Financial forecasting is more than just crunching numbers and projecting future earnings – it’s a critical process for businesses, investors, and even individuals. It’s the art of anticipating what will happen in the financial markets and within an organization, allowing for proactive decision-making and mitigating potential risks. Financial forecasting is no longer a luxury; it’s a necessity for navigating an increasingly volatile and complex economic landscape. The ability to accurately predict trends and anticipate challenges is what separates successful players from those who are left behind. This article will delve into various strategies and techniques for effective financial forecasting, providing you with the knowledge to build more robust and reliable models. Let’s explore how to leverage data, analysis, and strategic thinking to gain a competitive edge.
Understanding the Importance of Financial Forecasting
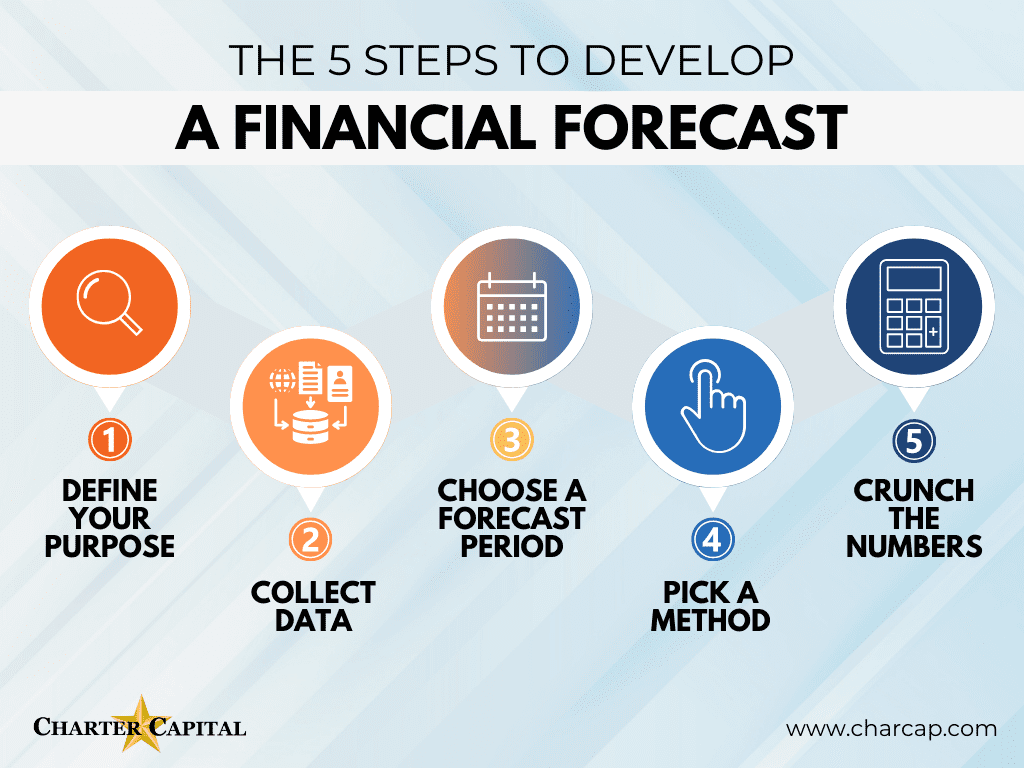
The benefits of robust financial forecasting extend far beyond simply predicting revenue. Effective forecasting allows organizations to:
- Optimize Resource Allocation: Knowing future demand and potential costs enables efficient investment decisions, shifting resources to areas with the highest potential return.
- Manage Risk: By identifying potential vulnerabilities and anticipating disruptions, businesses can develop contingency plans and mitigate negative impacts.
- Secure Funding: Investors and lenders rely on forecasts to assess the viability of a business or investment opportunity. Accurate projections build confidence and increase the likelihood of securing funding.
- Improve Operational Efficiency: Forecasting helps anticipate changes in production, inventory, and staffing needs, leading to streamlined operations and reduced waste.
- Strategic Planning: A strong forecasting capability forms the foundation for long-term strategic planning, guiding the company towards its goals.
