Quality control is more than just a department; it’s a fundamental philosophy woven into every stage of product or service development. It’s about proactively identifying and addressing potential issues before they impact the customer experience, leading to increased satisfaction, reduced costs, and ultimately, a stronger brand reputation. In today’s competitive landscape, a robust quality control system isn’t a luxury – it’s a necessity. This article will delve into the core strategies, best practices, and tools essential for implementing effective quality control across various industries. Quality control is the cornerstone of delivering consistently excellent results. It’s about continuous improvement and a relentless focus on exceeding expectations. Let’s explore how to build a system that truly delivers.

Understanding the Importance of Quality Control

The benefits of implementing a comprehensive quality control program are far-reaching. Firstly, it directly impacts customer satisfaction. When products or services consistently meet or exceed customer expectations, they are more likely to become loyal advocates for your brand. Secondly, quality control significantly reduces costs. Identifying and correcting defects early in the process prevents costly rework, scrap, and warranty claims. Thirdly, it enhances operational efficiency. Streamlined processes and minimized errors lead to increased productivity and reduced waste. Finally, and perhaps most importantly, a strong quality control system builds trust – a crucial element for long-term success. Without it, customers are hesitant to invest in your offerings, fearing potential problems. Ignoring quality control is akin to building a house on sand – it’s destined to crumble.
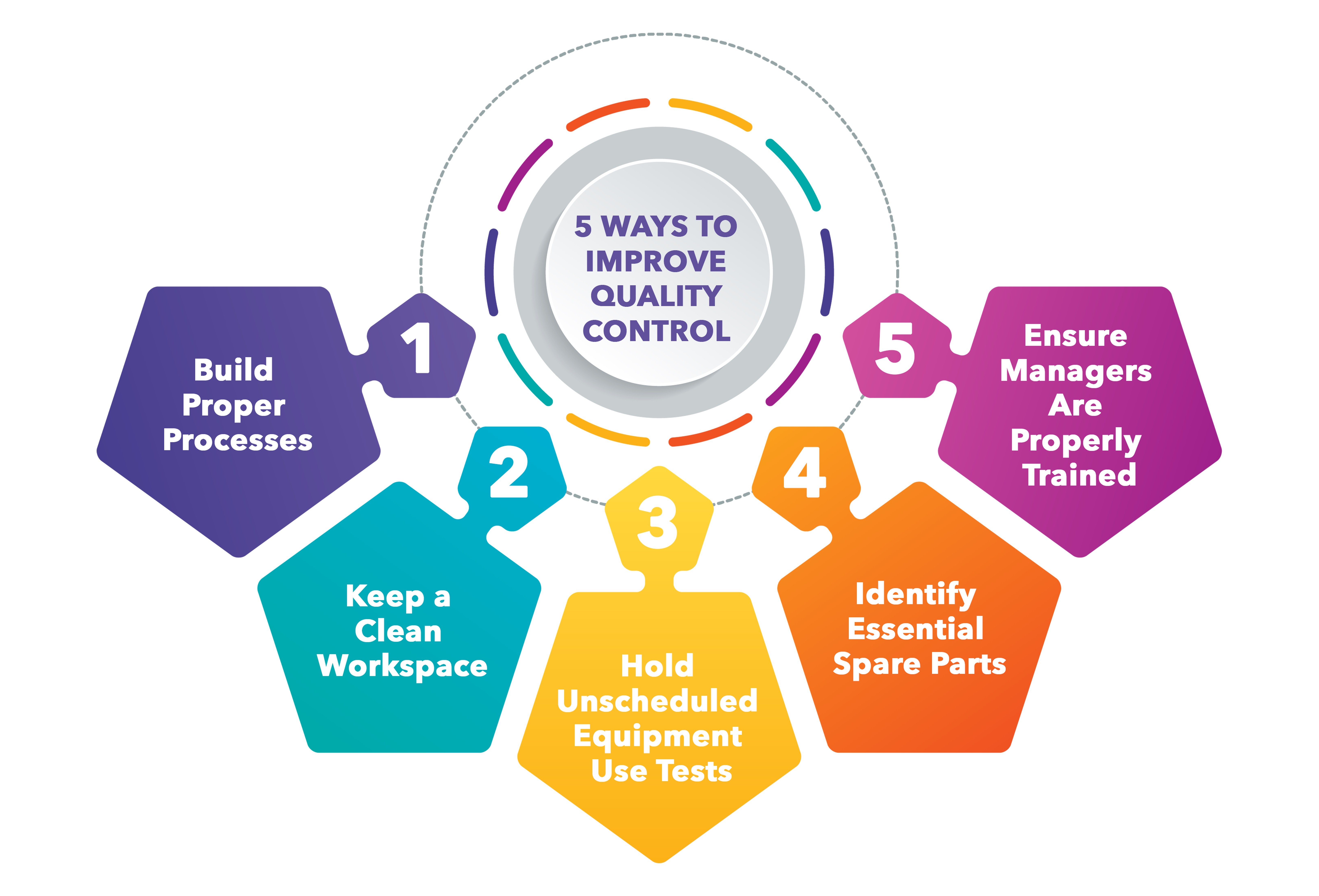
Key Strategies for Effective Quality Control
Several key strategies form the foundation of a successful quality control program. These strategies aren’t mutually exclusive; they should be integrated to create a holistic approach. Process mapping is a critical first step. Visually representing the entire production or service process allows you to identify bottlenecks, areas of potential failure, and opportunities for improvement. This isn’t just about documenting; it’s about analyzing the flow of work. Another vital strategy is statistical process control (SPC). SPC utilizes statistical methods to monitor and control processes, identifying trends and deviations from established standards. This allows for early detection of problems before they escalate. Furthermore, supplier quality management is paramount. Your quality control efforts extend beyond your own operations; you need to assess and manage the quality of the materials and components you receive from your suppliers. Regular audits and performance reviews are essential. Finally, employee training and empowerment are crucial. Well-trained employees are more likely to identify and report potential issues, and empowered employees are more likely to take ownership of quality.

