Effective project management is no longer a luxury; it’s a necessity for businesses of all sizes. Whether you’re launching a new product, implementing a significant organizational change, or simply trying to complete a routine task, a structured approach is crucial for success. Project management methodologies provide the framework for achieving these goals, offering a systematic way to plan, execute, and monitor projects. Choosing the right methodology can significantly impact project outcomes, efficiency, and overall profitability. This article will delve into several prominent project management methodologies, exploring their strengths, weaknesses, and suitability for different types of projects. Understanding these approaches is vital for any leader or team member involved in delivering successful results.
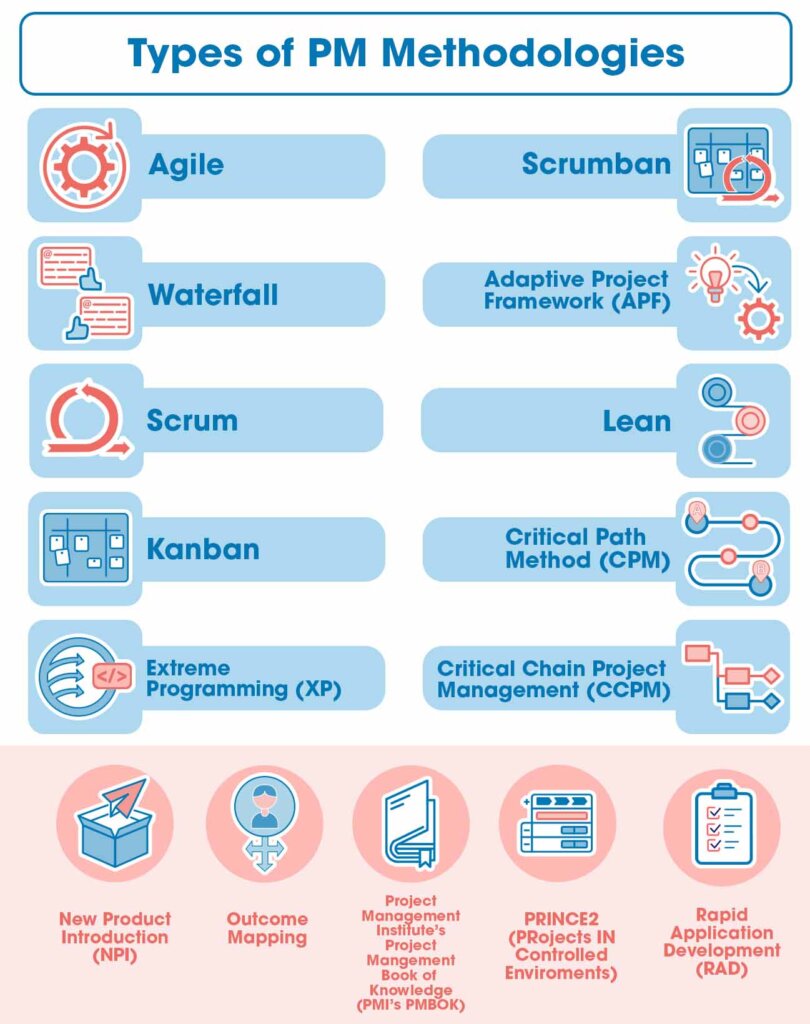
What Are Project Management Methodologies?
