The landscape of business is constantly shifting. Traditional models are increasingly challenged by disruptive forces, requiring companies to embrace business model innovation – a fundamental shift in how a company creates, delivers, and captures value. This article will explore key strategies for fostering and implementing innovative business models, offering practical insights for businesses of all sizes. It’s no longer enough to simply improve existing operations; true success demands a proactive and adaptable approach to reimagining how you operate. Understanding the principles of business model innovation is crucial for long-term competitiveness and sustainable growth.

Understanding the Core Principles of Business Model Innovation
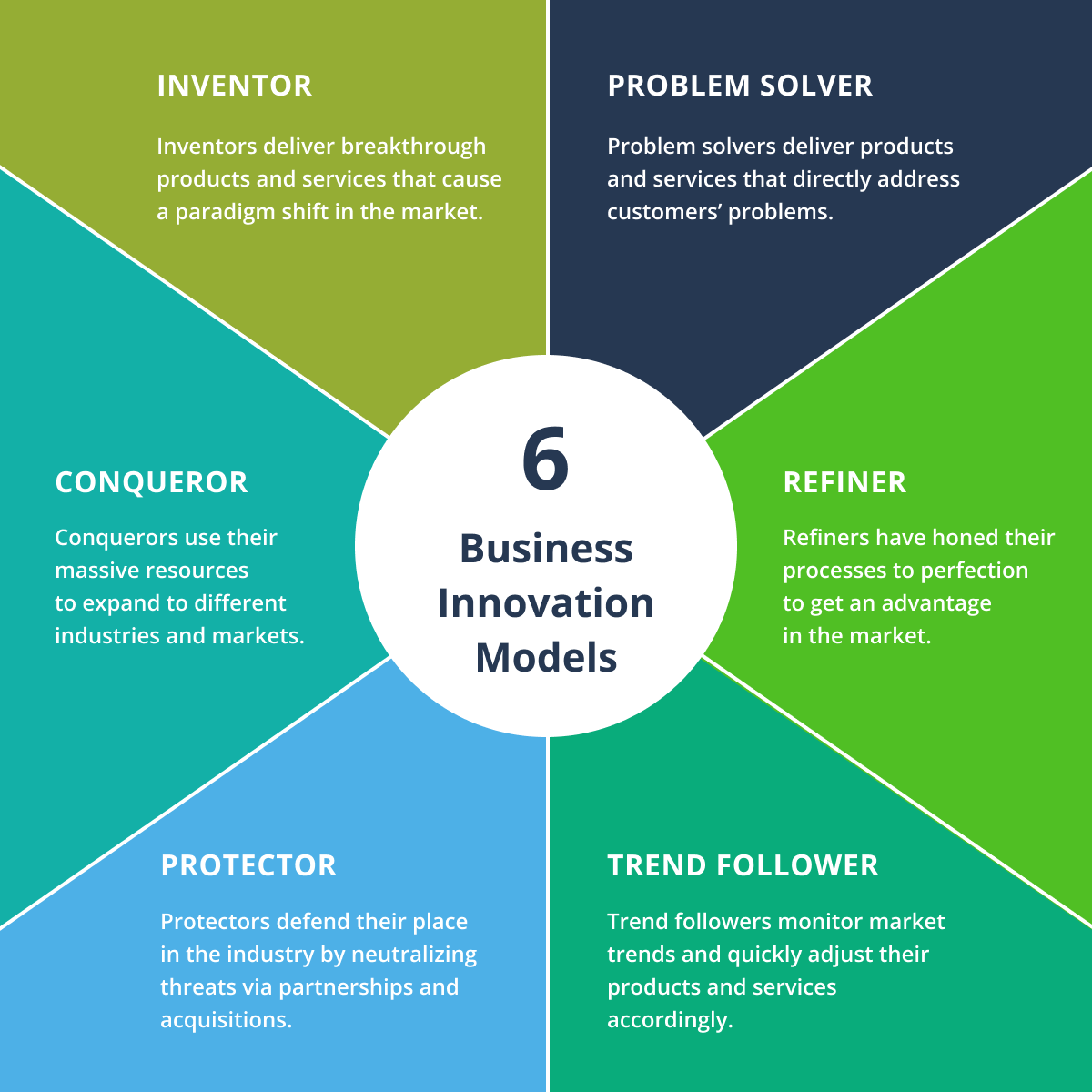
