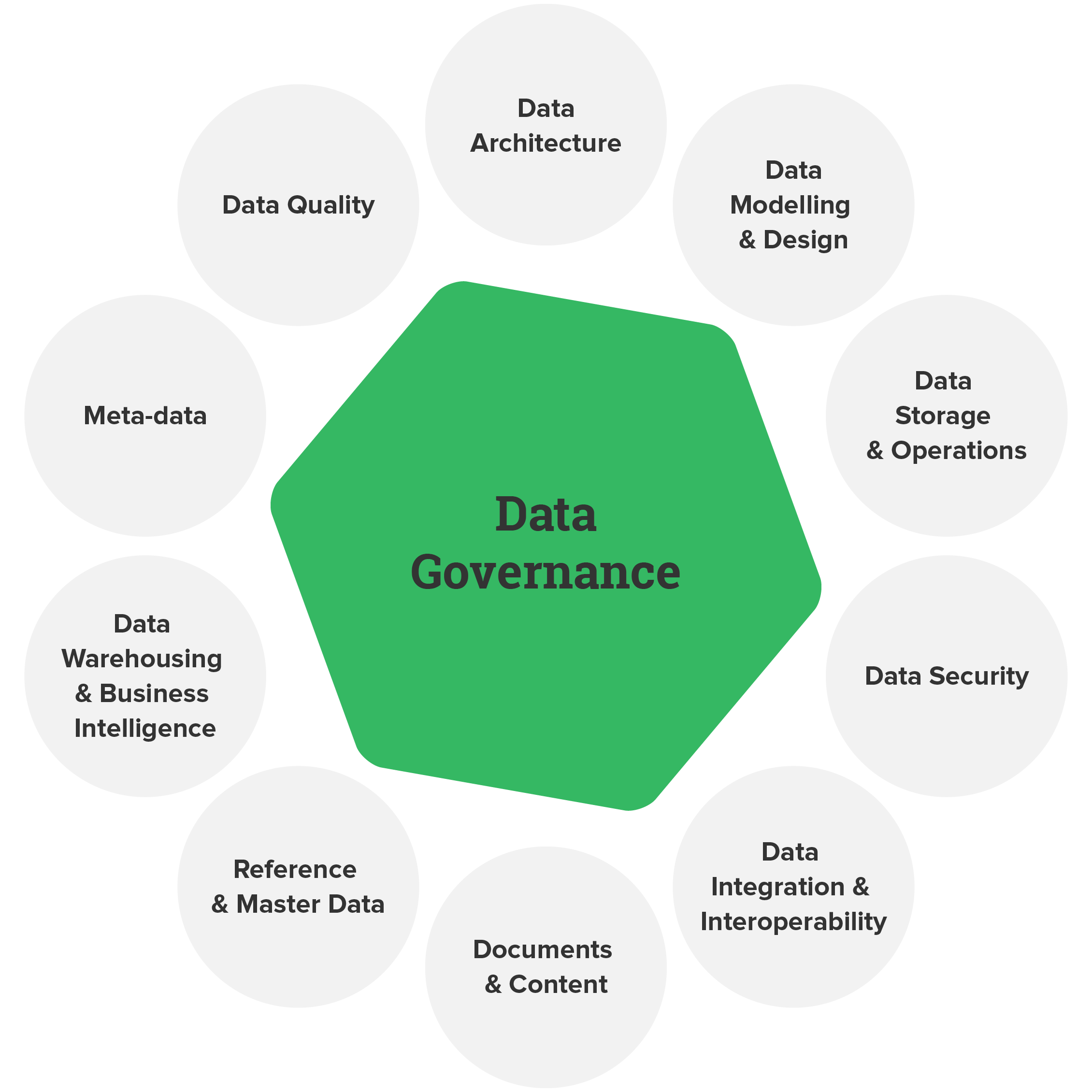
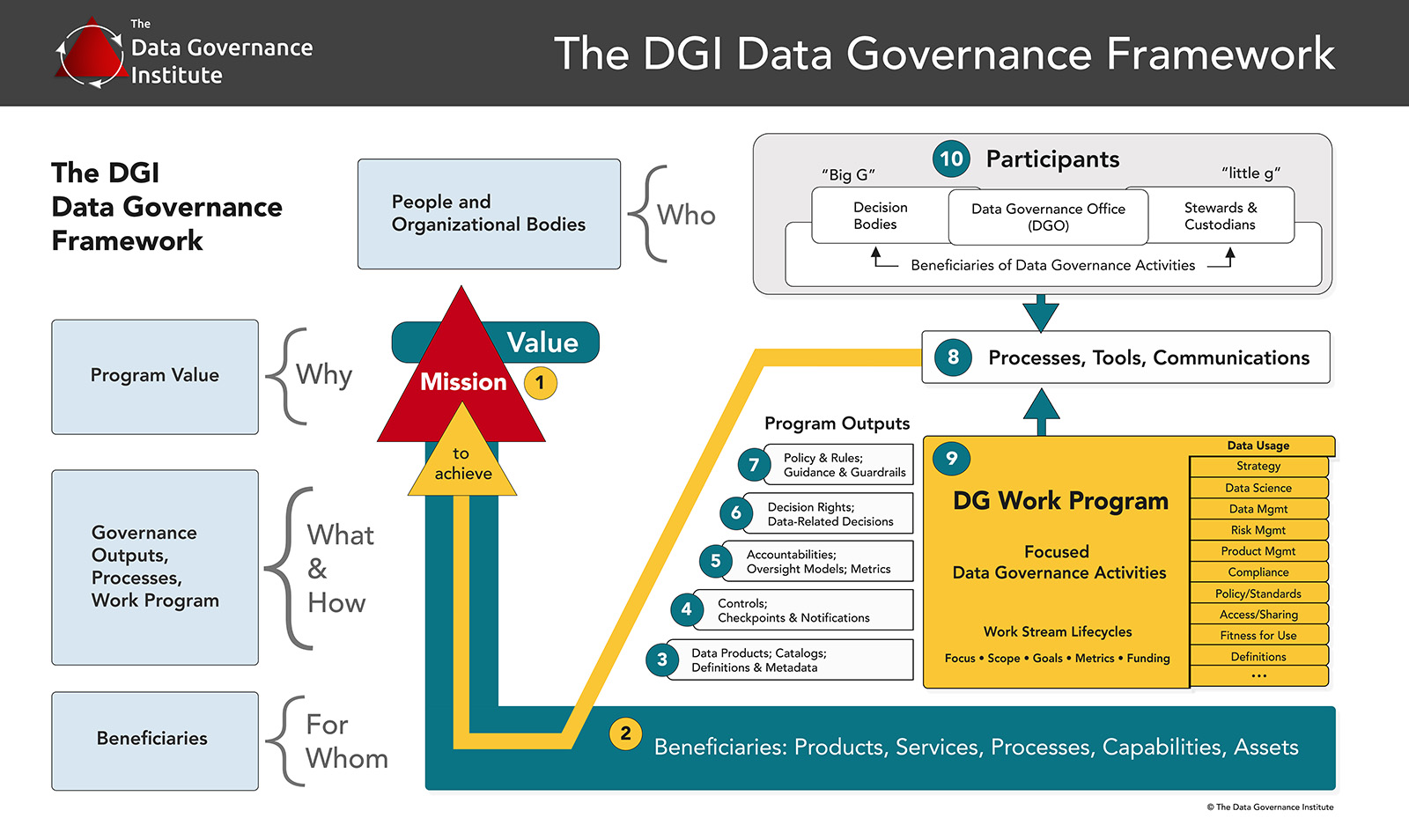
Data governance is no longer a nice-to-have; it’s a fundamental necessity for any organization striving for success in today’s data-driven world. It’s the framework of policies, processes, and responsibilities designed to ensure data is managed effectively, securely, and ethically. Data governance encompasses a broad range of activities, from defining data quality standards to establishing clear roles and responsibilities. Without a robust data governance strategy, organizations risk losing valuable insights, facing compliance issues, and ultimately hindering their ability to innovate and compete. This article will delve into the core principles of data governance, exploring its key components and practical strategies for implementation. It’s designed to provide a comprehensive understanding of what data governance truly means and how to build a successful program.