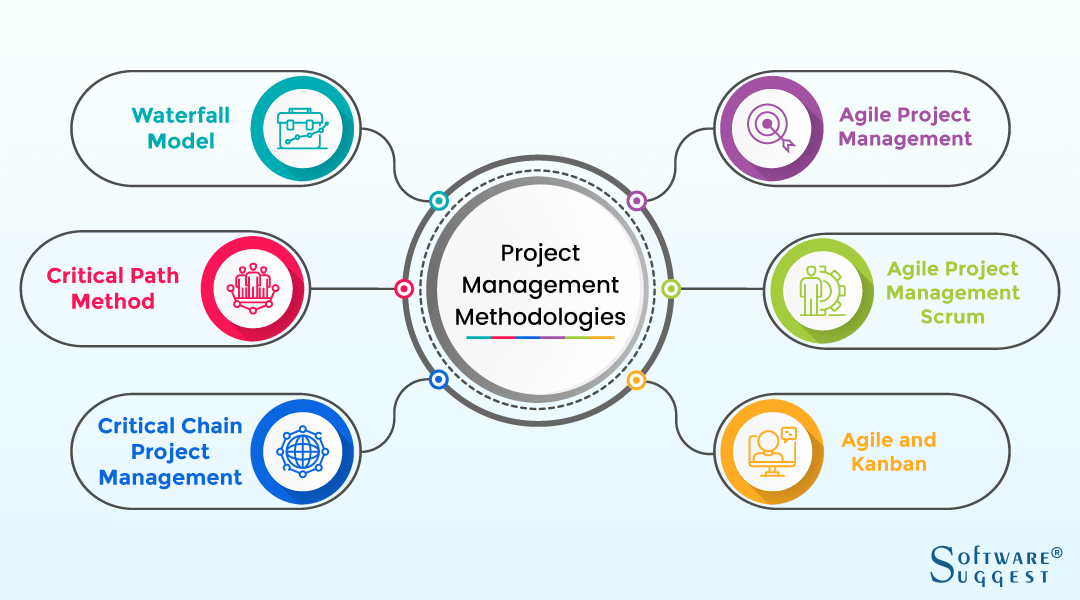
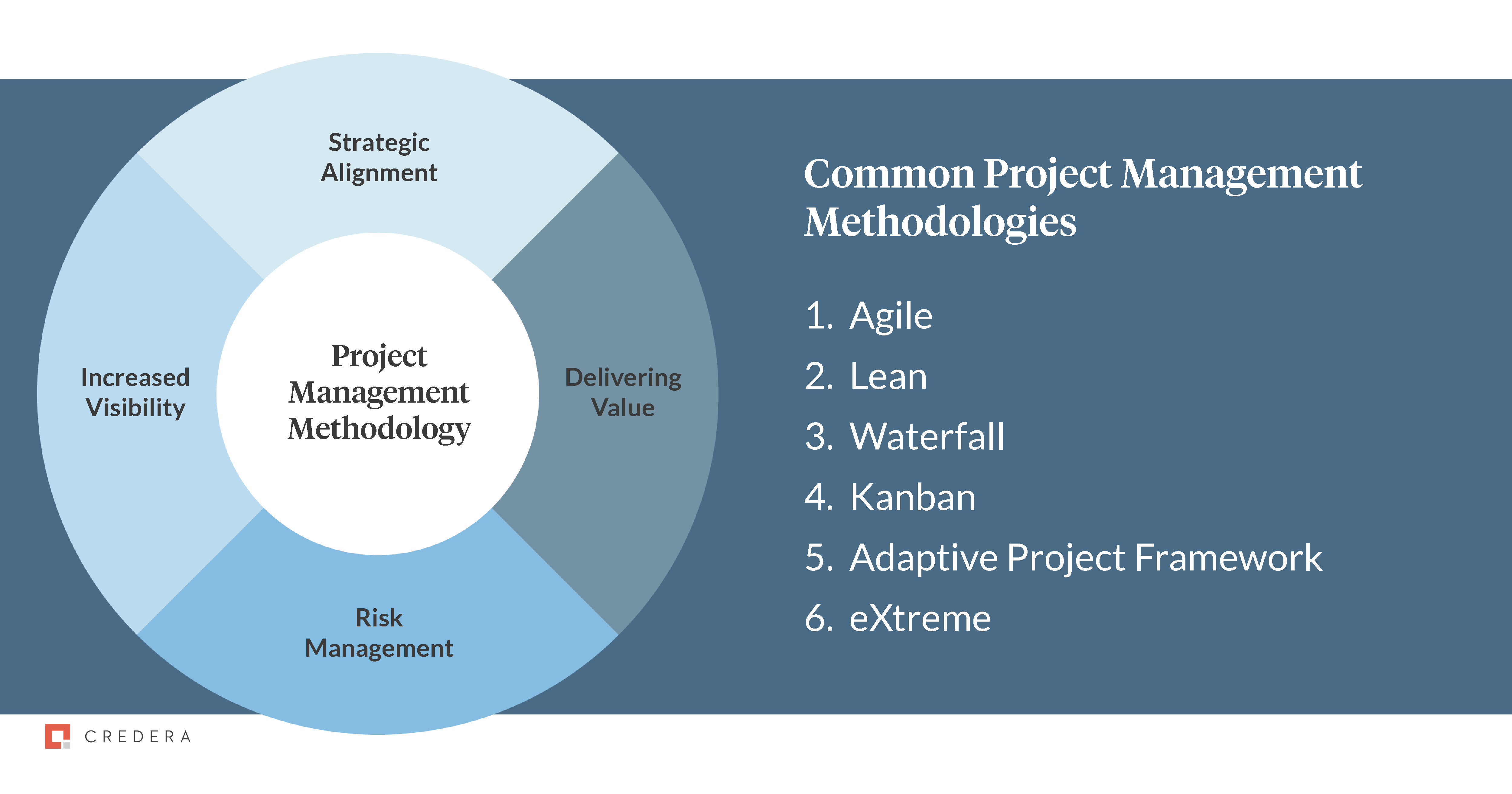
At their core, project management methodologies are sets of principles, processes, and tools designed to manage and control projects. They provide a standardized way to approach project planning, execution, monitoring, and closure. They’re not a one-size-fits-all solution; instead, they offer a range of options tailored to specific project characteristics and organizational cultures. The goal is to improve predictability, reduce risks, and ultimately deliver projects on time, within budget, and to the required quality standards. Different methodologies emphasize different aspects, leading to varying levels of complexity and suitability for different project types. A well-defined methodology ensures everyone involved understands their roles and responsibilities, fostering collaboration and accountability.