At its heart, business model innovation isn’t about inventing entirely new products or services. It’s about fundamentally rethinking the entire value proposition – how you create value for your customers, how you deliver it, and how you capture revenue. It’s about identifying unmet needs, leveraging emerging technologies, and adapting to changing market dynamics. Several key principles underpin successful innovation:
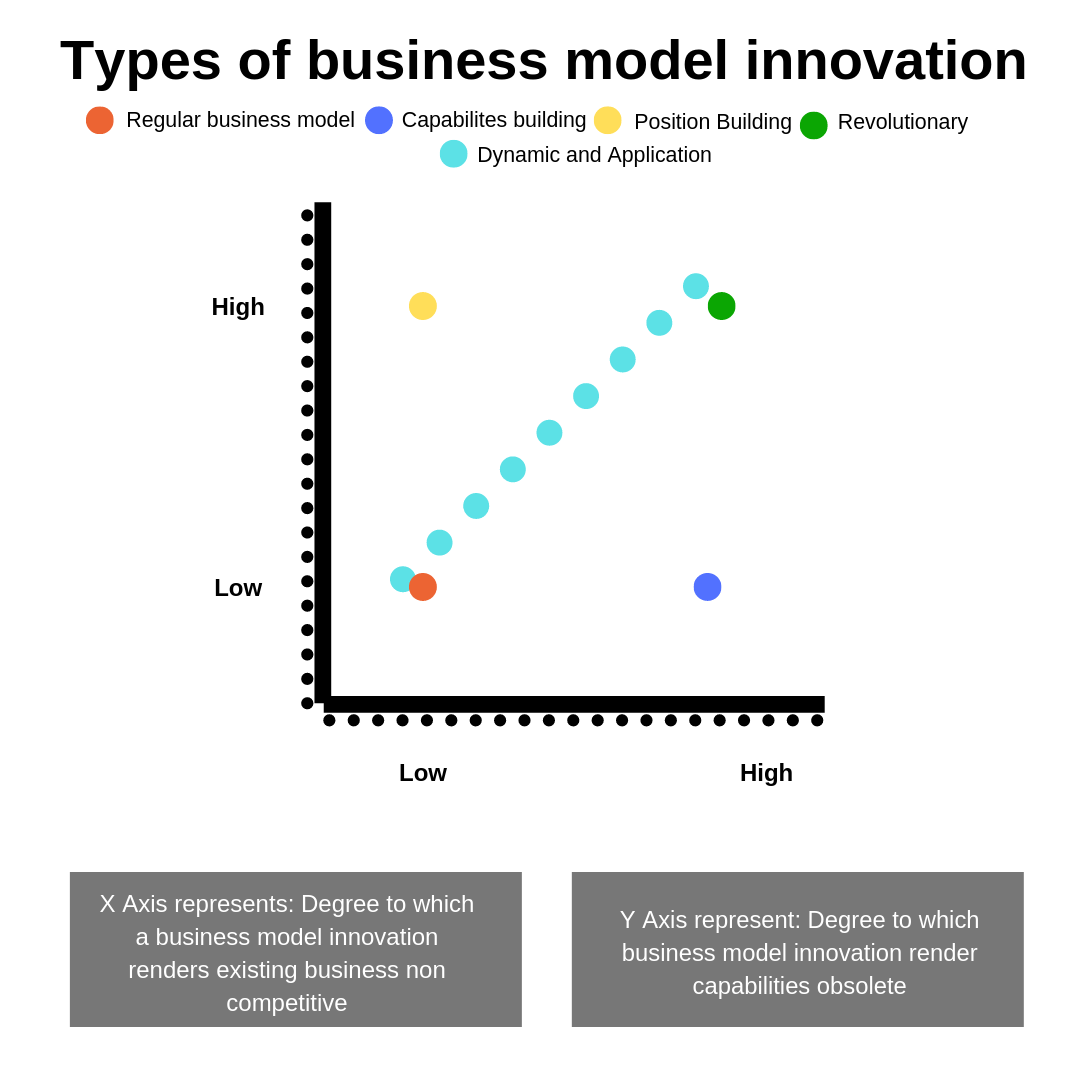
- Customer-Centricity: The foundation of any good business model is a deep understanding of your target customer. What are their pain points? What are their aspirations? How can you better serve them? This goes beyond simply understanding demographics; it’s about creating a genuine connection and delivering value that resonates with their specific needs.
