The modern global economy relies on a complex and intricate network of suppliers, manufacturers, distributors, and retailers – a supply chain. Effective supply chain management (SCM) is no longer a ‘nice-to-have’ but a critical imperative for businesses seeking competitiveness, profitability, and resilience. In today’s volatile market, organizations must proactively adapt their SCM strategies to navigate disruptions, optimize efficiency, and deliver superior customer experiences. This article will explore key strategies and best practices for building and maintaining a robust and responsive supply chain. Supply chain management is about more than just moving goods; it’s about optimizing the entire process from sourcing raw materials to delivering the final product to the customer. It’s a dynamic field constantly evolving with technological advancements and shifting consumer demands. Let’s delve into how businesses can leverage modern tools and techniques to thrive in this challenging landscape.
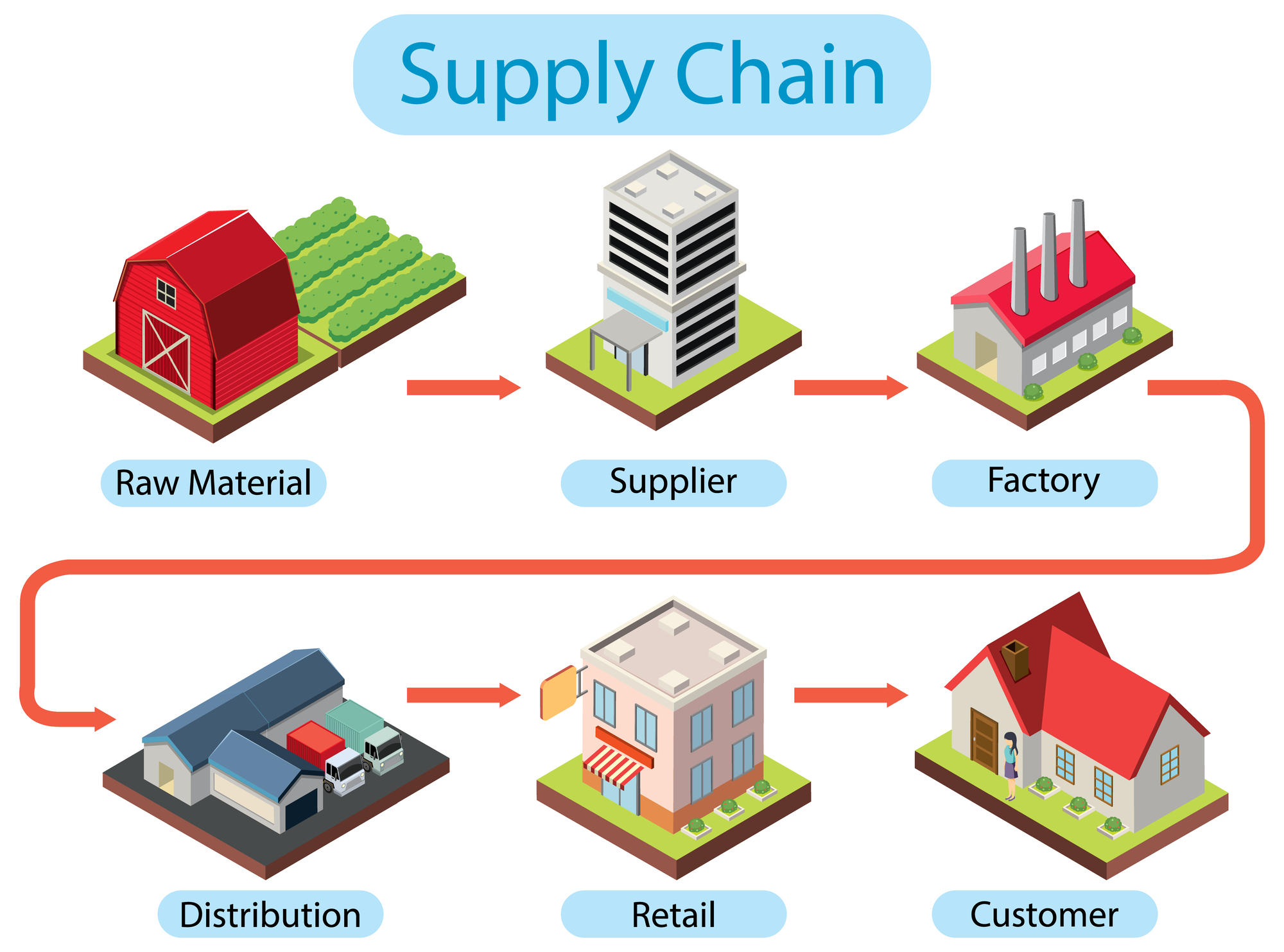
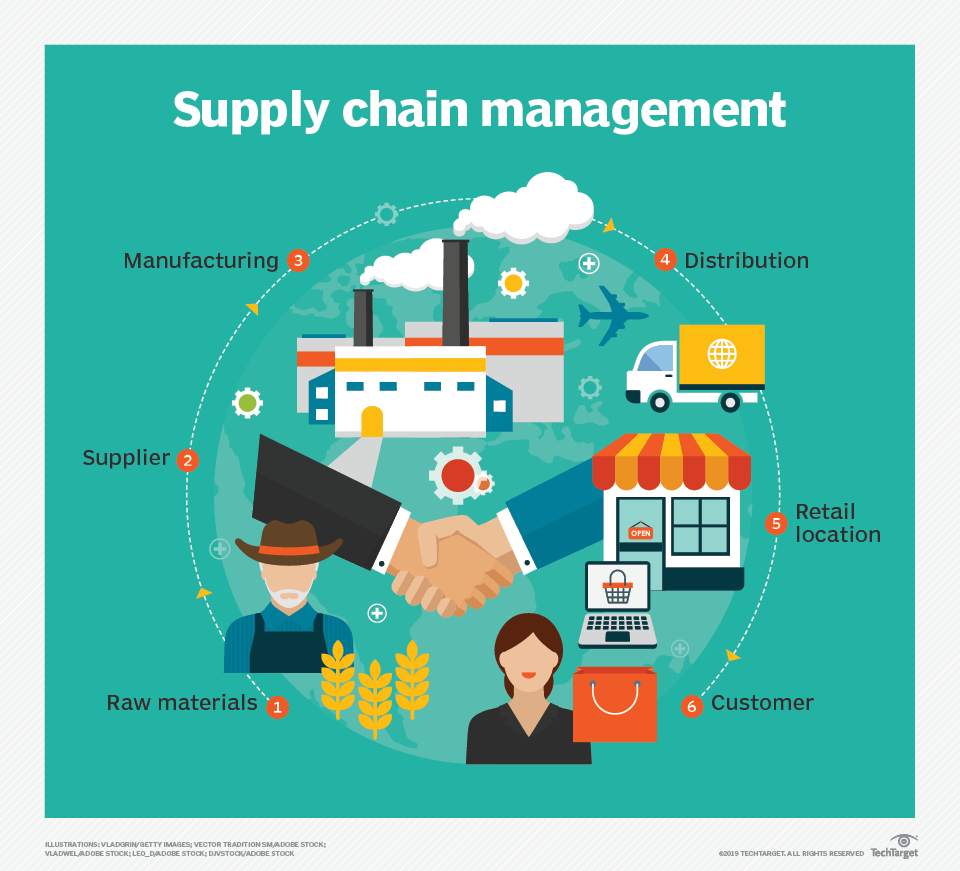
Understanding the Core Components of Supply Chain Management

A successful supply chain is built upon a foundation of interconnected elements. These elements include:
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/GettyImages-875110490-5b9ea85fc9e77c0050b86841.jpg)
- Sourcing: This involves identifying and selecting reliable suppliers who can meet quality, cost, and delivery requirements. Diversifying sourcing options is crucial to mitigate risk.
- Manufacturing: This encompasses the production process, ensuring efficient and timely delivery of goods. Lean manufacturing principles and automation are increasingly important.
- Logistics & Transportation: Efficient transportation networks – including warehousing, distribution centers, and trucking – are vital for getting products to the right place at the right time.
- Demand Planning: Accurately forecasting customer demand is fundamental to optimizing inventory levels and production schedules.
- Information Technology (IT): Robust IT systems are essential for tracking inventory, managing orders, and collaborating with suppliers and customers.