Key Forecasting Methods and Techniques
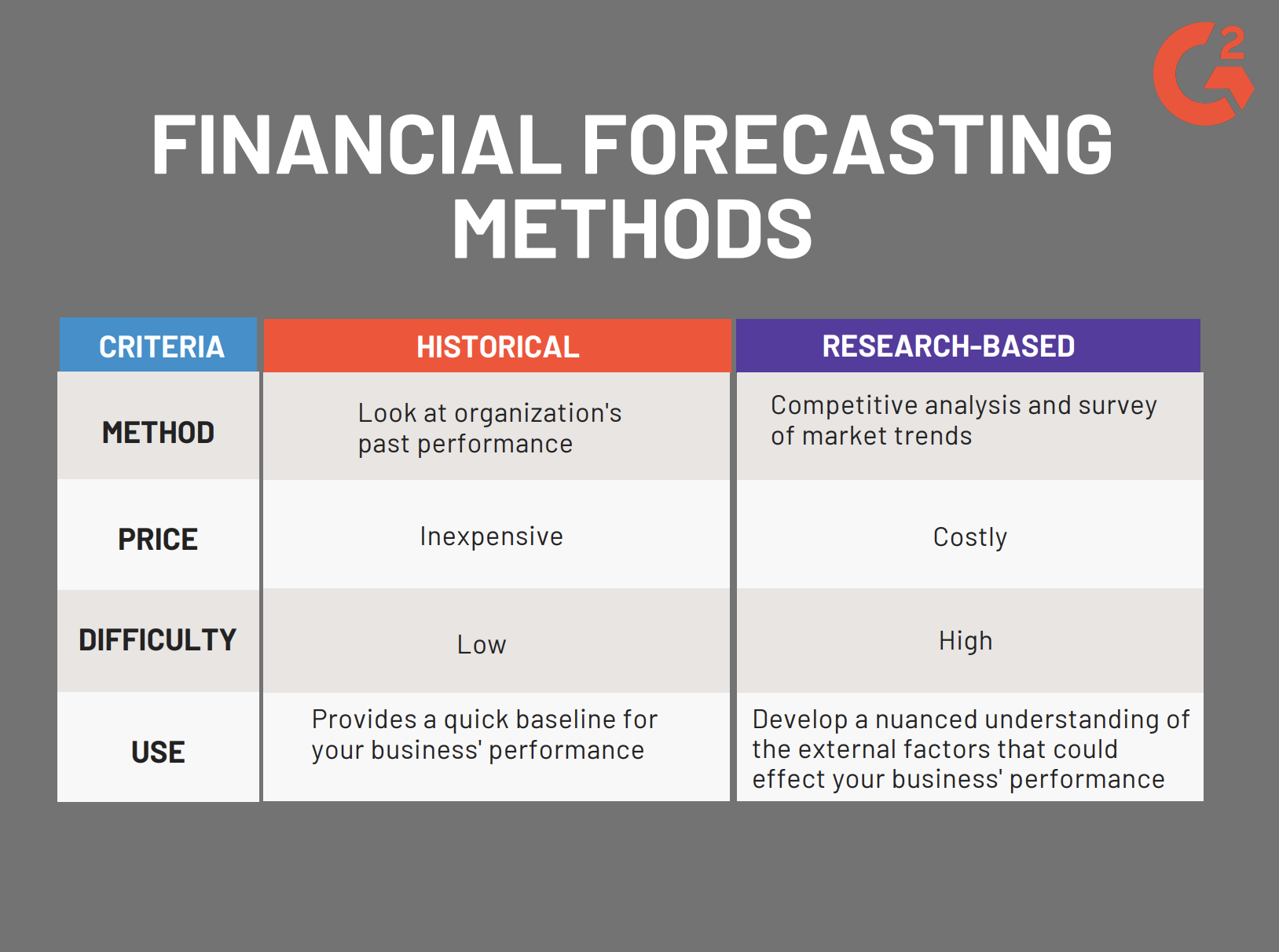
Several methods exist for generating financial forecasts, each with its own strengths and weaknesses. Choosing the right approach depends on the specific industry, business model, and available data.

