Risk mitigation is no longer simply about avoiding disasters; it’s about proactively preparing for, understanding, and minimizing the potential impact of adverse events. In today’s complex and rapidly changing business environment, organizations of all sizes are increasingly recognizing the critical need to implement robust risk mitigation strategies. It’s about shifting from reactive responses to a proactive approach, building resilience into your operations and ensuring business continuity. This article will delve into the core principles of risk mitigation, exploring various techniques and providing practical guidance on how to tailor these strategies to your specific needs. Risk mitigation is a fundamental element of sustainable success, safeguarding assets, reputation, and ultimately, profitability. Let’s explore how to build a strong defense against potential threats.

Understanding the Importance of Risk Mitigation

The world is full of uncertainties – technological advancements, economic fluctuations, natural disasters, and even human error – all capable of disrupting operations and causing significant financial losses. Ignoring these risks is a recipe for disaster. Effective risk mitigation goes beyond simply identifying potential problems; it’s about understanding the likelihood and impact of those risks, and then developing plans to minimize their potential consequences. Without a proactive approach, organizations are often caught off guard, leading to costly delays, damaged relationships, and a significant decline in performance. A well-defined risk mitigation strategy isn’t just a best practice; it’s a strategic imperative for survival and growth. It’s about building a foundation of preparedness, allowing you to navigate challenges with greater confidence and resilience.
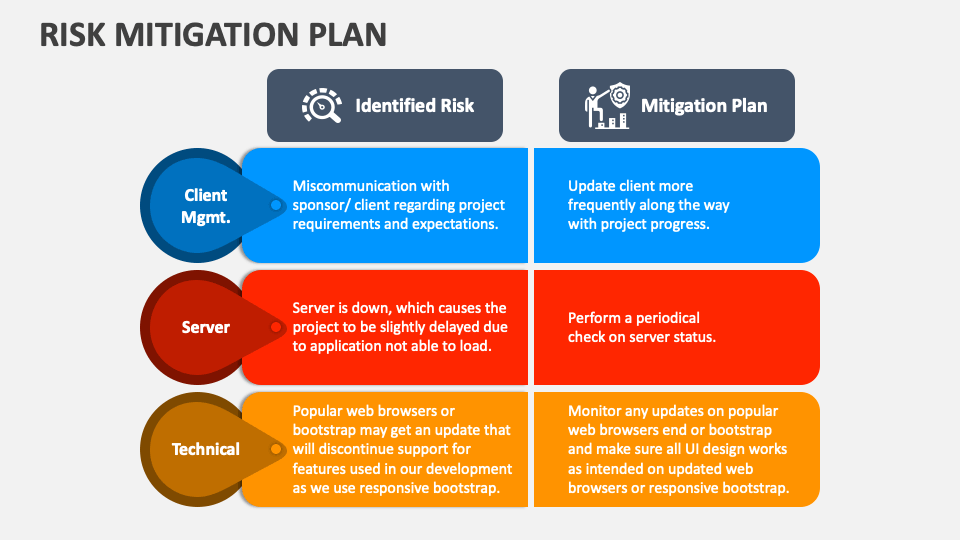
Identifying Potential Risks
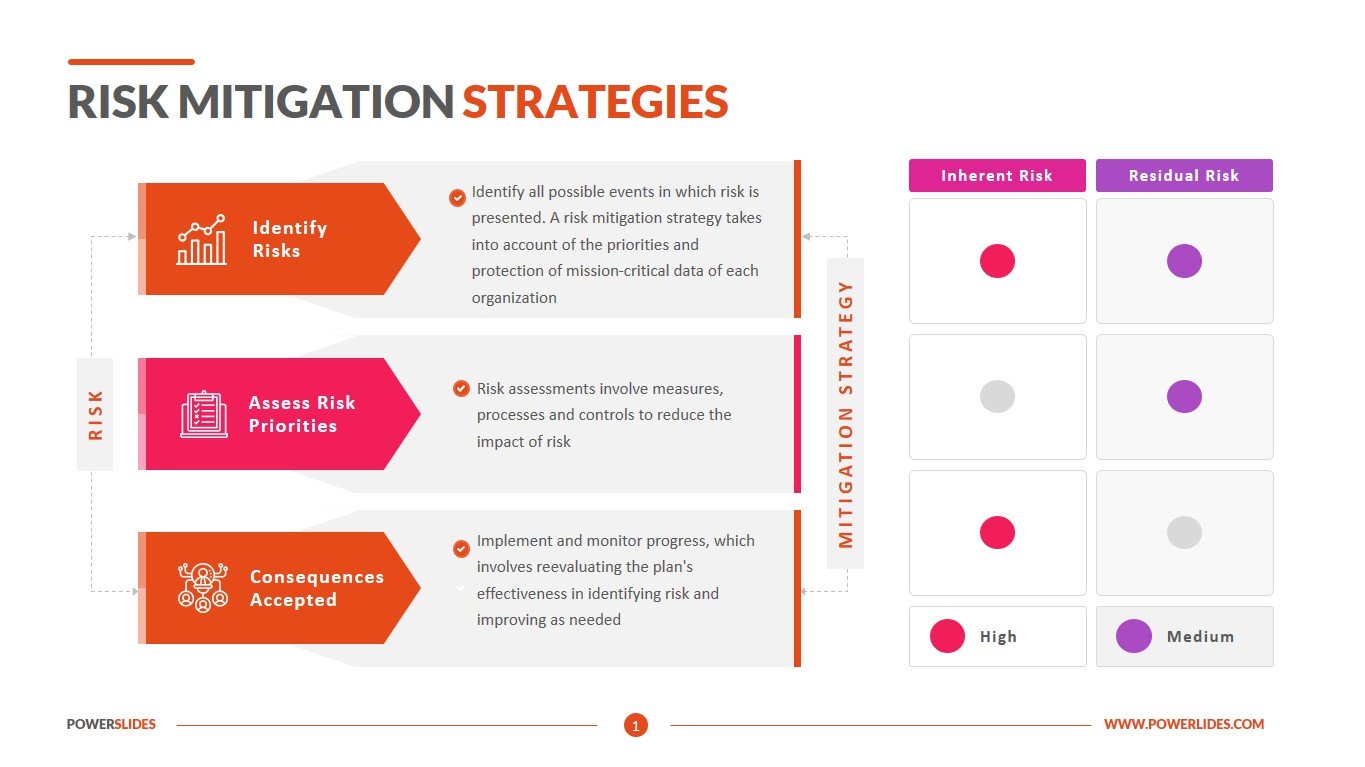
The first step in effective risk mitigation is a thorough identification process. This involves systematically brainstorming and documenting all potential threats that could impact your organization. Don’t limit yourself to obvious risks; consider the less tangible, but equally significant, factors. Consider these categories:
- Operational Risks: These relate to the day-to-day processes and activities within your organization. Examples include system failures, supply chain disruptions, human error, and inadequate training.
- Financial Risks: These encompass potential losses related to money, investments, and debt. This includes market volatility, credit risk, fraud, and currency fluctuations.