Detailed Quality Control Processes Across Industries
The specific techniques and tools employed will vary depending on the industry and the nature of the product or service. Let’s examine some examples:

Manufacturing
In manufacturing, quality control often begins with raw material inspection. This includes verifying the material’s composition, dimensions, and adherence to specifications. Then, during the production process, continuous monitoring using sensors and automated testing is employed. Statistical process control is routinely used to track key metrics like defect rates and identify trends. After production, rigorous final inspection and testing are conducted to ensure that the final product meets all required standards. Lean manufacturing principles are increasingly adopted, focusing on eliminating waste and streamlining the production process to minimize defects. Root cause analysis is a critical component of this process, helping to identify the underlying causes of defects rather than simply treating the symptoms.

Healthcare
Quality control in healthcare is arguably the most stringent, demanding a high level of accuracy and patient safety. This involves meticulous documentation of all procedures, rigorous adherence to protocols, and continuous monitoring of patient outcomes. Medical device quality systems (e.g., FDA regulations) are designed to ensure that medical devices meet specific performance standards. Clinical trials are conducted to evaluate the safety and efficacy of new products. Electronic health record (EHR) audits are performed to ensure data integrity and compliance with regulations. Patient feedback mechanisms are vital for identifying areas for improvement. Regular audits of clinical workflows are conducted to identify potential errors or inconsistencies.
Software Development
Software quality control is a complex undertaking, requiring a combination of testing methodologies and automation. Unit testing, where individual components are tested in isolation, is a foundational practice. Integration testing verifies that different components work together correctly. System testing assesses the entire system against requirements. User acceptance testing (UAT) involves real users testing the software to ensure it meets their needs. Automated testing tools are increasingly used to speed up the testing process and improve accuracy. Code reviews are performed by developers to identify potential bugs and improve code quality. Static analysis tools can automatically detect code defects and vulnerabilities. Continuous integration and continuous delivery (CI/CD) pipelines are used to automate the build, test, and deployment process.

The Role of Data and Analytics in Quality Control
Modern quality control relies heavily on data. Collecting and analyzing data – from production logs to customer feedback – provides valuable insights into process performance and potential problems. Data visualization tools are essential for identifying trends and patterns. Key performance indicators (KPIs) – such as defect rates, customer satisfaction scores, and first-pass yield – are tracked and monitored to assess the effectiveness of the quality control program. Predictive analytics can be used to forecast potential quality issues before they occur, allowing for proactive intervention. Root cause analysis (RCA) using statistical methods is crucial for understanding the underlying causes of defects. Analyzing data allows for continuous improvement and optimization of the quality control process. Simply tracking metrics isn’t enough; you need to understand the data and use it to drive action.

Tools and Technologies for Quality Control
A variety of tools and technologies are available to support quality control efforts. Statistical process control (SPC) software (e.g., Minitab, JMP) is used for monitoring and controlling processes. Electronic data capture (EDC) systems automate data collection and reporting. Quality management software (e.g., Qualio, MetricStream) provides a centralized platform for managing quality data and workflows. Automated testing tools (e.g., Selenium, Appium) automate the testing process. Machine learning (ML) algorithms are increasingly being used for predictive analytics and anomaly detection. Cloud-based platforms offer scalability and accessibility for quality control initiatives.

Continuous Improvement – The Key to Sustained Quality
Quality control isn’t a one-time project; it’s an ongoing process of continuous improvement. Regularly reviewing the quality control program, identifying areas for improvement, and implementing changes is essential. Kaizen – a Japanese philosophy of continuous improvement – is a particularly effective approach. Six Sigma methodologies provide a structured framework for reducing variation and improving process performance. Lean principles focus on eliminating waste and streamlining processes. Customer feedback loops are critical for identifying areas for improvement and ensuring that quality control efforts are aligned with customer needs. The ultimate goal is to create a culture of quality throughout the organization.
Conclusion
Quality control is a critical component of any successful business. It’s not simply about preventing defects; it’s about proactively identifying and addressing potential issues, ultimately delivering consistently excellent results. By implementing a robust quality control strategy, leveraging the right tools and technologies, and fostering a culture of continuous improvement, organizations can significantly enhance customer satisfaction, reduce costs, and build a stronger, more sustainable business. The investment in quality control is an investment in the long-term success of your organization. Remember, quality control is an ongoing journey, not a destination. Continuous monitoring, analysis, and adaptation are key to maintaining a high level of quality. Finally, consistently communicating the importance of quality to all stakeholders reinforces the commitment to excellence.