Risk assessment methodologies are the cornerstone of effective business operations, ensuring organizations proactively identify, analyze, and mitigate potential threats. In today’s complex and rapidly changing environment, the ability to understand and manage risks is no longer a luxury – it’s a necessity for survival and sustainable growth. This article will delve into the various methodologies available, exploring their strengths, weaknesses, and practical applications across diverse industries. Understanding these approaches is crucial for anyone involved in decision-making, strategic planning, or simply striving to minimize potential negative impacts. The core principle underpinning all effective risk assessment is a systematic and data-driven approach, moving beyond reactive responses to proactive prevention. Let’s explore how these methodologies work and how to choose the right one for your specific needs.
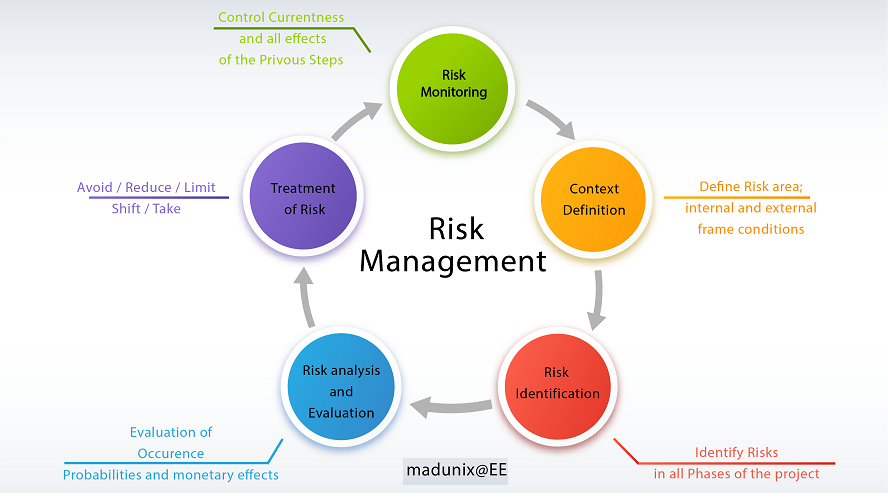
Introduction

The modern business landscape is characterized by an unprecedented volume of potential disruptions – from natural disasters and cyberattacks to economic downturns and regulatory changes. Organizations are increasingly confronted with a deluge of risks, many of which are difficult to predict or fully understand. Traditional risk management often relied on gut feelings and reactive measures, leading to costly mistakes and missed opportunities. The rise of digital technologies and globalization has exponentially increased the complexity of risk exposure, demanding a more sophisticated and adaptable approach. Risk assessment methodologies provide the framework for systematically identifying, analyzing, and evaluating these risks, enabling organizations to make informed decisions and implement effective mitigation strategies. This article will provide a comprehensive overview of several prominent risk assessment methodologies, highlighting their key features and practical considerations. We’ll move beyond simply defining these methods and explore how they can be tailored to fit unique organizational contexts. Ultimately, this exploration aims to equip readers with the knowledge to confidently navigate the ever-present challenges of risk management.