- Compliance Risks: These arise from failing to adhere to relevant laws, regulations, and industry standards. Examples include data privacy violations, environmental regulations, and labor laws.
- Strategic Risks: These pertain to the long-term direction and effectiveness of your business. This could involve competitive pressures, technological obsolescence, or changes in consumer preferences.
- Reputational Risks: Damage to your brand image, customer trust, and public perception. This can stem from negative publicity, ethical lapses, or social media crises.
Utilizing techniques like SWOT analysis, risk matrices, and brainstorming sessions can significantly enhance the identification process. Documenting these risks in a centralized location ensures everyone involved is aware of potential vulnerabilities.

Implementing Risk Mitigation Strategies
Once risks are identified, the next step is to develop and implement strategies to reduce their likelihood or impact. There’s no one-size-fits-all solution; the best approach depends on the specific risks and the organization’s resources. Here are some common risk mitigation strategies:
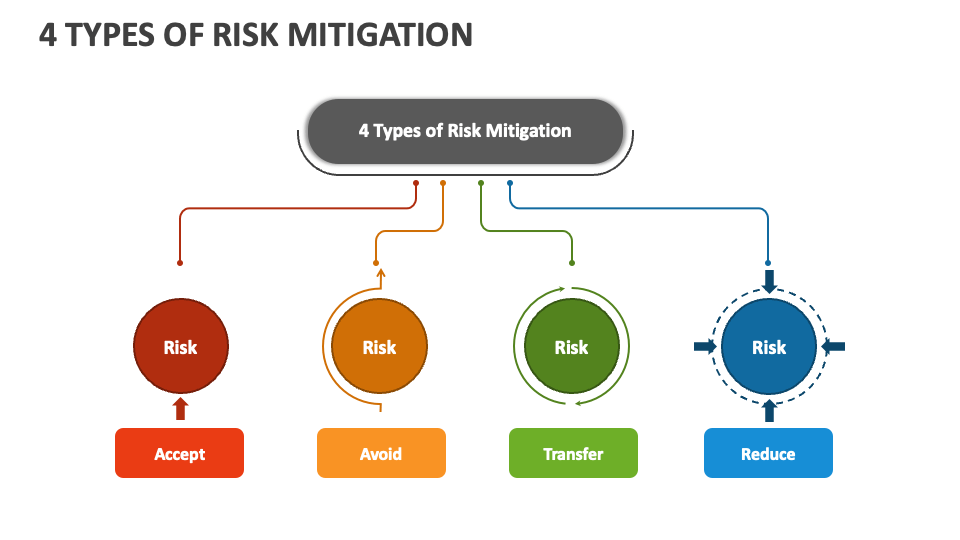
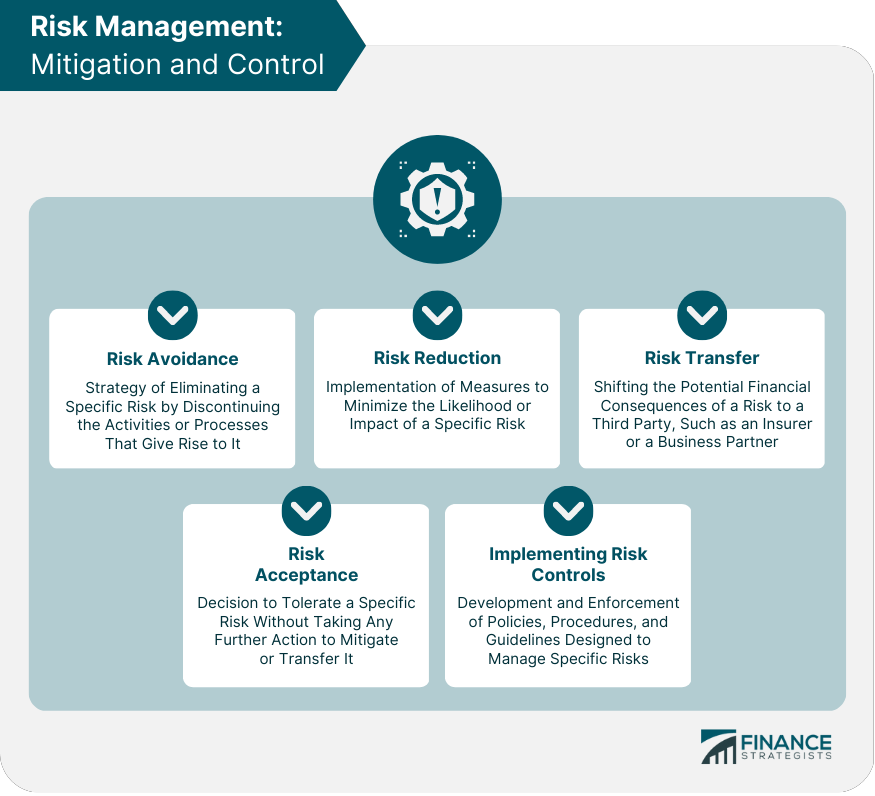
- Avoidance: Completely eliminating the risk by choosing not to engage in the activity that creates it. This is often the most drastic option, but it may be necessary in certain circumstances.
- Reduction: Implementing controls and measures to lessen the likelihood or impact of the risk. This could involve investing in new technology, improving training, or implementing stricter security protocols.
- Transfer: Shifting the risk to another party, typically through insurance or outsourcing. This can be a cost-effective way to manage certain risks, but it’s important to carefully evaluate the terms of the agreement.
- Acceptance: Acknowledging the risk and deciding to take no action, typically when the cost of mitigation outweighs the potential benefits. This should be a conscious decision based on a thorough assessment of the risks and their potential consequences.
Specific Risk Mitigation Techniques
Let’s look at some specific techniques that can be applied across various industries:
 (1).png)
- Cybersecurity Measures: Implementing firewalls, intrusion detection systems, and employee training to protect against cyberattacks. This is increasingly critical given the rise of ransomware and data breaches.