- Value Proposition Design: A compelling value proposition articulates the benefits customers receive from your offering. It’s not enough to simply sell a product; you need to demonstrate why a customer should choose you over the competition. This requires careful consideration of features, pricing, and the overall customer experience.
- Revenue Streams Diversification: Relying on a single revenue stream can be risky. Diversifying revenue streams – whether through subscription models, freemium offerings, partnerships, or new product lines – creates resilience and expands your potential for growth.
- Operational Efficiency: Innovation doesn’t have to be disruptive; it can also be about streamlining operations and reducing costs. Improving efficiency across the entire value chain – from sourcing to delivery – can free up resources to invest in innovation.
1. Platform Business Models
One of the most prevalent and effective approaches to business model innovation is the platform business model. These models leverage existing platforms – social media networks, e-commerce marketplaces, or even transportation systems – to connect buyers and sellers, creating new opportunities for growth.
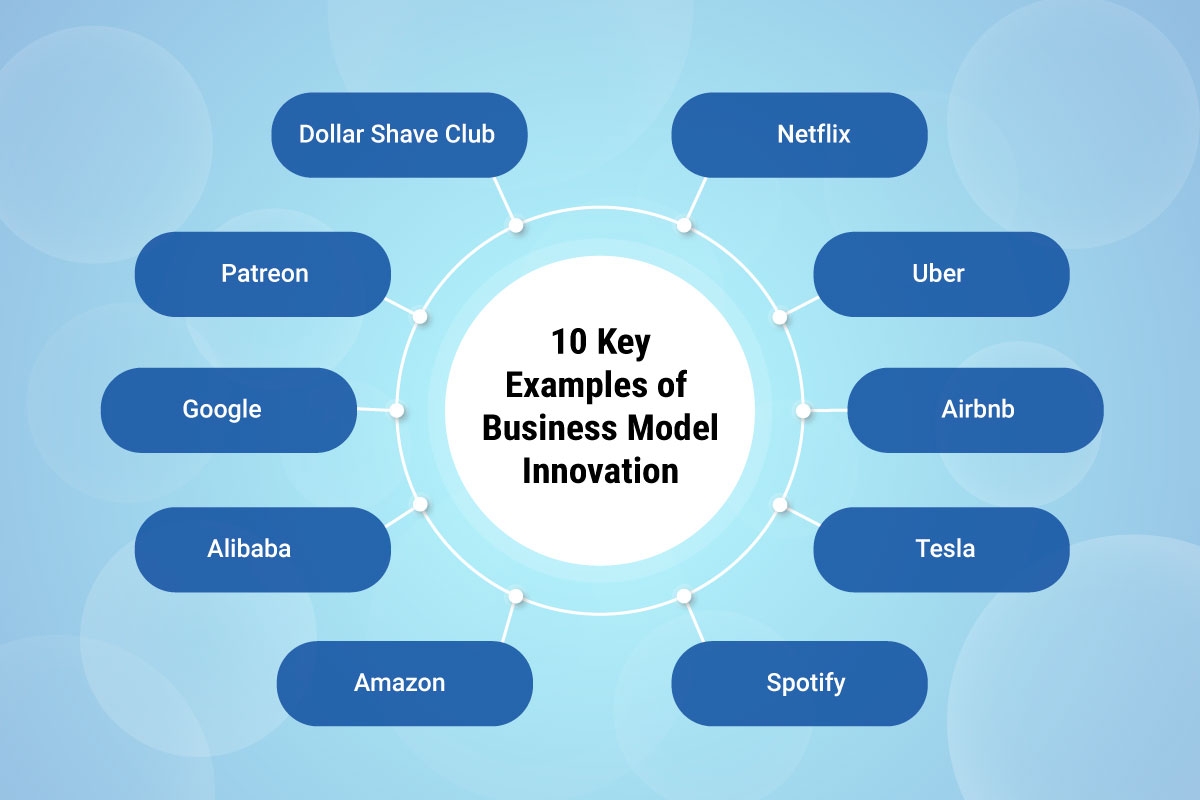
- Examples: Uber, Airbnb, Amazon Marketplace – these platforms have fundamentally altered industries. They don’t create everything; they facilitate interactions and create value through their infrastructure.