Scenario-Based Risk Assessment – A Practical Approach
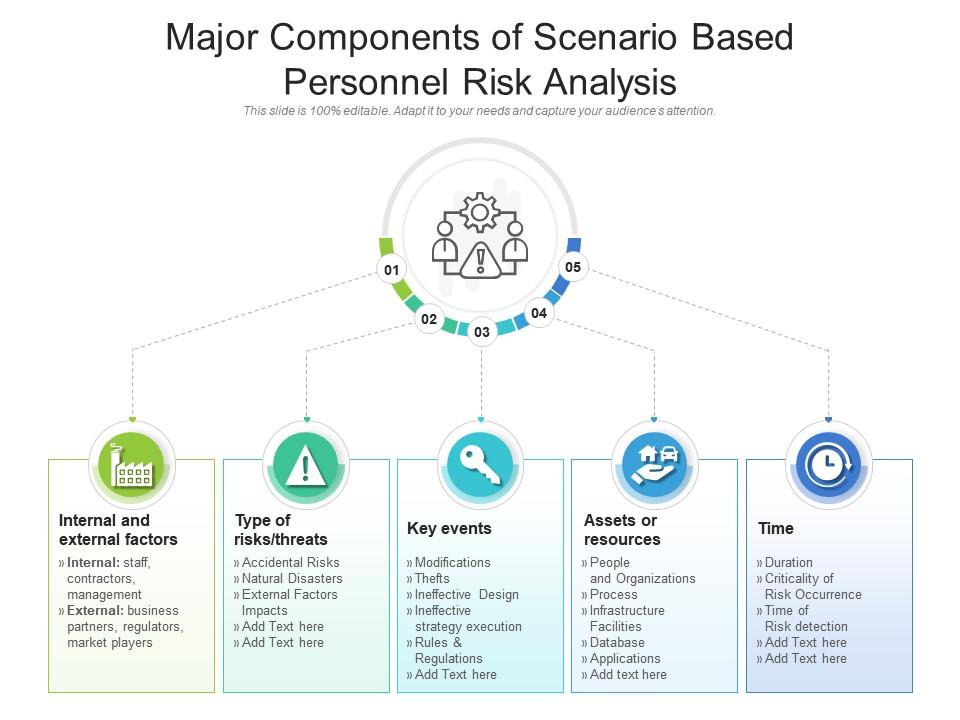
One of the most widely used risk assessment methodologies is scenario-based risk assessment. This approach focuses on identifying potential future events – “scenarios” – that could impact an organization’s operations. Instead of focusing solely on historical data, scenario analysis allows organizations to explore a range of possibilities, considering their potential consequences and the likelihood of occurrence. For example, a manufacturing company might develop scenarios involving supply chain disruptions, increased raw material costs, or a sudden shift in consumer demand. Each scenario is then analyzed to determine the potential impact on profitability, reputation, and operational efficiency. The process typically involves:
- Identifying Key Stakeholders: Determining who is affected by each scenario.
- Defining Potential Events: Brainstorming a range of possible events that could trigger each scenario.
- Assessing Impact: Evaluating the potential consequences of each event on each stakeholder.
- Developing Mitigation Strategies: Creating plans to reduce the likelihood or impact of each scenario.
This method is particularly useful for organizations operating in volatile industries or those with complex supply chains. It’s a flexible approach that can be adapted to a wide range of situations. The benefits of scenario-based risk assessment include its ability to identify unexpected risks and to develop proactive responses.

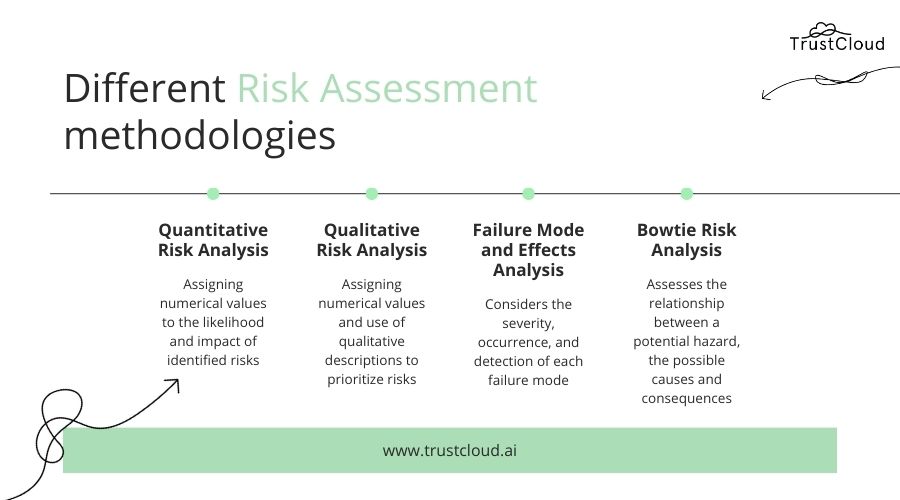
Quantitative Risk Assessment – Numbers and Data
Quantitative risk assessment methods rely on numerical data and statistical analysis to estimate the potential impact of risks. These methods are often used when the likelihood and impact of a risk are well-defined and quantifiable. Common techniques include:
- Probability and Impact Matrix: This is a simple but effective tool that plots risks based on their probability of occurrence and their potential impact on the organization. The matrix helps prioritize risks based on their severity.
- Sensitivity Analysis: This technique examines how changes in key variables affect the overall risk level. By systematically varying these variables, organizations can identify the most sensitive risks.