Implementing Agile Supply Chain Strategies
Traditional, linear supply chains are becoming increasingly obsolete. Organizations are adopting agile strategies that emphasize flexibility, responsiveness, and collaboration. Here are some key elements of an agile approach:

- Collaboration: Breaking down silos between departments (sales, marketing, operations, procurement) is critical. Sharing information and working together fosters better decision-making.
- Technology Adoption: Implementing technologies like cloud-based platforms, blockchain, and IoT (Internet of Things) enables real-time visibility and improved communication.
- Demand Sensing: Using real-time data to quickly identify and respond to changes in customer demand. This goes beyond traditional forecasting methods.
- Risk Management: Proactively identifying and mitigating potential disruptions – such as natural disasters, geopolitical instability, or supplier failures – is paramount.
- Circular Economy Principles: Exploring opportunities to reduce waste, reuse materials, and recycle products to create a more sustainable and resilient supply chain.
Optimizing Inventory Management
Effective inventory management is a cornerstone of SCM. Strategies include:
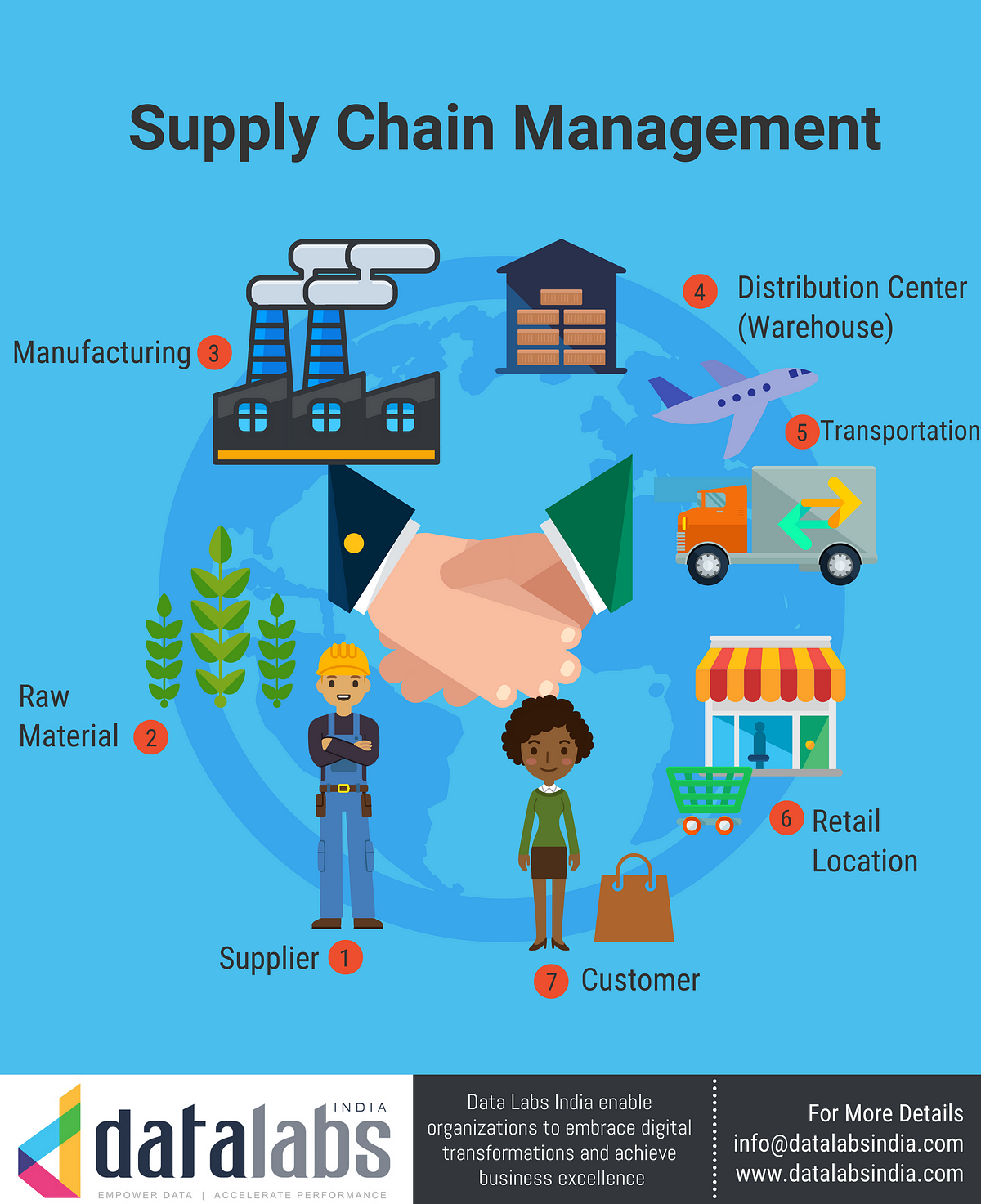
- Just-in-Time (JIT) Inventory: Minimizing inventory levels by receiving goods only when needed. This requires close coordination with suppliers.