- Business Continuity Planning (BCP): Developing a plan to ensure business operations can continue in the event of a disruption, such as a natural disaster or pandemic. This includes identifying critical business functions, establishing backup systems, and testing the plan regularly.
- Supply Chain Diversification: Reducing reliance on a single supplier by sourcing materials and components from multiple vendors. This mitigates the risk of disruptions caused by supplier failures.
- Employee Training and Development: Providing employees with the skills and knowledge they need to perform their jobs safely and effectively. This is particularly important for high-risk industries.
- Insurance Coverage: Purchasing appropriate insurance policies to protect against financial losses resulting from specific risks. This includes property insurance, liability insurance, and business interruption insurance.
The Role of Technology in Risk Mitigation
Technology is playing an increasingly vital role in risk mitigation. Various software solutions and tools can automate risk assessments, monitor compliance, and provide real-time alerts. Examples include:
- Risk Management Software: Platforms that centralize risk data, track mitigation efforts, and generate reports.
- Data Analytics: Using data to identify patterns and trends that can help predict and prevent risks.
- AI and Machine Learning: Employing AI to automate risk analysis and improve the accuracy of risk assessments.
Continuous Monitoring and Review
Risk mitigation is not a one-time activity; it’s an ongoing process. Organizations must continuously monitor their risk landscape, reassess their strategies, and adapt to changing circumstances. Regularly reviewing and updating risk assessments is crucial to ensure they remain relevant and effective. This includes conducting periodic audits, stress testing, and scenario planning.

Conclusion
Risk mitigation is a critical component of organizational success. By proactively identifying, assessing, and managing potential threats, businesses can protect their assets, maintain their reputation, and ensure long-term sustainability. A comprehensive risk mitigation strategy requires a combination of careful planning, robust controls, and continuous monitoring. It’s an investment in resilience, enabling organizations to navigate challenges with confidence and achieve their goals. Ultimately, prioritizing risk mitigation is about building a future where uncertainty is minimized and opportunities are maximized. Risk mitigation is a continuous journey, not a destination.
