Data security protocols are no longer a niche concern; they are a fundamental necessity for businesses of all sizes and individuals alike. In today’s digital landscape, where sensitive information is constantly at risk, robust data security protocols are essential for protecting valuable assets, maintaining customer trust, and complying with regulations. This article will delve into the core principles of data security protocols, exploring various techniques and best practices to safeguard your data. Understanding these protocols is crucial for anyone involved in collecting, storing, or processing data. Data security protocols are the framework for protecting information from unauthorized access, use, disclosure, disruption, modification, or destruction. They encompass a wide range of measures, from technical safeguards to organizational policies, all working together to minimize risk. Ignoring these protocols can lead to devastating consequences, including financial losses, reputational damage, and legal penalties. Let’s explore how these protocols can be implemented effectively.

Understanding the Importance of Data Security

The value of data is constantly increasing, driven by advancements in technology and the proliferation of digital services. This increased value makes data a prime target for cybercriminals. A data breach can result in significant financial losses, including remediation costs, legal fees, regulatory fines, and lost revenue. Beyond financial repercussions, a data breach can erode customer trust, damage brand reputation, and lead to legal action. Furthermore, compliance with regulations like GDPR, CCPA, and HIPAA adds another layer of complexity and necessitates stringent data security measures. Data security protocols are not simply about preventing breaches; they are about building a resilient and trustworthy data ecosystem. They represent a proactive approach to risk management, demonstrating a commitment to protecting sensitive information. Without a well-defined and consistently enforced data security strategy, organizations are essentially inviting risk.
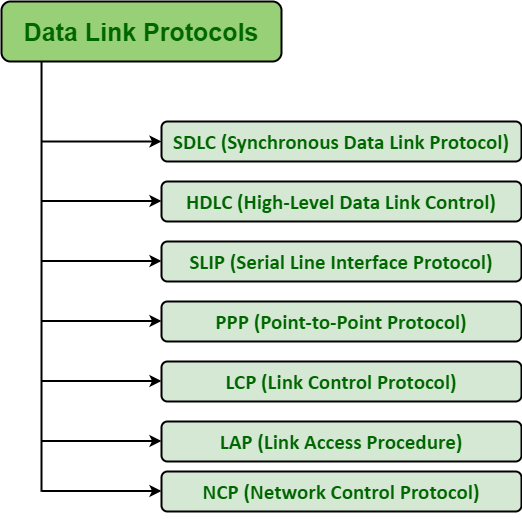
Key Components of a Robust Data Security Protocol
A comprehensive data security protocol typically incorporates several key components working in concert. These include:

Access Control: This is arguably the most critical element. It involves implementing measures to restrict access to data based on the principle of least privilege – granting users only the minimum level of access necessary to perform their job duties. Strong authentication methods, such as multi-factor authentication (MFA), are vital for verifying user identities. Regularly reviewing and updating access permissions is also essential.

Encryption: Data encryption transforms data into an unreadable format, making it incomprehensible to unauthorized individuals even if they gain access to it. Both data at rest (stored on devices and servers) and data in transit (transmitted over networks) should be encrypted. Using strong encryption algorithms and managing encryption keys securely are paramount.

Data Loss Prevention (DLP): DLP systems monitor data movement and identify potential security threats. They can block unauthorized data transfers, prevent sensitive information from leaving the organization’s control, and alert administrators to suspicious activity. DLP tools often integrate with email, file sharing, and cloud storage services.

Network Security: Protecting your network infrastructure is crucial. This includes firewalls, intrusion detection/prevention systems (IDS/IPS), and network segmentation to isolate sensitive systems and data. Regular vulnerability scanning and patching of network devices are also essential.
Endpoint Security: Protecting individual devices (laptops, desktops, mobile devices) is vital. Endpoint security solutions include antivirus software, endpoint detection and response (EDR) tools, and device encryption.

Regular Backups and Disaster Recovery: Having a robust backup and disaster recovery plan is critical for mitigating the impact of a data breach or other disruptive event. Regularly backing up data to offsite locations and testing the recovery process are essential. A well-defined disaster recovery plan ensures business continuity.

Data Security Protocols for Specific Industries
The specific data security protocols required will vary depending on the industry and the type of data being handled. Here are some examples:
Healthcare: Healthcare organizations must adhere to strict regulations like HIPAA, which mandate robust data security measures to protect patient information. This includes encryption, access controls, audit trails, and business continuity plans.
Finance: Financial institutions must comply with regulations like PCI DSS (Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard) to protect cardholder data. This requires robust encryption, access controls, and monitoring systems.
Retail: Retailers need to protect customer data, including credit card information and personal details. This involves implementing strong authentication, data masking, and secure data storage.
Government: Government agencies must comply with strict data security regulations, such as FedRAMP, to protect sensitive information.
Best Practices for Data Security
Beyond the core components, adopting best practices can significantly enhance data security:
Employee Training: Regular training on data security awareness is essential. Employees need to understand the risks they face and how to protect data.
Data Minimization: Only collect and retain the data that is absolutely necessary. Reduce the amount of data stored and processed.
Data Retention Policies: Establish clear data retention policies that specify how long data should be stored and when it should be securely deleted.
Security Audits: Conduct regular security audits to identify vulnerabilities and assess the effectiveness of security controls.
Incident Response Plan: Develop and regularly test an incident response plan to effectively handle data breaches and other security incidents.
Vendor Risk Management: Assess the security practices of third-party vendors who have access to your data.
The Role of Technology in Data Security
Technology plays a crucial role in implementing and maintaining data security protocols. Security Information and Event Management (SIEM) systems, data loss prevention (DLP) tools, and encryption software are just a few examples of technologies that can enhance security. However, technology alone is not enough. It must be integrated with appropriate policies and procedures to be truly effective. Furthermore, automation can streamline security processes and improve efficiency.
Conclusion
Data security protocols are a complex and evolving field. A proactive and layered approach, incorporating technical safeguards, organizational policies, and employee training, is essential for protecting valuable data assets. The increasing threat of cyberattacks necessitates a continuous commitment to data security. By understanding the key components of a robust protocol and adopting best practices, organizations can significantly reduce their risk and maintain the trust of their customers. Data security protocols are not a one-time investment; they are an ongoing process that requires continuous monitoring, evaluation, and adaptation. Ultimately, prioritizing data security is an investment in the long-term success and sustainability of any organization.