- Monte Carlo Simulation: This more complex technique uses computer simulations to model the potential outcomes of a risk, incorporating uncertainty in the input data. It provides a probabilistic view of the potential range of outcomes.
Quantitative risk assessment is particularly valuable for high-stakes projects or operations where precise risk estimates are required. However, it requires a significant investment in data collection and analysis.
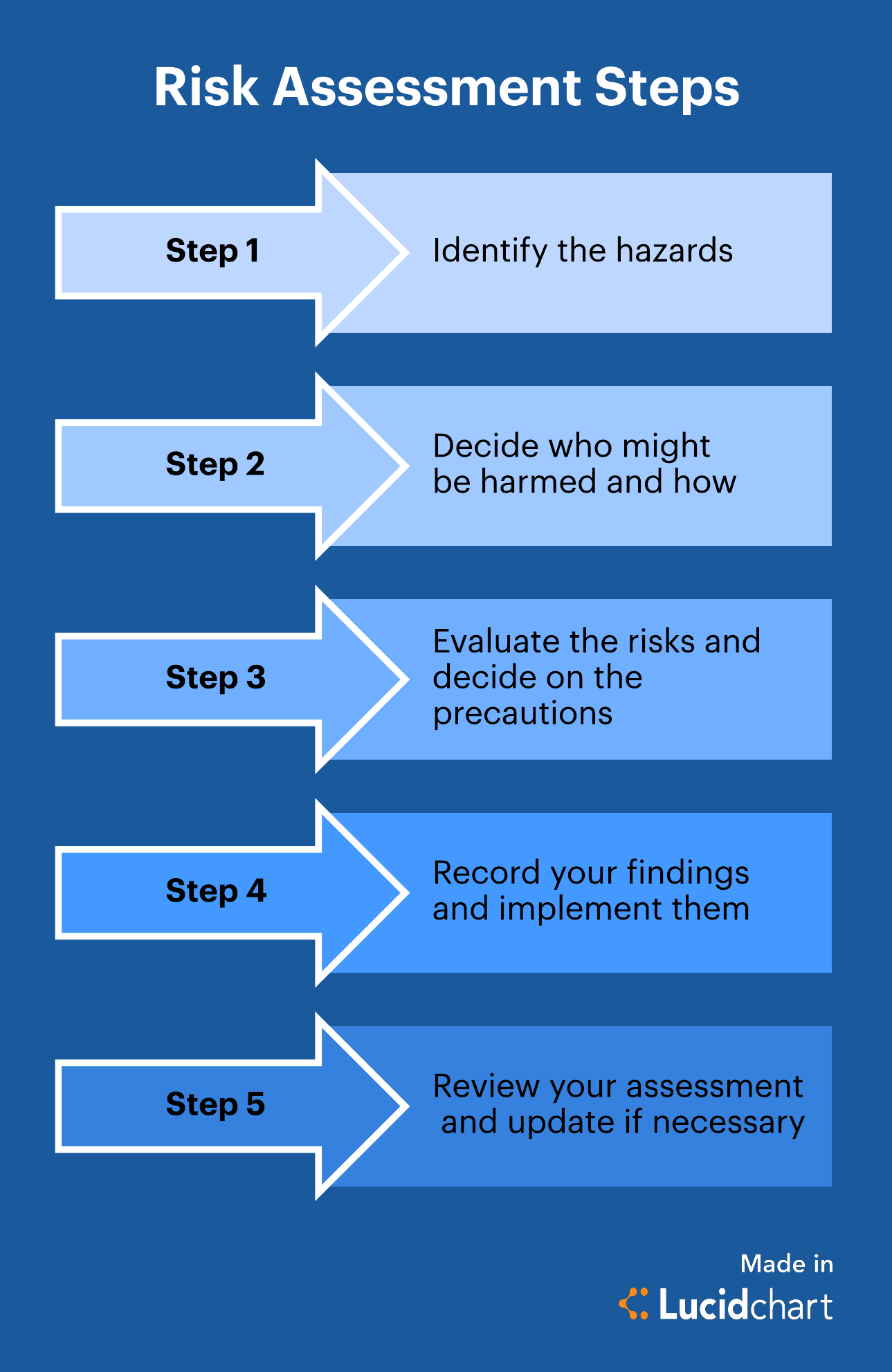
Qualitative Risk Assessment – Expert Judgment and Intuition
While quantitative methods provide numerical estimates, qualitative risk assessment relies on expert judgment and intuition to identify and assess risks. This approach is often used when data is limited or when the potential impact of a risk is difficult to quantify. Key techniques include:

- Risk Matrix: Similar to the probability and impact matrix, but utilizes qualitative judgments to assess the severity of risks. The matrix is often color-coded to represent the level of risk (e.g., low, medium, high).