- Vendor-Managed Inventory (VMI): Allowing suppliers to manage inventory levels at the customer’s location.
- Safety Stock Optimization: Calculating and maintaining appropriate safety stock levels to buffer against unexpected demand fluctuations.
- ABC Analysis: Categorizing inventory based on value and prioritizing management efforts accordingly. High-value items require more stringent control.
The Role of Data Analytics in SCM
Data analytics is transforming SCM. Organizations can leverage data to gain insights into:
- Supply Chain Performance: Tracking key metrics like on-time delivery, order fulfillment rates, and inventory turnover.
- Demand Forecasting Accuracy: Improving the accuracy of demand forecasts through advanced statistical modeling and machine learning.
- Risk Identification: Identifying potential disruptions and vulnerabilities in the supply chain.
- Process Optimization: Identifying bottlenecks and inefficiencies in the supply chain and implementing improvements.
- Predictive Maintenance: Using sensor data to predict equipment failures and schedule maintenance proactively.
Sustainability in Supply Chain Management
Consumers and regulators are increasingly demanding sustainable practices throughout the supply chain. This includes:

- Ethical Sourcing: Ensuring that suppliers adhere to fair labor practices and environmental standards.
- Carbon Footprint Reduction: Minimizing the environmental impact of transportation and manufacturing processes.
- Waste Reduction: Implementing strategies to reduce waste throughout the supply chain.
- Green Packaging: Utilizing sustainable packaging materials.
- Traceability: Tracking the origin and movement of products to ensure transparency and accountability.
Challenges and Future Trends
Despite advancements, SCM still faces several challenges:

- Globalization Complexity: Managing complex global supply chains can be challenging due to varying regulations, cultural differences, and logistical hurdles.
- Cybersecurity Risks: Supply chains are increasingly vulnerable to cyberattacks, which can disrupt operations and compromise sensitive data.
- Labor Shortages: Finding and retaining skilled workers in the logistics and manufacturing sectors remains a challenge.
- Geopolitical Instability: Trade wars and political tensions can disrupt supply chains and increase costs.
Looking ahead, several trends are shaping the future of SCM:
- Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML): AI and ML will play an increasingly important role in optimizing supply chain operations, from demand forecasting to route optimization.
- Blockchain Technology: Blockchain can enhance transparency and traceability throughout the supply chain, improving trust and security.
- Additive Manufacturing (3D Printing): 3D printing offers the potential to reduce lead times, customize products, and optimize inventory levels.
- The Rise of the Platform Supply Chain: Platforms are emerging that connect buyers and suppliers, creating new opportunities for collaboration and efficiency.
Conclusion
Effective supply chain management is no longer a competitive advantage; it’s a strategic necessity. By embracing agile strategies, leveraging technology, prioritizing sustainability, and proactively addressing challenges, businesses can build resilient and responsive supply chains that drive growth and success. Supply chain management is a continuous journey of improvement, requiring ongoing assessment, adaptation, and investment. The ability to anticipate change, collaborate effectively, and optimize processes will be the key to thriving in the increasingly complex global marketplace. Ultimately, a well-managed supply chain is a key driver of a company’s bottom line and its ability to meet the evolving needs of its customers.

Conclusion
The implementation of robust supply chain management strategies is a multifaceted endeavor requiring a holistic approach. Organizations that prioritize collaboration, embrace technology, and demonstrate a commitment to sustainability will be best positioned to navigate the challenges of today’s dynamic global economy and secure a competitive advantage in the years to come. Continuous monitoring, analysis, and adaptation are essential for maintaining a thriving and resilient supply chain.