Waterfall Methodology – A Traditional Approach
The Waterfall methodology is perhaps the most widely recognized project management approach. It’s a sequential, linear process, often described as a "waterfall" because of its stages – requirements gathering, design, implementation, testing, deployment, and maintenance. Each phase must be completed before the next begins. Waterfall methodologies are particularly well-suited for projects with clearly defined requirements and a stable scope. However, their rigidity can be a drawback when requirements are likely to change during the project lifecycle. A significant challenge with Waterfall is its difficulty in adapting to evolving needs. It’s best suited for projects where the outcome is well-understood from the outset. Companies often use Waterfall for large-scale construction projects or systems implementations where detailed documentation is essential.
Key Characteristics of Waterfall
- Sequential Stages: The project progresses through distinct phases.
- Detailed Documentation: Extensive documentation is created at each stage.
- Fixed Scope: The project scope is defined upfront and rarely changes.
- Limited Flexibility: Adapting to changes is difficult and costly.
- Suitable for: Projects with well-defined requirements and stable scope.
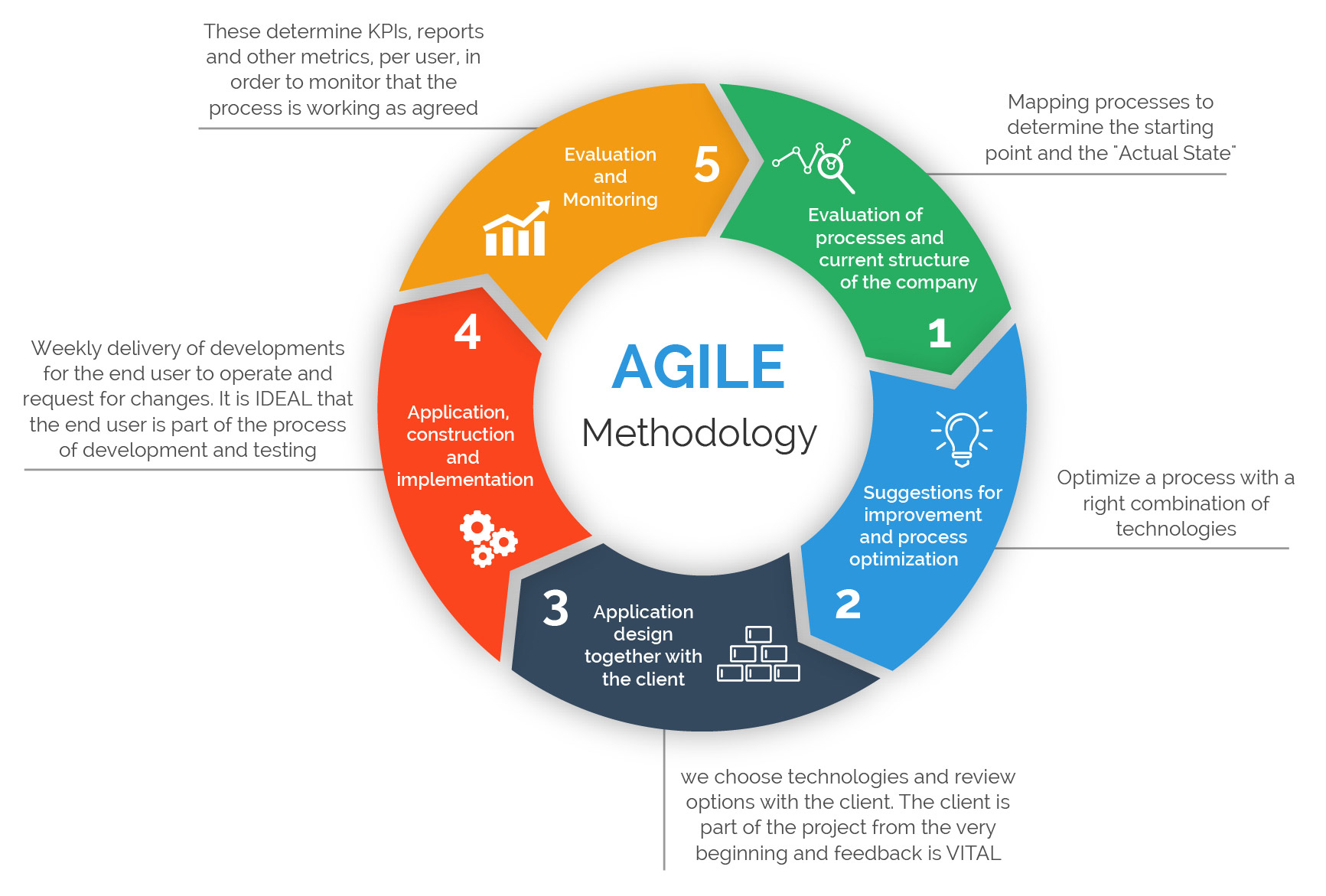
Agile Methodologies – Embracing Change
In contrast to the Waterfall approach, Agile methodologies are iterative and incremental. They emphasize collaboration, flexibility, and continuous improvement. Instead of a linear sequence, Agile projects are broken down into short cycles called sprints, typically lasting 1-4 weeks. Each sprint results in a working increment of the product, allowing for frequent feedback and adaptation. Agile methodologies are particularly popular for software development, but are increasingly being adopted for other types of projects as well. They prioritize customer satisfaction and responsiveness to change. The core principles of Agile include frequent communication, self-organizing teams, and continuous integration.

Agile Frameworks
Several popular Agile frameworks exist, each with its own nuances:
- Scrum: A highly structured framework that uses sprints, daily stand-up meetings, and sprint reviews.
- Kanban: A visual system that focuses on workflow management and limiting work in progress.
- Extreme Programming (XP): Emphasizes technical practices like pair programming and test-driven development.
Benefits of Agile
- Increased Flexibility: Adapts to changing requirements easily.
- Faster Time to Market: Delivers working software in short iterations.
- Improved Customer Satisfaction: Frequent feedback loops ensure alignment with customer needs.
- Enhanced Team Collaboration: Promotes communication and teamwork.