Understanding the Importance of Data Governance
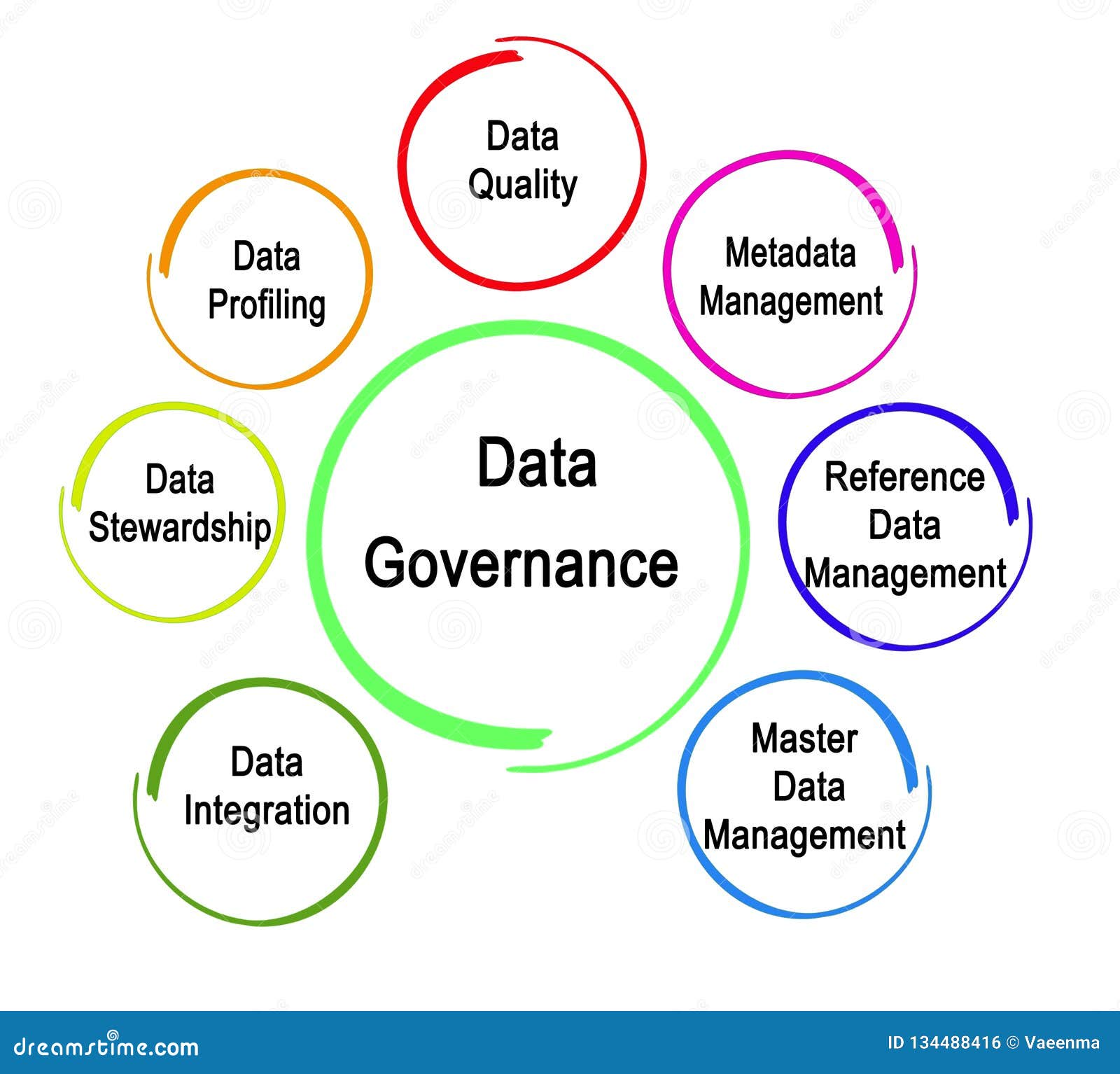
The sheer volume of data being generated and processed by organizations today is staggering. From customer interactions and operational data to financial records and research findings, data is the lifeblood of modern businesses. However, this abundance of data presents significant challenges. Without proper management, data can become fragmented, inconsistent, and unreliable, leading to poor decision-making and operational inefficiencies. Poor data quality directly impacts everything from marketing campaigns to product development, and ultimately, profitability. Investing in data governance is therefore an investment in the long-term health and success of any organization. It’s about more than just compliance; it’s about unlocking the true value hidden within your data assets.

Defining Data Governance Principles
At its core, data governance is built upon a set of guiding principles. These principles provide a framework for decision-making and ensure alignment across the organization. Data quality is paramount, requiring meticulous monitoring and improvement of data accuracy, completeness, and consistency. Data security is critical, protecting sensitive information from unauthorized access and breaches. Data lineage – tracing the origin and movement of data – is essential for understanding data transformations and ensuring accountability. Compliance with regulations like GDPR, CCPA, and HIPAA is a key consideration, demanding adherence to specific data privacy and security requirements. Finally, data accessibility – making data readily available to authorized users – is vital for informed decision-making. These principles are not static; they should be continuously reviewed and adapted to reflect evolving business needs and regulatory changes.
