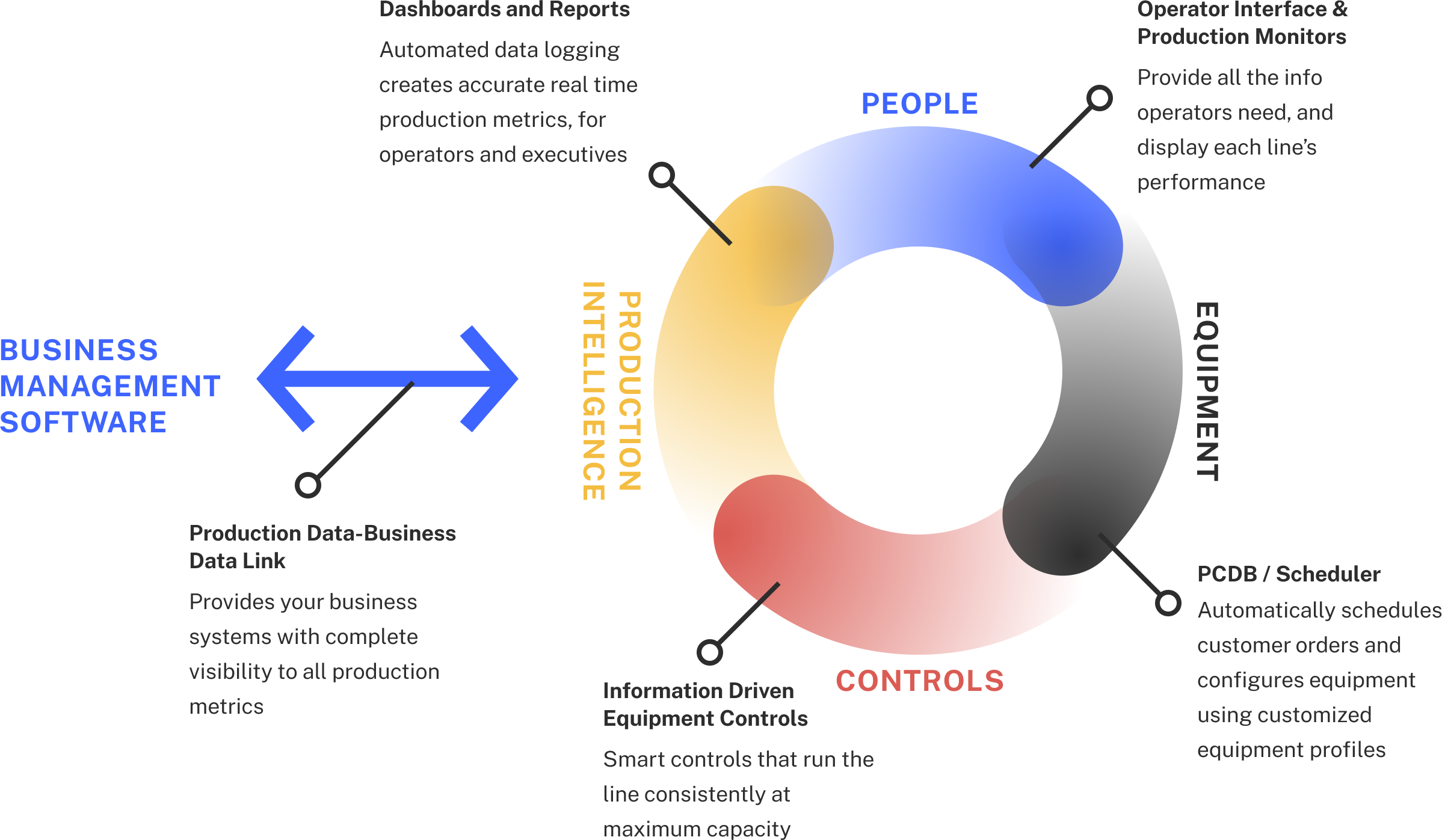
- Automation: Robotics, automated guided vehicles (AGVs), and other automation technologies can perform repetitive tasks with greater speed and accuracy than human workers, reducing errors and increasing throughput.
- Manufacturing Execution Systems (MES): MES systems provide real-time visibility into production processes, allowing for better monitoring, control, and optimization.
- Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) Systems: ERP systems integrate all aspects of a business – finance, inventory, production, and sales – into a single platform, streamlining operations and improving data visibility.
- Internet of Things (IoT): IoT devices, such as sensors and connected machines, can collect data on equipment performance, environmental conditions, and production parameters, enabling predictive maintenance and process optimization.
- 3D Printing (Additive Manufacturing): This technology allows for rapid prototyping and on-demand production, reducing lead times and enabling customized products.
3. Process Optimization
Beyond technology, optimizing existing processes is equally important. This involves analyzing workflows, identifying bottlenecks, and implementing changes to improve efficiency.

- Standard Operating Procedures (SOPs): Clearly defined SOPs ensure consistency and repeatability in production processes, reducing errors and improving quality.
- Process Mapping: Visually mapping out each step in a process helps identify areas where improvements can be made.
- Root Cause Analysis: Using techniques like the 5 Whys to identify the underlying causes of problems, rather than just treating the symptoms.
- Workflow Analysis: Examining how tasks are performed to identify redundancies, delays, and inefficiencies.
4. Employee Training and Empowerment
Employee training is a cornerstone of improved production efficiency. Well-trained employees are more productive, better equipped to handle complex tasks, and more likely to identify and report problems.

- Skill Development: Providing employees with the skills they need to operate and maintain equipment, troubleshoot problems, and improve processes.
- Cross-Training: Training employees to perform multiple tasks allows for greater flexibility and reduces reliance on individual specialists.
- Employee Empowerment: Giving employees the authority to make decisions and take action within their areas of responsibility fosters a sense of ownership and accountability.
- Teamwork and Collaboration: Encouraging collaboration and communication among team members can lead to more efficient problem-solving and process improvement.
5. Data-Driven Decision Making
Effective production efficiency relies on the ability to collect, analyze, and interpret data. Businesses need to track key performance indicators (KPIs) such as throughput, cycle time, defect rates, and inventory levels.

- Key Performance Indicators (KPIs): Selecting the right KPIs to measure progress and identify areas for improvement.
- Data Analytics Tools: Utilizing tools like dashboards and reporting software to visualize data and identify trends.
- Predictive Analytics: Using data to forecast future demand, identify potential problems, and optimize production schedules.
Conclusion
Boosting production efficiency is no longer a desirable goal; it’s a strategic imperative for businesses seeking to thrive in today’s competitive environment. By embracing a holistic approach that combines lean manufacturing principles, technology adoption, process optimization, employee empowerment, and data-driven decision making, organizations can unlock significant improvements in productivity, reduce costs, and enhance their overall competitiveness. The journey towards greater efficiency is an ongoing process, requiring continuous monitoring, adaptation, and a commitment to improvement. Ultimately, prioritizing production efficiency is an investment in the long-term success and sustainability of any business.