1. Trend Analysis
Trend analysis involves examining historical data to identify patterns and predict future trends. This is a foundational technique and often forms the basis for more sophisticated forecasting models. It’s particularly useful for industries with stable, predictable growth. For example, in the retail sector, sales trends often exhibit a consistent upward trajectory, making trend analysis a valuable tool. Analyzing seasonality – the recurring patterns of demand across different periods – is crucial for accurate trend identification. Tools like moving averages and exponential smoothing can be employed to smooth out short-term fluctuations and reveal underlying trends.

2. Regression Analysis
Regression analysis is a statistical technique used to identify the relationship between a dependent variable (the variable being predicted) and one or more independent variables (the factors influencing the dependent variable). It’s particularly effective when there’s a clear correlation between variables. In finance, regression can be used to forecast stock prices based on various factors like market indicators, economic data, and company-specific metrics. However, remember that correlation does not equal causation, and regression models should be interpreted with caution.
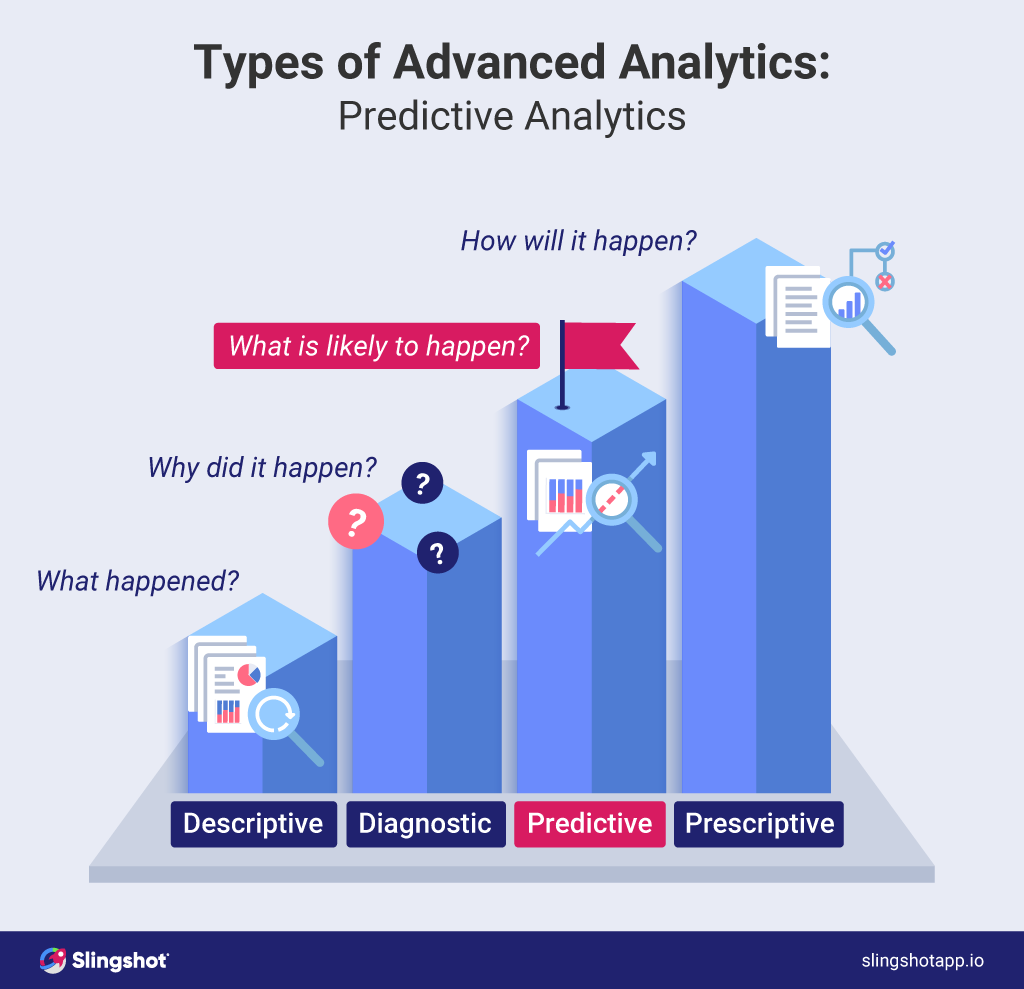
3. Scenario Planning
Scenario planning involves developing multiple plausible future scenarios based on different assumptions about key variables. Instead of focusing on a single prediction, it explores a range of possibilities – best-case, worst-case, and most-likely scenarios – to prepare for a variety of potential outcomes. This is particularly useful for businesses operating in uncertain environments. For instance, a manufacturing company might develop scenarios based on different economic growth rates, commodity prices, and regulatory changes.