- Brainstorming Sessions: Facilitated discussions with stakeholders to identify potential risks and assess their likelihood and impact.
- Root Cause Analysis: Identifying the underlying causes of risks to develop more effective mitigation strategies.
Qualitative risk assessment is often used as a preliminary step in a more comprehensive risk assessment process. It can help to identify the most critical risks and to prioritize efforts for mitigation.

Risk Registers – A Structured Approach to Management
A risk register is a crucial tool for managing and tracking risks throughout their lifecycle. It’s a centralized repository for information related to identified risks, their potential impact, and the planned mitigation strategies. A well-maintained risk register provides a clear and consistent record of risk management activities. Key components typically include:

- Risk ID: A unique identifier for each risk.
- Risk Description: A clear and concise description of the risk.
- Risk Category: Categorizing the risk (e.g., financial, operational, strategic).
- Likelihood: The probability of the risk occurring (e.g., low, medium, high).
- Impact: The potential consequences of the risk occurring (e.g., low, medium, high).
- Risk Score: A calculated score based on likelihood and impact (e.g., a risk matrix score).
- Mitigation Strategy: The planned actions to reduce the likelihood or impact of the risk.
- Responsible Party: The individual or team responsible for implementing the mitigation strategy.
- Status: The current status of the risk (e.g., open, closed, in progress).
Regularly updating and reviewing the risk register is essential for maintaining an effective risk management program.
Applying Risk Assessment Methodologies – Industry Variations
The effectiveness of risk assessment methodologies can vary significantly depending on the industry and the specific risks being addressed. For example:
- Healthcare: Focus on patient safety, data security, and regulatory compliance. Quantitative methods are often used to assess the potential impact of adverse events.
- Financial Services: Emphasis on cybersecurity, fraud detection, and regulatory risk. Scenario-based analysis is frequently employed to model potential market disruptions.
- Manufacturing: Focus on supply chain disruptions, equipment failures, and product defects. Quantitative methods are used to assess the potential impact on production and profitability.
- Technology: Emphasis on cybersecurity, data privacy, and intellectual property protection. Qualitative methods are often used to assess the potential impact of cyberattacks and data breaches.
Understanding these industry-specific nuances is critical for tailoring risk assessment methodologies to maximize their effectiveness.
Tools and Technology for Risk Assessment
Several software tools and technologies can streamline the risk assessment process:
- Risk Management Software: Platforms like RSA Archer, MetricStream, and ServiceNow offer comprehensive risk management capabilities, including scenario analysis, risk modeling, and reporting.
- Spreadsheet Software (Excel, Google Sheets): Simple spreadsheets can be used for basic risk assessment, particularly for smaller organizations.
- Data Visualization Tools (Tableau, Power BI): These tools can help to visualize risk data and identify trends.
The choice of tool depends on the organization’s size, complexity, and budget.
Conclusion
Risk assessment methodologies are an indispensable component of any organization seeking to proactively manage its risks. By systematically identifying, analyzing, and mitigating potential threats, organizations can protect their assets, enhance their resilience, and achieve their strategic goals. The selection of the appropriate methodology – whether it’s scenario-based, quantitative, or qualitative – depends on the specific context and the nature of the risks being addressed. Furthermore, a robust risk management program requires a well-maintained risk register and a commitment to continuous improvement. Ultimately, effective risk assessment is not just about identifying risks; it’s about building a culture of risk awareness and accountability throughout the organization. Risk assessment methodologies are constantly evolving, incorporating new technologies and best practices. Staying informed about these advancements is crucial for organizations seeking to maintain a competitive advantage in an increasingly complex and uncertain world. The key takeaway is that a proactive and adaptable approach to risk management is essential for long-term success.