Lean Project Management – Optimizing Value
Lean project management focuses on eliminating waste and maximizing value. It’s a philosophy that emphasizes identifying and removing any activity that doesn’t add value to the customer. Lean methodologies are particularly effective in optimizing processes and reducing costs. Key principles include value stream mapping, continuous improvement, and the 8 wastes (delay, overproduction, waiting, transportation, inventory, motion, extra-processing, and defects). Lean projects prioritize delivering the most value to the customer with the fewest resources. It’s often used in manufacturing but can be adapted to other industries.

Core Lean Principles
- Value: Identifying and prioritizing what the customer values.
- Value Stream: Mapping the entire process from start to finish.
- Flow: Streamlining the process to minimize delays.
- Pull: Producing only what is needed, when it’s needed.
- Perfection: Continuously seeking ways to improve.
Hybrid Methodologies – Combining Strengths
Many organizations adopt hybrid methodologies, combining elements of different approaches to create a tailored solution. For example, a project might utilize Waterfall for initial planning and requirements gathering, but then transition to Agile for implementation and testing. This approach leverages the strengths of each methodology, resulting in a more robust and adaptable project management process. The key is to select the right tools and techniques for the specific project context.
Selecting the Right Methodology
The choice of project management methodology depends on a variety of factors, including the project’s complexity, the team’s experience, and the organization’s culture. There’s no one-size-fits-all solution. Carefully consider the project’s characteristics and choose a methodology that aligns with your goals and resources. It’s also important to remember that methodologies are not static; they should be adapted and refined as the project evolves. Regularly reviewing and updating your methodology is crucial for maintaining its effectiveness.
Conclusion
Effective project management methodologies are essential for delivering successful projects. Understanding the different approaches available – Waterfall, Agile, Lean, and hybrid models – allows you to select the most appropriate strategy for your specific needs. By embracing a structured and adaptable approach, you can significantly increase the likelihood of achieving project goals, minimizing risks, and maximizing value. Project management methodologies are not just tools; they are a mindset – a commitment to continuous improvement and a focus on delivering exceptional results. Investing in the right methodologies is an investment in the success of your projects and your organization.