4. Quantitative Forecasting Models
These models use mathematical formulas and statistical algorithms to generate forecasts. Popular examples include:

- ARIMA (Autoregressive Integrated Moving Average): A widely used model for time series forecasting, particularly effective for data with autocorrelation.
- Exponential Smoothing: A simple and effective method that assigns exponentially decreasing weights to past observations.
- Support Vector Regression (SVR): A powerful machine learning technique that can handle complex relationships between variables.
5. Qualitative Forecasting
While quantitative methods are valuable, qualitative forecasting incorporates expert opinions, market research, and industry knowledge to supplement data-driven predictions. This is particularly useful when historical data is limited or when external factors are difficult to quantify. Consulting with industry experts, analyzing competitor strategies, and conducting surveys can provide valuable qualitative insights.

Data Sources for Financial Forecasting
The quality of your forecasts depends heavily on the data you use. Here are some key data sources:

- Historical Financial Statements: Balance sheets, income statements, and cash flow statements provide a wealth of information about a company’s financial performance.
- Market Data: Stock prices, exchange rates, and commodity prices can be used to assess market trends and predict future movements.
- Economic Indicators: GDP growth, inflation rates, unemployment rates, and interest rates provide insights into the overall economic environment.
- Industry Reports: Industry-specific reports offer valuable information about market trends, competitive dynamics, and regulatory changes.
- Social Media Data: Analyzing social media sentiment can provide insights into consumer preferences and market trends. (Use with caution and validation)
- Customer Data: Understanding customer behavior and purchasing patterns can inform sales forecasts.
Challenges and Limitations of Financial Forecasting
Despite the benefits, financial forecasting is not without its challenges. Several factors can impact the accuracy of forecasts:
- Unforeseen Events: Unexpected events, such as natural disasters, geopolitical crises, and pandemics, can significantly disrupt financial forecasts.
- Data Quality Issues: Inaccurate or incomplete data can lead to flawed forecasts.
- Model Limitations: No forecasting model is perfect, and all models have limitations.
- Behavioral Biases: Human biases can influence forecasting decisions, leading to inaccurate predictions.
- Changing Market Conditions: Market dynamics are constantly evolving, requiring forecasts to be regularly updated.
The Role of Technology in Modern Financial Forecasting
Technology is playing an increasingly important role in enhancing financial forecasting capabilities.
- Big Data Analytics: The ability to analyze vast amounts of data from various sources is transforming forecasting.
- Machine Learning: Algorithms like neural networks can identify complex patterns and relationships in data that traditional methods might miss.
- Artificial Intelligence (AI): AI-powered tools are automating forecasting tasks and improving accuracy.
- Spreadsheet Software: Tools like Excel and Google Sheets remain essential for basic forecasting and data manipulation.
Best Practices for Effective Financial Forecasting
To maximize the effectiveness of your forecasting efforts, consider these best practices:
- Start with a Clear Objective: Define the purpose of your forecast and the specific questions you need to answer.
- Gather High-Quality Data: Ensure that your data is accurate, complete, and relevant.
- Validate Your Assumptions: Test your assumptions and be prepared to adjust them as new information becomes available.
- Use Multiple Methods: Combine different forecasting techniques to improve accuracy.
- Regularly Review and Update: Forecasts should be reviewed and updated regularly to reflect changing conditions.
- Communicate Clearly: Share your forecasts with stakeholders and explain the underlying assumptions.
Conclusion
Financial forecasting is a dynamic and essential discipline for businesses and individuals alike. By understanding the various forecasting methods, leveraging relevant data sources, and adopting best practices, you can significantly improve your ability to anticipate future trends and make informed decisions. Financial forecasting is not simply about predicting the past; it’s about shaping the future. As the business landscape continues to evolve, the ability to anticipate change and adapt accordingly will remain a critical competitive advantage. Investing in robust forecasting capabilities is an investment in long-term success. The future of financial planning hinges on the ability to accurately model and respond to the ever-changing forces shaping the global economy.