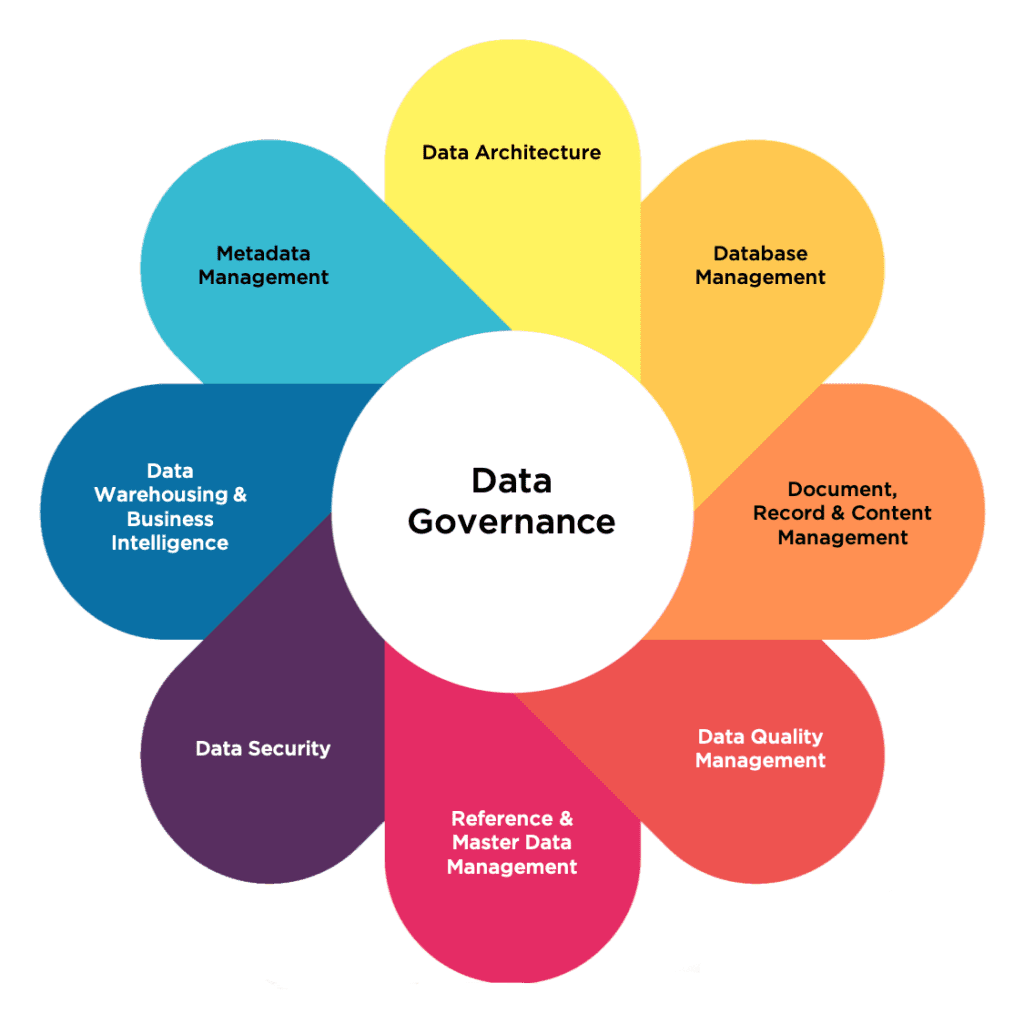
Key Components of a Data Governance Framework
A successful data governance program isn’t a one-size-fits-all solution. It requires a carefully designed framework incorporating several key components. Data stewardship is a crucial role, typically assigned to business users who are responsible for the quality and usability of data within their respective areas. Data owners are accountable for the overall management of specific data domains, defining policies and standards. Data custodians are responsible for the technical aspects of data management, including data storage, backup, and recovery. Data architects design and implement the data infrastructure, ensuring that data is stored and accessed efficiently. Data governance committees provide oversight and guidance, ensuring alignment across the organization. Finally, data quality monitoring processes are established to track and measure data quality metrics, identifying areas for improvement. These components work together to create a cohesive and effective data governance program.