- Key Characteristics: Platform businesses typically generate revenue through transaction fees, subscription fees, advertising, or data monetization. They require strong network effects – the value of the platform increases as more users join.
- Challenges: Maintaining network effects, ensuring user experience, and managing platform governance are significant challenges. Competition can be fierce, and platform businesses must constantly adapt to evolving user behavior.
2. The Sharing Economy Model
The sharing economy, encompassing services like car rentals, accommodation, and tools, represents a significant shift in how people consume goods and services. It’s driven by the desire for efficiency, affordability, and sustainability.
- Key Components: Sharing economies often involve peer-to-peer transactions, leveraging existing assets rather than creating new ones. Trust and reputation systems are crucial for fostering participation.
- Examples: Turo (car rentals), Airbnb (accommodation), TaskRabbit (services).
- Benefits: Reduced waste, increased access to resources, and potential for increased profitability. However, challenges include managing quality control, ensuring fair compensation for providers, and addressing regulatory concerns.
3. Subscription-Based Models
Subscription models are gaining traction as a way to generate recurring revenue and build customer loyalty. Customers pay a regular fee for access to a product or service.

- Types: Tiered subscriptions (offering different levels of access), bundled subscriptions (combining multiple services), and usage-based subscriptions (charging based on consumption).
- Advantages: Predictable revenue streams, increased customer retention, and opportunities for upselling and cross-selling.
- Considerations: Careful planning of pricing and service offerings is essential to ensure customer satisfaction and avoid churn. Maintaining a high level of customer service is paramount.
4. Micro-SaaS Models
Micro-SaaS (Small Software as a Service) models are becoming increasingly popular, offering targeted solutions for specific needs. They’re typically smaller, more agile, and easier to develop than traditional SaaS companies.
- Characteristics: Focused on solving a niche problem, offering a simple and affordable solution, and prioritizing customer support.
- Examples: Tools for social media scheduling, email marketing automation, or project management.
- Benefits: Faster time to market, lower development costs, and the ability to quickly adapt to changing customer needs.
5. Hybrid Models – Combining Approaches
Many successful businesses adopt hybrid models that combine elements of different approaches. For example, a company might offer a subscription service plus a platform for sharing resources.

- Strategic Integration: The key is to strategically integrate different elements to create a cohesive and compelling value proposition.
- Example: A ride-sharing company might offer a subscription service for unlimited rides and a platform for connecting drivers with passengers.
The Role of Technology in Driving Innovation
Technology plays a critical role in enabling and accelerating business model innovation. Cloud computing, artificial intelligence, blockchain, and the Internet of Things (IoT) are just a few of the technologies that are transforming the way businesses operate.

- Data Analytics: Leveraging data analytics to understand customer behavior, identify trends, and optimize business processes.
- Automation: Automating repetitive tasks to free up human resources for more strategic initiatives.
- Digital Transformation: Adopting digital technologies to improve customer experience, streamline operations, and create new revenue streams.
Overcoming Challenges to Innovation
While the potential of business model innovation is immense, businesses often face significant challenges in implementing these changes.
- Resistance to Change: Employees may be resistant to new ideas and processes. Effective communication and change management are essential.
- Lack of Resources: Innovation requires investment in research and development, talent, and infrastructure.
- Risk Aversion: Companies may be hesitant to take risks, particularly when it comes to experimenting with new ideas.
- Measuring Success: It’s important to establish clear metrics to track the impact of innovation efforts.
Conclusion: Embracing a Future-Focused Approach
Business model innovation is no longer a luxury; it’s a necessity for survival and success in today’s dynamic marketplace. By embracing a customer-centric mindset, diversifying revenue streams, leveraging technology, and fostering a culture of experimentation, businesses can unlock new opportunities for growth and create lasting value. The future of business is about adaptability, disruption, and a relentless pursuit of innovative solutions. Continuously evaluating and refining your business model is vital for long-term prosperity. Remember to consistently analyze market trends and customer feedback to identify areas for improvement and potential new opportunities. Focusing on creating a truly differentiated value proposition is the key to sustained success.