Data Governance Policies and Procedures
Clearly defined policies and procedures are the backbone of any data governance program. These documents outline the rules and guidelines for data management, ensuring consistency and accountability. Data access policies dictate who can access what data and under what circumstances. Data retention policies specify how long data should be stored and when it should be archived or deleted. Data quality standards define acceptable levels of data accuracy, completeness, and consistency. Data security policies address how data is protected from unauthorized access and breaches. Data privacy policies comply with relevant regulations, such as GDPR and CCPA. These policies should be readily accessible to all employees and regularly reviewed and updated. Effective communication and training are essential for ensuring that employees understand and adhere to these policies.
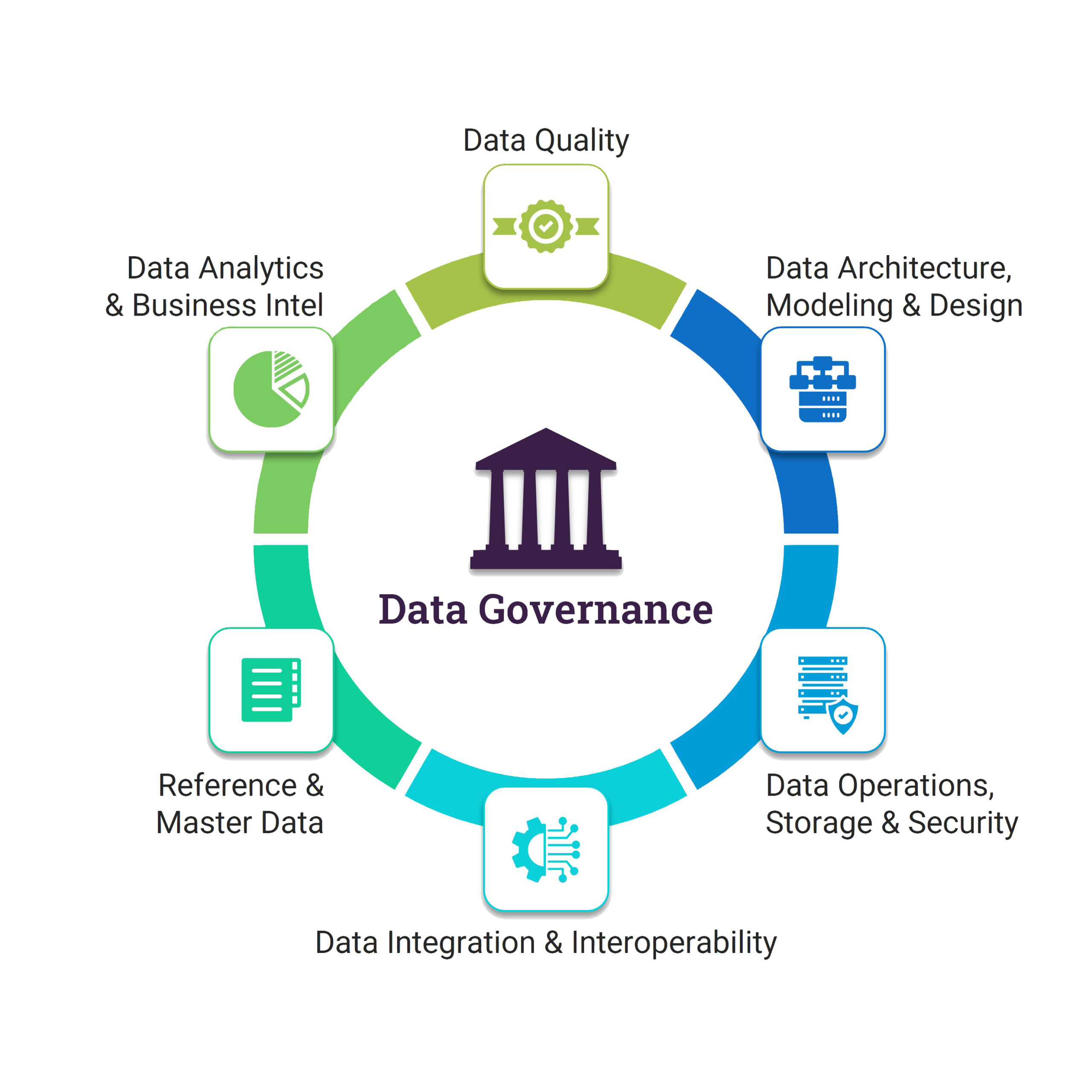
Data Governance Tools and Technologies
Fortunately, a variety of tools and technologies can streamline and automate data governance processes. Data catalog tools provide a central repository for metadata, making it easier to discover and understand data assets. Data quality tools automate data profiling, cleansing, and monitoring. Data lineage tools track the origin and movement of data, providing a clear audit trail. Data masking and anonymization tools protect sensitive data while still allowing for analysis. Workflow management tools automate data governance processes, such as data access requests and data quality remediation. Choosing the right tools is crucial for maximizing the effectiveness of your data governance program. Many vendors offer comprehensive solutions tailored to specific industry needs.
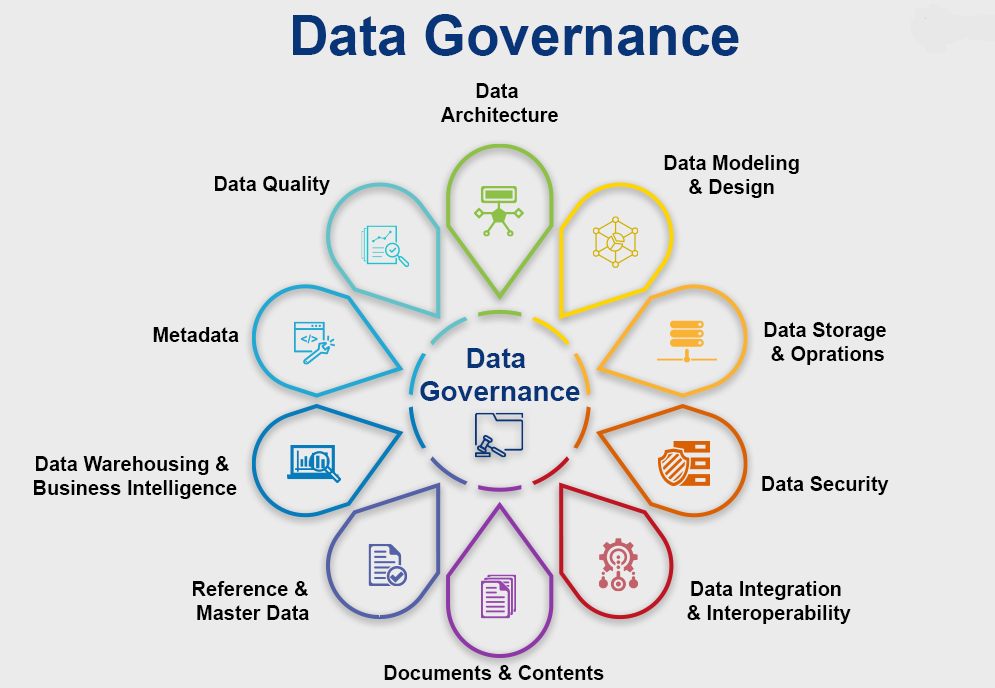
Data Governance in Different Business Contexts
The specific needs and challenges of data governance vary significantly depending on the industry and the organization’s size and complexity. Healthcare data governance faces unique challenges related to patient privacy and regulatory compliance. Financial services require stringent data security and compliance measures. Retail organizations need to manage data related to customer behavior and loyalty programs. Manufacturing often deals with large volumes of operational data. Government agencies must adhere to strict data privacy regulations. Understanding these nuances is critical for tailoring a data governance strategy that addresses the specific risks and requirements of each sector. A phased approach, starting with a pilot project in a specific area, is often a sensible way to implement data governance across an entire organization.
The Benefits of a Robust Data Governance Program
The benefits of investing in a robust data governance program extend far beyond simply meeting compliance requirements. Improved data quality leads to more accurate insights and better decision-making. Increased operational efficiency results from streamlined data processes. Reduced risk of data breaches protects sensitive information and maintains customer trust. Enhanced regulatory compliance minimizes legal and financial penalties. Better data-driven innovation unlocks new opportunities for growth and competitive advantage. Ultimately, data governance is a strategic investment that delivers tangible business value.

Conclusion: Embracing Data Governance for Future Success
Data governance is no longer a luxury; it’s a strategic imperative for organizations seeking to thrive in the digital age. By implementing a well-defined data governance framework, businesses can unlock the full potential of their data assets, improve decision-making, and achieve sustainable competitive advantage. The key lies in understanding the principles of data quality, security, lineage, and accessibility, and then tailoring a program to the specific needs of your organization. As data continues to grow in volume and complexity, the importance of data governance will only increase. Organizations that embrace this approach will be well-positioned to navigate the challenges of the future and capitalize on the opportunities presented by data. Moving forward, continuous monitoring, evaluation, and adaptation are crucial to maintaining the effectiveness of your data governance program. It’s an ongoing journey, not a destination.